1.0.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT
Copyright © 2016
Copies of this document may be made for your own use and for distribution to others, provided that you do not charge any fee for such copies and further provided that each copy contains this Copyright Notice, whether distributed in print or electronically.
Spring Cloud Spinnaker Documentation
This section provides a brief overview of Spring Cloud Spinnaker reference documentation. Think of it as map for the rest of the document. You can read this reference guide in a linear fashion, or you can skip sections if something doesn’t interest you.
About the documentation
The Spring Cloud Spinnaker reference guide is available as html and pdf documents. The latest copy is available at docs.spring.io/spring-cloud-spinnaker/docs/current/reference.
Copies of this document may be made for your own use and for distribution to others, provided that you do not charge any fee for such copies and further provided that each copy contains this Copyright Notice, whether distributed in print or electronically.
Getting started
Interested in deploying applications to the cloud with complex rollouts, sophisticated notifications (Slack, Email, etc.)? Then this document is for you. It will coach you on using this application to install Spinnaker.
Introducing Spring Cloud Spinnaker
Spinnaker is a multi-cloud continuous deployment platform released by Netflix with contributions from Pivotal, Google, Microsoft and others. Spring Cloud Spinnaker is an installation tool meant to gather all the necessary information and use it to deploy Spinnaker’s microservices into a certified Cloud Foundry installation.
It installs the follow Spinnaker components:
| Module | Purpose |
|---|---|
clouddriver |
Carries out all cloud-based operations, e.g. deploy, resize, destroy, etc. |
deck |
Frontend UI |
echo |
Sends messages out over various channels like Slack and email |
fiat |
Security enforcement module. Coming soon! |
front50 |
Manages long term and inflight data, e.g. pipeline definitions and currently running pipelines |
gate |
Gateway API between the frontend (deck) and the backend services |
igor |
Polls for CI job status, e.g. Jenkins and Travis |
orca |
Orchestration engine used for all operations and pipelines |
| Spinnaker has other modules, but they aren’t needed for a Cloud Foundry setup. For example, there is a module dedicate to wrapping JAR artifacts as Amazon AMIs, also known as "baking", but Cloud Foundry doesn’t need baking. |
Before installing Spinnaker
Before you actually install Spinnaker, you must decide where it will run, i.e. pick an organization and space. You also need the following services created as well:
-
An instance of Redis in the same space.
Installing Spinnaker
Composed of Boot-based microservices, Spinnaker is highly customizable. Instead of tuning ever single setting, Spring Cloud Spinnaker lets you pick several options from a web page, and will in turn apply the needed property settings for you.
To get the bits, visit cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-spinnaker. Included are download directions to run it locally, to upload it somewhere in your CF, or to run a hosted solution from Pivotal Web Services.
Settings
After installing Spring Cloud Spinnaker, whether locally or in PCF somewhere, you will be faced with a collection of settings. This may look like a lot, but compared to ALL the options Spinnaker comes with, this is a vast simplification.
The settings are split into two parts: Target and Settings.
-
Target describes information needed to "cf push" all the Spinnaker modules.
-
Settings is information used to apply the right property settings after installation so that Spinnaker can do its own deployments.
The following settings are needed to install Spinnaker modules.
| Setting | Purpose |
|---|---|
Target API |
URL for the API where Spinnaker will be installed (Using PWS? There’s a shortcut button to enter its URL.) |
Target Email |
Email to log into CF and install Spinnaker |
Target Password |
Password to log into CF and install Spinnaker |
Refresh |
With API, email, and password hit this button and you’ll be presented with all the org/space pairs you have access to pick a destination. |
Target Organization |
Drop down showing organization you want Spinnaker installed in |
Target Space |
Drop down showing space you want Spinnaker installed in |
Namespace |
Optional suffix to apply to Spinnaker module names (e.g. test will yield deck-test) |
The following information is used by Spinnaker after installation to do its job.
| Setting | Purpose |
|---|---|
Redis Service |
Name of the Redis service clouddriver, echo, front50, and orca must bind to. Click "Pick from a list" to get a drop down of redis services in your selected space. NOTE: You must create this instance of Redis yourself. Spring Cloud Spinnaker doesn’t have the option to create it for you. |
Default Org |
Organization where Spinnaker will make deployments. This is pre-filled from Target Organization up above, but can be overridden. (Coming: Multiple organization support) |
Default Space |
Space where Spinnaker will make deployments. This is pre-filled from Target Space up above, but can be overridden. (Coming: Multiple space support) |
Primary Account API |
URL for the API where Spinnaker will make deployments. This is pre-filled from Target API up above, but can be overridden. |
Primary Account Console |
URL for App Manager (In PWS, it’s console.run.pivotal.io) |
Second Account? |
Enable you to add a second organzation and space, along with similar settings. |
Account Name |
Account name for Spinnaker to use when logging into PCF. Copied from Target Email but can be overriden. |
Account Password |
Account password for Spinnaker to use when logging into PCF. Copied from Target Password but can be overriden. |
Repository Name/Access Code |
If you are pulling deployment artifacts from an http-based repository, put your username. If s3, put your access code NOTE: If your repository isn’t secured, leave blank |
Repository Password/Secret Code |
If you are pulling deployment artifacts from an http-based repository, put your password. If s3, put your secret code NOTE: If your repository isn’t secured, leave blank |
SSL? |
If using PCF on a closed network, disable SSL to avoid failing security checks between Spinnaker components caused by self-signed certificates. |
Jenkins? |
Enable you to enter Jenkins details. |
Travis? |
Enable you to enter Travis details. |
Slack? |
Enable Slack notifications. (Includes hyperlink to proper place to create a Bot token value.) |
Email? |
Enable Email notifications by entering a collection of attributes. Certain values are pre-loaded if you enter a Gmail or Yahoo email address. Otherwise you’ll need to find proper settings for your email server. |
OAuth? |
Enable authentication with an OAuth provider. (Includes links to Github and Google pages to create a client/secret pair). |
Refresh list of omains |
Click to look up a list of valid domains for the Spinnaker modules. |
Domain |
Domain that Spinnaker will be installed into. |
All Account Names |
List of account names Spinnaker will interact with (separated by commas). This is pre-filled from Primary Account Name, but can be overridden. |
With your settings filled in, click on the Status tab.
Deploying
On the Status tab, you have the ability to check each module, or deal with them all.
-
Click on Deploy All.
-
Sit back and sip on a cup of coffee. This will take some time.
Once completed, you can click Stop All or Start All to stop/start the whole set.
You can click Link All and the names of each module will have a hyperlink added, taking you to App Manager.
Next Steps
After getting Spinnaker up and running, you should be able to access deck, the UI for Spinnaker, by visiting deck.<your domain>
Debugging Your Installation
Having trouble with your Spinnaker install? This section is meant to help you unravel things before you open a ticket.
Logs, logs, and more logs
When you are attempting to install Spinnaker, there are logs everywhere. The key is to find the right ones.
-
Spring Cloud Spinnaker can log information about the deployment process, but once completed, it doesn’t gather any more information
-
Each Spinnaker module will print out its own logs.
Assuming you installed Spinnaker with a namespace of "test", you can gather information like this…
$ cf logs clouddriver-test
In another shell
$ cf restart clouddriver-test
If you watch the "cf logs" command, you should see your copy of clouddriver start up. If there’s a major issue, it should render an error, especially it it’s missing settings.
2016-09-06T11:32:31.91-0500 [API/0] OUT Updated app with guid 39bc3f7b-ee7f-45f2-bac9-053069092c7a ({"state"=>"STARTED"})
2016-09-06T11:32:32.22-0500 [APP/0] OUT Exit status 143
2016-09-06T11:32:32.25-0500 [CELL/0] OUT Creating container
2016-09-06T11:32:32.25-0500 [CELL/0] OUT Destroying container
2016-09-06T11:32:32.71-0500 [CELL/0] OUT Successfully destroyed container
2016-09-06T11:32:33.02-0500 [CELL/0] OUT Successfully created container
2016-09-06T11:32:39.29-0500 [CELL/0] OUT Starting health monitoring of container
2016-09-06T11:32:44.71-0500 [APP/0] OUT . ____ _ __ _ _
2016-09-06T11:32:44.71-0500 [APP/0] OUT /\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
2016-09-06T11:32:44.71-0500 [APP/0] OUT ( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \
2016-09-06T11:32:44.71-0500 [APP/0] OUT \\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
2016-09-06T11:32:44.71-0500 [APP/0] OUT ' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /
2016-09-06T11:32:44.71-0500 [APP/0] OUT =========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
2016-09-06T11:32:44.71-0500 [APP/0] OUT :: Spring Boot :: (v1.2.8.RELEASE)
2016-09-06T11:32:44.85-0500 [APP/0] OUT 2016-09-06 16:32:44.851 INFO 18 --- [ main] pertySourceApplicationContextInitializer : Adding 'cloud' PropertySource to ApplicationContext
...
...
2016-09-06T11:33:06.12-0500 [APP/0] OUT 2016-09-06 16:33:06.126 INFO 18 --- [ main] s.d.spring.web.caching.CachingAspect : Caching aspect applied for cache modelProperties with key com.netflix.spinnaker.clouddriver.model.Network(true)
2016-09-06T11:33:06.12-0500 [APP/0] OUT 2016-09-06 16:33:06.126 INFO 18 --- [ main] s.d.spring.web.OperationsKeyGenerator : Cache key generated: /vpcs.com.netflix.spinnaker.clouddriver.controllers.VpcController.list.DefaultGenericTypeNamingStrategy
2016-09-06T11:33:06.12-0500 [APP/0] OUT 2016-09-06 16:33:06.126 INFO 18 --- [ main] s.d.spring.web.caching.CachingAspect : Caching aspect applied for cache operations with key /vpcs.com.netflix.spinnaker.clouddriver.controllers.VpcController.list.DefaultGenericTypeNamingStrategy
2016-09-06T11:33:06.12-0500 [APP/0] OUT 2016-09-06 16:33:06.126 INFO 18 --- [ main] s.w.ClassOrApiAnnotationResourceGrouping : Group for method list was vpc-controller
2016-09-06T11:33:06.12-0500 [APP/0] OUT 2016-09-06 16:33:06.127 INFO 18 --- [ main] s.w.ClassOrApiAnnotationResourceGrouping : Group for method list was vpc-controller
2016-09-06T11:33:06.12-0500 [APP/0] OUT 2016-09-06 16:33:06.127 INFO 18 --- [ main] .d.s.w.r.o.CachingOperationNameGenerator : Generating unique operation named: listUsingGET_10
2016-09-06T11:33:06.28-0500 [APP/0] OUT 2016-09-06 16:33:06.282 INFO 18 --- [ main] s.b.c.e.t.TomcatEmbeddedServletContainer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http)
2016-09-06T11:33:06.28-0500 [APP/0] OUT 2016-09-06 16:33:06.286 INFO 18 --- [ main] com.netflix.spinnaker.clouddriver.Main : Started Main in 24.791 seconds (JVM running for 26.911)
2016-09-06T11:33:06.57-0500 [CELL/0] OUT Container became healthy
-
In this console output, you can see that clouddriver is running with Spring Boot 1.2.8.RELEASE.
-
The "Started Main in 24.791 seconds" is the indicator that the app is finally up.
-
"Container became healthy" is the indicator that the platform can see the app as being up.
Environment settings
To apply various settings, Spring Cloud Spinnaker "cf pushes" the module and then applies various environment variables settings in Cloud Foundry. Pay note: it’s a LOT of settings. If you see a deployment either empty of environment variables or only containing SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON, then something has gone terribly wrong with the deployment.
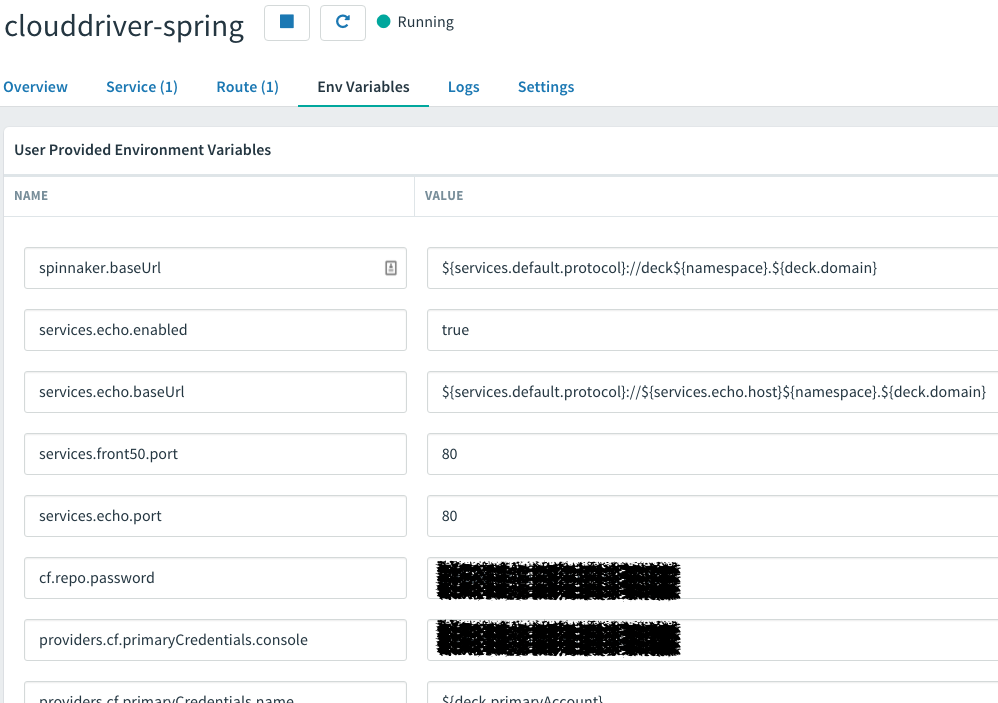
Each of the services has a URL to reach the other relevant microservices. In this case, you can how it builds up the URL for clouddriver to speak to echo.
In this specific example:
-
service.echo.baseUrl = ${services.default.protocol}://${services.echo.host}${namespace}.${deck.domain}
-
services.default.protocol = https
-
services.echo.host = echo
-
namespace = -spring
-
deck.domain = cfapps.io
This allows the deployer to flexibly adjust each piece as needed.
Manually deploying Spinnaker
You may be tempted to simple grab the fat JARs for clouddriver, deck, etc. and push them yourself. Unfortunately, that’s not an option (yet).
-
Each module needs its own property file. clouddriver has clouddriver.yml, igor has igor.yml, etc. But they aren’t included in the JARs pulled from bintray. Netflix wraps each module in a Debian package and has those files in a different location. Spring Cloud Spinnaker grabs those JARs and dynamically inserts such files right before pushing to your Cloud Foundry instance.