The Spring’s @MVC style of web application development is used in which the central type
is the Controller class.
The GreenPages application is divided into OSGi bundles that are represented as Eclipse
projects. In this step import the greenpages.web project.
Starting with no projects, import the web project by right-clicking in the Package Explorer
view and selecting the Import… menu item.
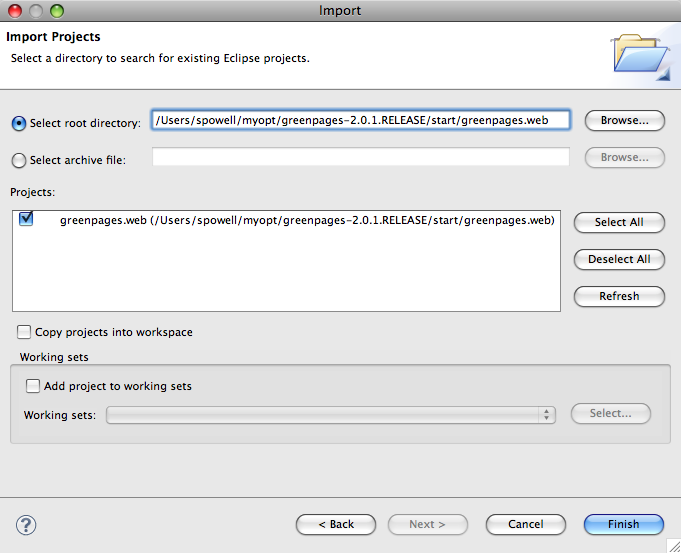
In the dialog that opens, choose → and select Next.
In the following dialog set the root directory to the value of
$GREENPAGES_HOME/start/greenpages.web and press Finish.
(Initially this project may have compiler errors; this is to be expected particularly if the Maven repository hasn’t yet been created.)
When this project is imported go to the next step.
In the src/main/java source folder of the greenpages.web project
the package greenpages.web
should contain the controller class named
GreenPagesController.
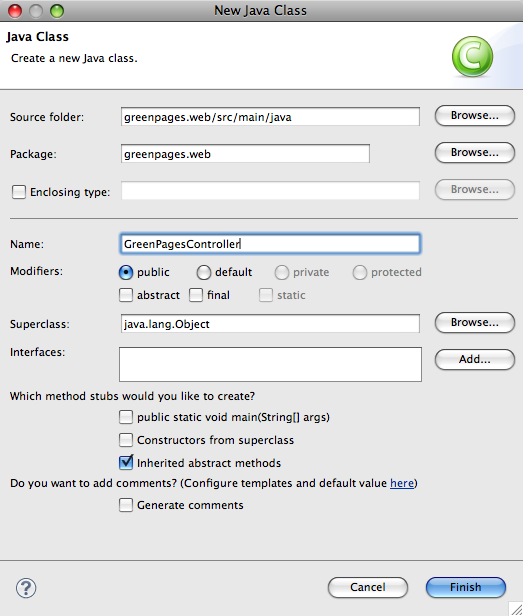
Create this by right-clicking on the greenpages.web package in the
src/main/java source folder and selecting
→ .
(If Class is not offered on the New menu
the Java perspective may not be being used, in which case look for
the Class option under Other… in the Java section.)
Name the new class GreenPagesController and press Finish.
The following code should be inserted:
@Controller public class GreenPagesController { … @RequestMapping("/home.htm") public void home() { } …
The annotations Controller and RequestMapping
are from Spring Framework and are imported by adding the lines:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
STS will offer (as a Quick Fix) to insert imports for these Spring Framework annotations the first time they are used. (Java 1.6 supports annotations, and the Spring Framework libraries are accessible by linking to the correct dm Server runtime environment or generating the correct dependencies for the Maven plug-in.)
Spring will detect the @Controller annotation and create a bean of controller type,
provided that it scans the classpath for these.
Spring’s component scanning is enabled by inserting a context tag
in one of the Spring bean definition files.
Open the WEB-INF/greenpages-servlet.xml file in the
src/main/webapp folder and ensure the following lines are present:
<!-- enable classpath scanning --> <context:component-scan base-package="greenpages.web" />
Experiment by adding and removing this line, saving the file after each change.
(Easily done by commenting it—use the
Toggle Comment
shortcut in STS.)
Look in the Spring Explorer view for a bean named greenPagesController
dynamically created by the component-scan tag.