This section provides answers to some common “how do I do that…?” questions that often arise when using Spring Cloud Contract. Its coverage is not exhaustive, but it does cover quite a lot.
If you have a specific problem that we do not cover here, you might want to check out
stackoverflow.com to see if someone has
already provided an answer. Stack Overflow is also a great place to ask new questions (please use
the spring-cloud-contract tag).
We are also more than happy to extend this section. If you want to add a “how-to”, send us a pull request.
1. Why use Spring Cloud Contract?
Spring Cloud Contract works great in a polyglot environment. This project has a lot of really interesting features. Quite a few of these features definitely make Spring Cloud Contract Verifier stand out on the market of Consumer Driven Contract (CDC) tooling. The most interesting features include the following:
-
Ability to do CDC with messaging.
-
Clear and easy to use, statically typed DSL.
-
Ability to copy-paste your current JSON file to the contract and edit only its elements.
-
Automatic generation of tests from the defined contract.
-
Stub Runner functionality: The stubs are automatically downloaded at runtime from Nexus or Artifactory.
-
Spring Cloud integration: No discovery service is needed for integration tests.
-
Spring Cloud Contract integrates with Pact and provides easy hooks to extend its functionality.
-
Ability to add support for any language & framework through Docker.
2. How Can I Write Contracts in a Language Other than Groovy?
You can write a contract in YAML. See this section for more information.
We are working on allowing more ways of describing the contracts. You can check the github-issues for more information.
3. How Can I Provide Dynamic Values to a Contract?
One of the biggest challenges related to stubs is their reusability. Only if they can be widely used can they serve their purpose. The hard-coded values (such as dates and IDs) of request and response elements generally make that difficult. Consider the following JSON request:
{
"time" : "2016-10-10 20:10:15",
"id" : "9febab1c-6f36-4a0b-88d6-3b6a6d81cd4a",
"body" : "foo"
}Now consider the following JSON response:
{
"time" : "2016-10-10 21:10:15",
"id" : "c4231e1f-3ca9-48d3-b7e7-567d55f0d051",
"body" : "bar"
}Imagine the pain required to set the proper value of the time field (assume that this content is generated by the
database) by changing the clock in the system or by providing stub implementations of data providers. The same is related
to the id field. You could create a stubbed implementation of UUID generator, but doing so makes little sense.
So, as a consumer, you want to send a request that matches any form of a time or any UUID. That way, your system
works as usual, generating data without you having to stub out anything. Assume that, in case of the aforementioned
JSON, the most important part is the body field. You can focus on that and provide matching for other fields. In other words,
you would like the stub to work as follows:
{
"time" : "SOMETHING THAT MATCHES TIME",
"id" : "SOMETHING THAT MATCHES UUID",
"body" : "foo"
}As far as the response goes, as a consumer, you need a concrete value on which you can operate. Consequently, the following JSON is valid:
{
"time" : "2016-10-10 21:10:15",
"id" : "c4231e1f-3ca9-48d3-b7e7-567d55f0d051",
"body" : "bar"
}In the previous sections, we generated tests from contracts. So, from the producer’s side, the situation looks much different. We parse the provided contract, and, in the test, we want to send a real request to your endpoints. So, for the case of a producer for the request, we cannot have any sort of matching. We need concrete values on which the producer’s backend can work. Consequently, the following JSON would be valid:
{
"time" : "2016-10-10 20:10:15",
"id" : "9febab1c-6f36-4a0b-88d6-3b6a6d81cd4a",
"body" : "foo"
}On the other hand, from the point of view of the validity of the contract, the response does not necessarily have to
contain concrete values for time or id. Suppose you generate those on the producer side. Again, you
have to do a lot of stubbing to ensure that you always return the same values. That is why, from the producer’s side,
you might want the following response:
{
"time" : "SOMETHING THAT MATCHES TIME",
"id" : "SOMETHING THAT MATCHES UUID",
"body" : "bar"
}How can you then provide a matcher for the consumer and a concrete value for the producer (and the opposite at some other time)? Spring Cloud Contract lets you provide a dynamic value. That means that it can differ for both sides of the communication.
You can read more about this in the Contract DSL section.
| Read the Groovy docs related to JSON to understand how to properly structure the request and response bodies. |
4. How to Do Stubs versioning?
This section covers versioning of the stubs, which you can handle in a number of different ways:
4.1. API Versioning
What does versioning really mean? If you refer to the API version, there are different approaches:
-
Use hypermedia links and do not version your API by any means
-
Pass the version through headers and URLs
We do not try to answer the question of which approach is better. You should pick whatever suits your needs and lets you generate business value.
Assume that you do version your API. In that case, you should provide as many contracts with as many versions as you support. You can create a subfolder for every version or append it to the contract name — whatever suits you best.
4.2. JAR versioning
If, by versioning, you mean the version of the JAR that contains the stubs, then there are essentially two main approaches.
Assume that you do continuous delivery and deployment, which means that you generate a new version of the jar each time you go through the pipeline and that the jar can go to production at any time. For example, your jar version looks like the following (because it got built on the 20.10.2016 at 20:15:21) :
1.0.0.20161020-201521-RELEASEIn that case, your generated stub jar should look like the following:
1.0.0.20161020-201521-RELEASE-stubs.jarIn this case, you should, inside your application.yml or @AutoConfigureStubRunner when
referencing stubs, provide the latest version of the stubs. You can do that by passing the
+ sign. the following example shows how to do so:
@AutoConfigureStubRunner(ids = {"com.example:http-server-dsl:+:stubs:8080"})If the versioning, however, is fixed (for example, 1.0.4.RELEASE or 2.1.1), you have to set the concrete value of the jar
version. The following example shows how to do so for version 2.1.1:
@AutoConfigureStubRunner(ids = {"com.example:http-server-dsl:2.1.1:stubs:8080"})4.3. Development or Production Stubs
You can manipulate the classifier to run the tests against the current development version
of the stubs of other services or the ones that were deployed to production. If you alter
your build to deploy the stubs with the prod-stubs classifier once you reach production
deployment, you can run tests in one case with development stubs and in another case with production stubs.
The following example works for tests that use the development version of the stubs:
@AutoConfigureStubRunner(ids = {"com.example:http-server-dsl:+:stubs:8080"})The following example works for tests that use the production version of stubs:
@AutoConfigureStubRunner(ids = {"com.example:http-server-dsl:+:prod-stubs:8080"})You can also pass those values also in properties from your deployment pipeline.
5. How Can I use a Common Repository with Contracts Instead of Storing Them with the Producer?
Another way of storing contracts, rather than having them with the producer, is to keep them in a common place. This situation can be related to security issues (where the consumers cannot clone the producer’s code). Also, if you keep contracts in a single place, then you, as a producer, know how many consumers you have and which consumer you may break with your local changes.
5.1. Repo Structure
Assume that we have a producer with coordinates of com.example:server and three
consumers: client1, client2, and client3. Then, in the repository with common
contracts, you could have the following setup (which you can check out
here).
The following listing shows such a structure:
├── com
│ └── example
│ └── server
│ ├── client1
│ │ └── expectation.groovy
│ ├── client2
│ │ └── expectation.groovy
│ ├── client3
│ │ └── expectation.groovy
│ └── pom.xml
├── mvnw
├── mvnw.cmd
├── pom.xml
└── src
└── assembly
└── contracts.xmlUnder the slash-delimited groupid/artifact id folder (com/example/server), you have
expectations of the three consumers (client1, client2, and client3). Expectations are the standard Groovy DSL
contract files, as described throughout this documentation. This repository has to produce a JAR file that maps
one-to-one to the contents of the repository.
The following example shows a pom.xml file inside the server folder:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>server</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1</version>
<name>Server Stubs</name>
<description>POM used to install locally stubs for consumer side</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.4.6</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring-cloud-contract.version>3.0.4-SNAPSHOT</spring-cloud-contract.version>
<spring-cloud-release.version>2020.0.3-SNAPSHOT</spring-cloud-release.version>
<excludeBuildFolders>true</excludeBuildFolders>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-release.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version>
<extensions>true</extensions>
<configuration>
<!-- By default it would search under src/test/resources/ -->
<contractsDirectory>${project.basedir}</contractsDirectory>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<name>Spring Snapshots</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/snapshot</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>spring-releases</id>
<name>Spring Releases</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/release</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<name>Spring Snapshots</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/snapshot</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-releases</id>
<name>Spring Releases</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/release</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
</project>There are no dependencies other than the Spring Cloud Contract Maven Plugin.
Those pom.xml files are necessary for the consumer side to run mvn clean install -DskipTests to locally install
the stubs of the producer project.
The pom.xml file in the root folder can look like the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example.standalone</groupId>
<artifactId>contracts</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1</version>
<name>Contracts</name>
<description>Contains all the Spring Cloud Contracts, well, contracts. JAR used by the
producers to generate tests and stubs
</description>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</artifactId>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>contracts</id>
<phase>prepare-package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>single</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<attach>true</attach>
<descriptor>${basedir}/src/assembly/contracts.xml</descriptor>
<!-- If you want an explicit classifier remove the following line -->
<appendAssemblyId>false</appendAssemblyId>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>It uses the assembly plugin to build the JAR with all the contracts. The following example shows such a setup:
<assembly xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-assembly-plugin/assembly/1.1.3"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-assembly-plugin/assembly/1.1.3 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/assembly-1.1.3.xsd">
<id>project</id>
<formats>
<format>jar</format>
</formats>
<includeBaseDirectory>false</includeBaseDirectory>
<fileSets>
<fileSet>
<directory>${project.basedir}</directory>
<outputDirectory>/</outputDirectory>
<useDefaultExcludes>true</useDefaultExcludes>
<excludes>
<exclude>**/${project.build.directory}/**</exclude>
<exclude>mvnw</exclude>
<exclude>mvnw.cmd</exclude>
<exclude>.mvn/**</exclude>
<exclude>src/**</exclude>
</excludes>
</fileSet>
</fileSets>
</assembly>5.2. Workflow
The workflow assumes that Spring Cloud Contract is set up both on the consumer and on the producer side. There is also the proper plugin setup in the common repository with contracts. The CI jobs are set for a common repository to build an artifact of all contracts and upload it to Nexus or Artifactory. The following image shows the UML for this workflow:
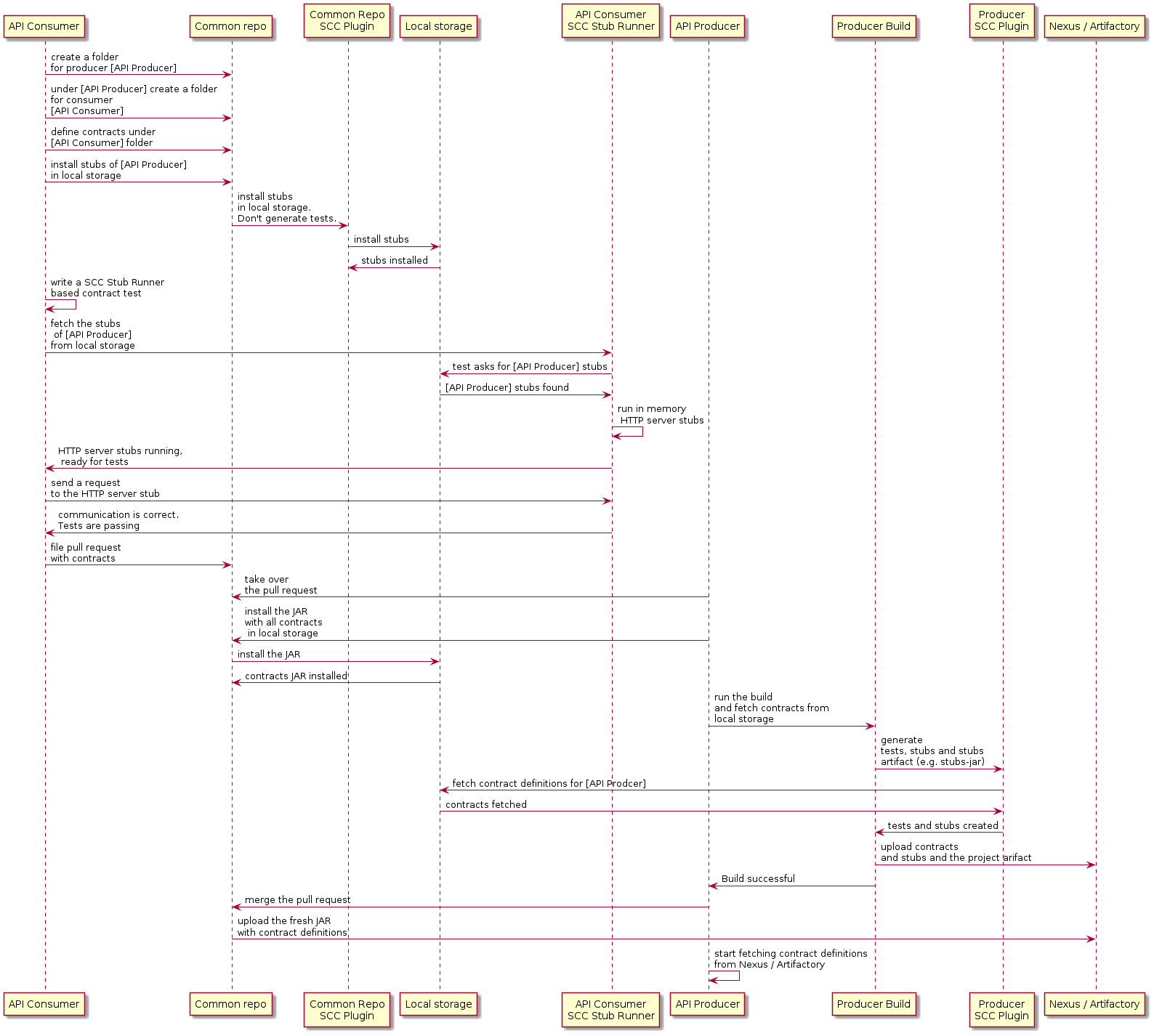
5.3. Consumer
When the consumer wants to work on the contracts offline, instead of cloning the producer
code, the consumer team clones the common repository, goes to the required producer’s
folder (for example, com/example/server) and runs mvn clean install -DskipTests to
locally install the stubs converted from the contracts.
| You need to have Maven installed locally. |
5.4. Producer
As a producer, you can alter the Spring Cloud Contract Verifier to provide the URL and the dependency of the JAR that contains the contracts, as follows:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<contractsMode>REMOTE</contractsMode>
<contractsRepositoryUrl>
https://link/to/your/nexus/or/artifactory/or/sth
</contractsRepositoryUrl>
<contractDependency>
<groupId>com.example.standalone</groupId>
<artifactId>contracts</artifactId>
</contractDependency>
</configuration>
</plugin>With this setup, the JAR with a groupid of com.example.standalone and an artifactid of
contracts is downloaded from link/to/your/nexus/or/artifactory/or/sth. It is
then unpacked in a local temporary folder, and the contracts present in
com/example/server are picked as the ones used to generate the tests and the stubs. Due
to this convention, the producer team can know which consumer teams are broken when
some incompatible changes are made.
The rest of the flow looks the same.
5.5. How Can I Define Messaging Contracts per Topic Rather than per Producer?
To avoid messaging contracts duplication in the common repository, when a few producers write messages to one topic, we could create a structure in which the REST contracts are placed in a folder per producer and messaging contracts are placed in the folder per topic.
5.5.1. For Maven Projects
To make it possible to work on the producer side, we should specify an inclusion pattern for
filtering common repository jar files by messaging topics we are interested in. The
includedFiles property of the Maven Spring Cloud Contract plugin
lets us do so. Also, contractsPath need to be specified, since the default path would be
the common repository groupid/artifactid. The following example shows a Maven
plugin for Spring Cloud Contract:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version>
<configuration>
<contractsMode>REMOTE</contractsMode>
<contractsRepositoryUrl>https://link/to/your/nexus/or/artifactory/or/sth</contractsRepositoryUrl>
<contractDependency>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>common-repo-with-contracts</artifactId>
<version>+</version>
</contractDependency>
<contractsPath>/</contractsPath>
<baseClassMappings>
<baseClassMapping>
<contractPackageRegex>.*messaging.*</contractPackageRegex>
<baseClassFQN>com.example.services.MessagingBase</baseClassFQN>
</baseClassMapping>
<baseClassMapping>
<contractPackageRegex>.*rest.*</contractPackageRegex>
<baseClassFQN>com.example.services.TestBase</baseClassFQN>
</baseClassMapping>
</baseClassMappings>
<includedFiles>
<includedFile>**/${project.artifactId}/**</includedFile>
<includedFile>**/${first-topic}/**</includedFile>
<includedFile>**/${second-topic}/**</includedFile>
</includedFiles>
</configuration>
</plugin>| Many of the values in the preceding Maven plugin can be changed. We included it for illustration purposes rather than trying to provide a “typical” example. |
5.5.2. For Gradle Projects
To work with a Gradle project:
-
Add a custom configuration for the common repository dependency, as follows:
ext { contractsGroupId = "com.example" contractsArtifactId = "common-repo" contractsVersion = "1.2.3" } configurations { contracts { transitive = false } } -
Add the common repository dependency to your classpath, as follows:
dependencies { contracts "${contractsGroupId}:${contractsArtifactId}:${contractsVersion}" testCompile "${contractsGroupId}:${contractsArtifactId}:${contractsVersion}" } -
Download the dependency to an appropriate folder, as follows:
task getContracts(type: Copy) { from configurations.contracts into new File(project.buildDir, "downloadedContracts") } -
Unzip the JAR, as follows:
task unzipContracts(type: Copy) { def zipFile = new File(project.buildDir, "downloadedContracts/${contractsArtifactId}-${contractsVersion}.jar") def outputDir = file("${buildDir}/unpackedContracts") from zipTree(zipFile) into outputDir } -
Cleanup unused contracts, as follows:
task deleteUnwantedContracts(type: Delete) { delete fileTree(dir: "${buildDir}/unpackedContracts", include: "**/*", excludes: [ "**/${project.name}/**"", "**/${first-topic}/**", "**/${second-topic}/**"]) } -
Create task dependencies, as follows:
unzipContracts.dependsOn("getContracts") deleteUnwantedContracts.dependsOn("unzipContracts") build.dependsOn("deleteUnwantedContracts") -
Configure the plugin by specifying the directory that contains the contracts, by setting the
contractsDslDirproperty, as follows:contracts { contractsDslDir = new File("${buildDir}/unpackedContracts") }
6. How Can I Use Git as the Storage for Contracts and Stubs?
In the polyglot world, there are languages that do not use binary storage, as Artifactory and Nexus do. Starting from Spring Cloud Contract version 2.0.0, we provide mechanisms to store contracts and stubs in a SCM (Source Control Management) repository. Currently, the only supported SCM is Git.
The repository would have to have the following setup (which you can checkout from here):
.
└── META-INF
└── com.example
└── beer-api-producer-git
└── 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
├── contracts
│ └── beer-api-consumer
│ ├── messaging
│ │ ├── shouldSendAcceptedVerification.groovy
│ │ └── shouldSendRejectedVerification.groovy
│ └── rest
│ ├── shouldGrantABeerIfOldEnough.groovy
│ └── shouldRejectABeerIfTooYoung.groovy
└── mappings
└── beer-api-consumer
└── rest
├── shouldGrantABeerIfOldEnough.json
└── shouldRejectABeerIfTooYoung.jsonUnder the META-INF folder:
-
We group applications by
groupId(such ascom.example). -
Each application is represented by its
artifactId(for example,beer-api-producer-git). -
Next, each application is organized by its version (such as
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT). Starting from Spring Cloud Contract version2.1.0, you can specify the versions as follows (assuming that your versions follow semantic versioning):-
+orlatest: To find the latest version of your stubs (assuming that the snapshots are always the latest artifact for a given revision number). That means:-
If you have
1.0.0.RELEASE,2.0.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT, and2.0.0.RELEASE, we assume that the latest is2.0.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT. -
If you have
1.0.0.RELEASEand2.0.0.RELEASE, we assume that the latest is2.0.0.RELEASE. -
If you have a version called
latestor+, we will pick that folder.
-
-
release: To find the latest release version of your stubs. That means:-
If you have
1.0.0.RELEASE,2.0.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT, and2.0.0.RELEASEwe assume that the latest is2.0.0.RELEASE. -
If you have a version called
release, we pick that folder.
-
-
Finally, there are two folders:
-
contracts: The good practice is to store the contracts required by each consumer in the folder with the consumer name (such asbeer-api-consumer). That way, you can use thestubs-per-consumerfeature. Further directory structure is arbitrary. -
mappings: The Maven or Gradle Spring Cloud Contract plugins push the stub server mappings in this folder. On the consumer side, Stub Runner scans this folder to start stub servers with stub definitions. The folder structure is a copy of the one created in thecontractssubfolder.
6.1. Protocol Convention
To control the type and location of the source of contracts (whether binary storage or an SCM repository), you can use the protocol in the URL of the repository. Spring Cloud Contract iterates over registered protocol resolvers and tries to fetch the contracts (by using a plugin) or stubs (from Stub Runner).
For the SCM functionality, currently, we support the Git repository. To use it,
in the property where the repository URL needs to be placed, you have to prefix
the connection URL with git://. The following listing shows some examples:
git://file:///foo/bar
git://https://github.com/spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git
git://[email protected]:spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git6.2. Producer
For the producer, to use the SCM (Source Control Management) approach, we can reuse the
same mechanism we use for external contracts. We route Spring Cloud Contract
to use the SCM implementation from the URL that starts with
the git:// protocol.
You have to manually add the pushStubsToScm
goal in Maven or use (bind) the pushStubsToScm task in
Gradle. We do not push stubs to the origin of your git
repository.
|
The following listing includes the relevant parts both Maven and Gradle build files:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version>
<extensions>true</extensions>
<configuration>
<!-- Base class mappings etc. -->
<!-- We want to pick contracts from a Git repository -->
<contractsRepositoryUrl>git://https://github.com/spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git</contractsRepositoryUrl>
<!-- We reuse the contract dependency section to set up the path
to the folder that contains the contract definitions. In our case the
path will be /groupId/artifactId/version/contracts -->
<contractDependency>
<groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId>
<artifactId>${project.artifactId}</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</contractDependency>
<!-- The contracts mode can't be classpath -->
<contractsMode>REMOTE</contractsMode>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<!-- By default we will not push the stubs back to SCM,
you have to explicitly add it as a goal -->
<goal>pushStubsToScm</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>contracts {
// We want to pick contracts from a Git repository
contractDependency {
stringNotation = "${project.group}:${project.name}:${project.version}"
}
/*
We reuse the contract dependency section to set up the path
to the folder that contains the contract definitions. In our case the
path will be /groupId/artifactId/version/contracts
*/
contractRepository {
repositoryUrl = "git://https://github.com/spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git"
}
// The mode can't be classpath
contractsMode = "REMOTE"
// Base class mappings etc.
}
/*
In this scenario we want to publish stubs to SCM whenever
the `publish` task is invoked
*/
publish.dependsOn("publishStubsToScm")You can also further customize the publishStubsToScm gradle task. In the following example,
the task is customized to pick contracts from a local git repository:
publishStubsToScm {
// We want to modify the default set up of the plugin when publish stubs to scm is called
// We want to pick contracts from a Git repository
contractDependency {
stringNotation = "${project.group}:${project.name}:${project.version}"
}
/*
We reuse the contract dependency section to set up the path
to the folder that contains the contract definitions. In our case the
path will be /groupId/artifactId/version/contracts
*/
contractRepository {
repositoryUrl = "git://file://${new File(project.rootDir, "../target")}/contract_empty_git/"
}
// We set the contracts mode to `LOCAL`
contractsMode = "LOCAL"
}- IMPORTANT
-
Starting with the
2.3.0.RELEASE, thecustomize{}closure previously used for thepublishStubsToScmcustomization is no longer available. The settings should be applied directly within thepublishStubsToScmclosure, as in the preceding example.
With such a setup:
-
A git project is cloned to a temporary directory
-
The SCM stub downloader goes to the
META-INF/groupId/artifactId/version/contractsfolder to find contracts. For example, forcom.example:foo:1.0.0, the path would beMETA-INF/com.example/foo/1.0.0/contracts. -
Tests are generated from the contracts.
-
Stubs are created from the contracts.
-
Once the tests pass, the stubs are committed in the cloned repository.
-
Finally, a push is sent to that repo’s
origin.
6.3. Producer with Contracts Stored Locally
Another option to use the SCM as the destination for stubs and contracts is to store the contracts locally, with the producer, and only push the contracts and the stubs to SCM. The following listing shows the setup required to achieve this with Maven and Gradle:
With such a setup:
-
Contracts from the default
src/test/resources/contractsdirectory are picked. -
Tests are generated from the contracts.
-
Stubs are created from the contracts.
-
Once the tests pass:
-
The git project is cloned to a temporary directory.
-
The stubs and contracts are committed in the cloned repository.
-
-
Finally, a push is done to that repository’s
origin.
6.4. Keeping Contracts with the Producer and Stubs in an External Repository
You can also keep the contracts in the producer repository but keep the stubs in an external git repository. This is most useful when you want to use the base consumer-producer collaboration flow but cannot use an artifact repository to store the stubs.
To do so, use the usual producer setup and then add the pushStubsToScm goal and set
contractsRepositoryUrl to the repository where you want to keep the stubs.
6.5. Consumer
On the consumer side, when passing the repositoryRoot parameter,
either from the @AutoConfigureStubRunner annotation, the
JUnit 4 rule, JUnit 5 extension, or properties, you can pass the URL of the
SCM repository, prefixed with the git:// protocol. The following example shows how to do so:
@AutoConfigureStubRunner(
stubsMode="REMOTE",
repositoryRoot="git://https://github.com/spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git",
ids="com.example:bookstore:0.0.1.RELEASE"
)With such a setup:
-
The git project is cloned to a temporary directory.
-
The SCM stub downloader goes to the
META-INF/groupId/artifactId/version/folder to find stub definitions and contracts. For example, forcom.example:foo:1.0.0, the path would beMETA-INF/com.example/foo/1.0.0/. -
Stub servers are started and fed with mappings.
-
Messaging definitions are read and used in the messaging tests.
7. How Can I Use the Pact Broker?
When using Pact, you can use the Pact Broker to store and share Pact definitions. Starting from Spring Cloud Contract 2.0.0, you can fetch Pact files from the Pact Broker to generate tests and stubs.
| Pact follows the consumer contract convention. That means that the consumer creates the Pact definitions first and then shares the files with the Producer. Those expectations are generated from the Consumer’s code and can break the Producer if the expectations are not met. |
7.1. How to Work with Pact
Spring Cloud Contract includes support for the Pact representation of
contracts up until version 4. Instead of using the DSL, you can use Pact files. In this section, we
show how to add Pact support for your project. Note, however, that not all functionality is supported.
Starting with version 3, you can combine multiple matchers for the same element:
You can use matchers for the body, headers, request and path, and you can use value generators.
Spring Cloud Contract currently only supports multiple matchers that are combined by using the AND rule logic.
Next to that, the request and path matchers are skipped during the conversion.
When using a date, time, or datetime value generator with a given format,
the given format is skipped and the ISO format is used.
7.2. Pact Converter
In order to properly support the Spring Cloud Contract way of doing messaging with Pact, you have to provide some additional metadata entries.
To define the destination to which a message gets sent, you have to
set a metaData entry in the Pact file with the sentTo key equal to the destination to
which a message is to be sent (for example, "metaData": { "sentTo": "activemq:output" }).
7.3. Pact Contract
Spring Cloud Contract can read the Pact JSON definition. You can place the file in the
src/test/resources/contracts folder. Remember to put the spring-cloud-contract-pact dependency to your classpath. The following example shows such a Pact contract:
{
"provider": {
"name": "Provider"
},
"consumer": {
"name": "Consumer"
},
"interactions": [
{
"description": "",
"request": {
"method": "PUT",
"path": "/pactfraudcheck",
"headers": {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"clientId": "1234567890",
"loanAmount": 99999
},
"generators": {
"body": {
"$.clientId": {
"type": "Regex",
"regex": "[0-9]{10}"
}
}
},
"matchingRules": {
"header": {
"Content-Type": {
"matchers": [
{
"match": "regex",
"regex": "application/json.*"
}
],
"combine": "AND"
}
},
"body": {
"$.clientId": {
"matchers": [
{
"match": "regex",
"regex": "[0-9]{10}"
}
],
"combine": "AND"
}
}
}
},
"response": {
"status": 200,
"headers": {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"fraudCheckStatus": "FRAUD",
"rejection.reason": "Amount too high"
},
"matchingRules": {
"header": {
"Content-Type": {
"matchers": [
{
"match": "regex",
"regex": "application/json.*"
}
],
"combine": "AND"
}
},
"body": {
"$.fraudCheckStatus": {
"matchers": [
{
"match": "regex",
"regex": "FRAUD"
}
],
"combine": "AND"
}
}
}
}
}
],
"metadata": {
"pact-specification": {
"version": "3.0.0"
},
"pact-jvm": {
"version": "3.5.13"
}
}
}7.4. Pact for Producers
On the producer side, you must add two additional dependencies to your plugin configuration. One is the Spring Cloud Contract Pact support, and the other represents the current Pact version that you use. The following listing shows how to do so for both Maven and Gradle:
When you build your application, a test and stub is generated. The following example shows a test and stub that came from this process:
@Test
public void validate_shouldMarkClientAsFraud() throws Exception {
// given:
MockMvcRequestSpecification request = given()
.header("Content-Type", "application/vnd.fraud.v1+json")
.body("{\"clientId\":\"1234567890\",\"loanAmount\":99999}");
// when:
ResponseOptions response = given().spec(request)
.put("/fraudcheck");
// then:
assertThat(response.statusCode()).isEqualTo(200);
assertThat(response.header("Content-Type")).matches("application/vnd\\.fraud\\.v1\\+json.*");
// and:
DocumentContext parsedJson = JsonPath.parse(response.getBody().asString());
assertThatJson(parsedJson).field("['rejectionReason']").isEqualTo("Amount too high");
// and:
assertThat(parsedJson.read("$.fraudCheckStatus", String.class)).matches("FRAUD");
}{
"id" : "996ae5ae-6834-4db6-8fac-358ca187ab62",
"uuid" : "996ae5ae-6834-4db6-8fac-358ca187ab62",
"request" : {
"url" : "/fraudcheck",
"method" : "PUT",
"headers" : {
"Content-Type" : {
"matches" : "application/vnd\\.fraud\\.v1\\+json.*"
}
},
"bodyPatterns" : [ {
"matchesJsonPath" : "$[?(@.['loanAmount'] = 99999)]"
}, {
"matchesJsonPath" : "$[?(@.clientId =~ /([0-9]{10})/)]"
} ]
},
"response" : {
"status" : 200,
"body" : "{\"fraudCheckStatus\":\"FRAUD\",\"rejectionReason\":\"Amount too high\"}",
"headers" : {
"Content-Type" : "application/vnd.fraud.v1+json;charset=UTF-8"
},
"transformers" : [ "response-template" ]
},
}7.5. Pact for Consumers
On the consumer side, you must add two additional dependencies to your project dependencies. One is the Spring Cloud Contract Pact support, and the other represents the current Pact version that you use. The following listing shows how to do so for both Maven and Gradle:
7.6. Communicating with the Pact Broker
Whenever the repositoryRoot property starts with a Pact protocol
(that is, starts with pact://), the stub downloader tries
to fetch the Pact contract definitions from the Pact Broker.
Whatever is set after pact:// is parsed as the Pact Broker URL.
By setting environment variables, system properties, or properties set inside the plugin or contracts repository configuration, you can tweak the downloader’s behavior. The following table describes the properties:
Name of a property |
Default |
Description |
* * * |
Host from URL passed to |
The URL of the Pact Broker. |
* * * |
Port from URL passed to |
The port of Pact Broker. |
* * * |
Protocol from URL passed to |
The protocol of Pact Broker. |
* * * |
Version of the stub, or |
The tags that should be used to fetch the stub. |
* * * |
|
The kind of authentication that should be used to connect to the Pact Broker. |
* * * |
The username passed to |
The username to use when connecting to the Pact Broker. |
* * * |
The password passed to |
The password to use when connecting to the Pact Broker. |
* * * |
false |
When |
7.7. Flow: Consumer Contract Approach with Pact Broker on the Consumer Side
The consumer uses the Pact framework to generate Pact files. The Pact files are sent to the Pact Broker. You can find an example of such a setup here.
7.8. Flow: Consumer Contract Approach with Pact Broker on the Producer Side
For the producer to use the Pact files from the Pact Broker, we can reuse the
same mechanism we use for external contracts. We route Spring Cloud Contract
to use the Pact implementation with the URL that contains
the pact:// protocol. You can pass the URL to the
Pact Broker. You can find an example of such a setup
here.
The following listing shows the configuration details for both Maven and Gradle:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version>
<extensions>true</extensions>
<configuration>
<!-- Base class mappings etc. -->
<!-- We want to pick contracts from a Git repository -->
<contractsRepositoryUrl>pact://http://localhost:8085</contractsRepositoryUrl>
<!-- We reuse the contract dependency section to set up the path
to the folder that contains the contract definitions. In our case the
path will be /groupId/artifactId/version/contracts -->
<contractDependency>
<groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId>
<artifactId>${project.artifactId}</artifactId>
<!-- When + is passed, a latest tag will be applied when fetching pacts -->
<version>+</version>
</contractDependency>
<!-- The contracts mode can't be classpath -->
<contractsMode>REMOTE</contractsMode>
</configuration>
<!-- Don't forget to add spring-cloud-contract-pact to the classpath! -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-pact</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>buildscript {
repositories {
//...
}
dependencies {
// ...
// Don't forget to add spring-cloud-contract-pact to the classpath!
classpath "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-contract-pact:${contractVersion}"
}
}
contracts {
// When + is passed, a latest tag will be applied when fetching pacts
contractDependency {
stringNotation = "${project.group}:${project.name}:+"
}
contractRepository {
repositoryUrl = "pact://http://localhost:8085"
}
// The mode can't be classpath
contractsMode = "REMOTE"
// Base class mappings etc.
}With such a setup:
-
Pact files are downloaded from the Pact Broker.
-
Spring Cloud Contract converts the Pact files into tests and stubs.
-
The JAR with the stubs gets automatically created, as usual.
7.9. Flow: Producer Contract Approach with Pact on the Consumer Side
In the scenario where you do not want to do the consumer contract approach (for every single consumer, define the expectations) but you prefer to do producer contracts (the producer provides the contracts and publishes stubs), you can use Spring Cloud Contract with the Stub Runner option. You can find an example of such a setup here.
Remember to add the Stub Runner and Spring Cloud Contract Pact modules as test dependencies.
The following listing shows the configuration details for both Maven and Gradle:
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<!-- Don't forget to add spring-cloud-contract-pact to the classpath! -->
<dependencies>
<!-- ... -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-contract-stub-runner</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-pact</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>dependencyManagement {
imports {
mavenBom "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-dependencies:${springCloudVersion}"
}
}
dependencies {
//...
testCompile("org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-contract-stub-runner")
// Don't forget to add spring-cloud-contract-pact to the classpath!
testCompile("org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-contract-pact")
}Next, you can pass the URL of the Pact Broker to repositoryRoot, prefixed
with the pact:// protocol (for example, pact://http://localhost:8085), as the following
example shows:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureStubRunner(stubsMode = StubRunnerProperties.StubsMode.REMOTE,
ids = "com.example:beer-api-producer-pact",
repositoryRoot = "pact://http://localhost:8085")
public class BeerControllerTest {
//Inject the port of the running stub
@StubRunnerPort("beer-api-producer-pact") int producerPort;
//...
}With such a setup:
-
Pact files are downloaded from the Pact Broker.
-
Spring Cloud Contract converts the Pact files into stub definitions.
-
The stub servers are started and fed with stubs.
8. How Can I Debug the Request/Response Being Sent by the Generated Tests Client?
The generated tests all boil down to RestAssured in some form or fashion. RestAssured relies on the Apache HttpClient. HttpClient has a facility called wire logging, which logs the entire request and response to HttpClient. Spring Boot has a logging common application property for doing this sort of thing. To use it, add it to your application properties, as follows:
logging.level.org.apache.http.wire=DEBUG9. How Can I Debug the Mapping, Request, or Response Being Sent by WireMock?
Starting from version 1.2.0, we set WireMock logging to
info and set the WireMock notifier to being verbose. Now you can
exactly know what request was received by the WireMock server and which
matching response definition was picked.
To turn off this feature, set WireMock logging to ERROR, as follows:
logging.level.com.github.tomakehurst.wiremock=ERROR10. How Can I See What Got Registered in the HTTP Server Stub?
You can use the mappingsOutputFolder property on @AutoConfigureStubRunner, StubRunnerRule, or
StubRunnerExtension to dump all mappings for each artifact ID. Also, the port at which the given stub server
was started is attached.
11. How Can I Reference Text from File?
In version 1.2.0, we added this ability. You can call a file(…) method in the
DSL and provide a path relative to where the contract lies.
If you use YAML, you can use the bodyFromFile property.
12. How Can I Generate Pact, YAML, or X files from Spring Cloud Contract Contracts?
Spring Cloud Contract comes with a ToFileContractsTransformer class that lets you dump
contracts as files for the given ContractConverter. It contains a static void main
method that lets you run the transformer as an executable. It takes the following
arguments:
-
argument 1 :
FQN: Fully qualified name of theContractConverter(for example,PactContractConverter). REQUIRED. -
argument 2 :
path: Path where the dumped files should be stored. OPTIONAL — defaults totarget/converted-contracts. -
argument 3 :
path: Path were the contracts should be searched for. OPTIONAL — defaults tosrc/test/resources/contracts.
After calling the transformer, the Spring Cloud Contract files are processed and,
depending on the provided FQN of the ContractTransformer, the contracts are transformed
to the required format and dumped to the provided folder.
The following example shows how to configure Pact integration for both Maven and Gradle:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>exec-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.6.0</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>convert-dsl-to-pact</id>
<phase>process-test-classes</phase>
<configuration>
<classpathScope>test</classpathScope>
<mainClass>
org.springframework.cloud.contract.verifier.util.ToFileContractsTransformer
</mainClass>
<arguments>
<argument>
org.springframework.cloud.contract.verifier.spec.pact.PactContractConverter
</argument>
<argument>${project.basedir}/target/pacts</argument>
<argument>
${project.basedir}/src/test/resources/contracts
</argument>
</arguments>
</configuration>
<goals>
<goal>java</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>task convertContracts(type: JavaExec) {
main = "org.springframework.cloud.contract.verifier.util.ToFileContractsTransformer"
classpath = sourceSets.test.compileClasspath
args("org.springframework.cloud.contract.verifier.spec.pact.PactContractConverter",
"${project.rootDir}/build/pacts", "${project.rootDir}/src/test/resources/contracts")
}
test.dependsOn("convertContracts")13. How Can I Work with Transitive Dependencies?
The Spring Cloud Contract plugins add the tasks that create the stubs jar for you. One
problem that arises is that, when reusing the stubs, you can mistakenly import all of
that stub’s dependencies. When building a Maven artifact, even though you have a couple
of different jars, all of them share one pom.xml file, as the following listing shows:
├── producer-0.0.1.BUILD-20160903.075506-1-stubs.jar
├── producer-0.0.1.BUILD-20160903.075506-1-stubs.jar.sha1
├── producer-0.0.1.BUILD-20160903.075655-2-stubs.jar
├── producer-0.0.1.BUILD-20160903.075655-2-stubs.jar.sha1
├── producer-0.0.1.BUILD-SNAPSHOT.jar
├── producer-0.0.1.BUILD-SNAPSHOT.pom
├── producer-0.0.1.BUILD-SNAPSHOT-stubs.jar
├── ...
└── ...There are three possibilities of working with those dependencies so as not to have any issues with transitive dependencies:
-
Mark all application dependencies as optional
-
Create a separate
artifactidfor the stubs -
Exclude dependencies on the consumer side
13.1. How Can I Mark All Application Dependencies as Optional?
If, in the producer application, you mark all of your dependencies as optional,
when you include the producer stubs in another application (or when that
dependency gets downloaded by Stub Runner), then, since all of the dependencies are
optional, they do not get downloaded.
13.2. How can I Create a Separate artifactid for the Stubs?
If you create a separate artifactid, you can set it up in whatever way you wish.
For example, you might decide to have no dependencies at all.
13.3. How can I Exclude Dependencies on the Consumer Side?
As a consumer, if you add the stub dependency to your classpath, you can explicitly exclude the unwanted dependencies.
14. How Can I Generate Spring REST Docs Snippets from the Contracts?
When you want to include the requests and responses of your API by using Spring REST Docs, you only need to make some minor changes to your setup if you are using MockMvc and RestAssuredMockMvc. To do so, include the following dependencies (if you have not already done so):
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-contract-verifier</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.restdocs</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-restdocs-mockmvc</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>testImplementation 'org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-contract-verifier'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.restdocs:spring-restdocs-mockmvc'Next, you need to make some changes to your base class. The following examples use
WebAppContext and the standalone option with RestAssured:
package com.example.fraud;
import io.restassured.module.mockmvc.RestAssuredMockMvc;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.TestInfo;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.restdocs.RestDocumentationContextProvider;
import org.springframework.restdocs.RestDocumentationExtension;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.setup.MockMvcBuilders;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import static org.springframework.restdocs.mockmvc.MockMvcRestDocumentation.document;
import static org.springframework.restdocs.mockmvc.MockMvcRestDocumentation.documentationConfiguration;
@ExtendWith(RestDocumentationExtension.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = Application.class)
public abstract class FraudBaseWithWebAppSetup {
@Autowired
private WebApplicationContext context;
@BeforeEach
public void setup(TestInfo info, RestDocumentationContextProvider restDocumentation) {
RestAssuredMockMvc.mockMvc(MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup(this.context)
.apply(documentationConfiguration(restDocumentation))
.alwaysDo(document(
getClass().getSimpleName() + "_" + info.getDisplayName()))
.build());
}
protected void assertThatRejectionReasonIsNull(Object rejectionReason) {
assert rejectionReason == null;
}
}package com.example.fraud;
import io.restassured.module.mockmvc.RestAssuredMockMvc;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.TestInfo;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.restdocs.RestDocumentationContextProvider;
import org.springframework.restdocs.RestDocumentationExtension;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.setup.MockMvcBuilders;
import static org.springframework.restdocs.mockmvc.MockMvcRestDocumentation.document;
import static org.springframework.restdocs.mockmvc.MockMvcRestDocumentation.documentationConfiguration;
@ExtendWith(RestDocumentationExtension.class)
public abstract class FraudBaseWithStandaloneSetup {
@BeforeEach
public void setup(TestInfo info, RestDocumentationContextProvider restDocumentation) {
RestAssuredMockMvc.standaloneSetup(MockMvcBuilders
.standaloneSetup(new FraudDetectionController())
.apply(documentationConfiguration(restDocumentation))
.alwaysDo(document(
getClass().getSimpleName() + "_" + info.getDisplayName())));
}
}| You need not specify the output directory for the generated snippets (since version 1.2.0.RELEASE of Spring REST Docs). |
15. How Can I Use Stubs from a Location
If you want to fetch contracts or stubs from a given location without cloning a repository or fetching a JAR, use the stubs:// protocol when providing the repository root argument for Stub Runner or the Spring Cloud Contract plugin. You can read more about this in this section of the documentation.
16. How Can I Generate Stubs at Runtime
If you want to generate stubs at runtime for contracts, switch the generateStubs property in the @AutoConfigureStubRunner annotation, or call the withGenerateStubs(true) method on the JUnit Rule or Extension. You can read more about this in this section of the documentation.
17. How Can I Make The Build Pass if There Are No Contracts or Stubs
If you want Stub Runner not to fail if no stubs were found, switch the generateStubs property in the @AutoConfigureStubRunner annotation or call the withFailOnNoStubs(false) method on the JUnit Rule or Extension. You can read more about this in this section of the documentation.
If you want the plugins not to fail the build when no contracts were found, you can set the failOnNoStubs flag in Maven or call the contractRepository { failOnNoStubs(false) } closure in Gradle.
18. How Can I Mark that a Contract Is in Progress
If a contract is in progress, it means that the, on the producer side, tests are not generated, but the stub is generated. You can read more about this in this section of the documentation.
In a CI build, before going to production, you would like to ensure that no in-progress contracts are on the classpath, because they may lead to false positives. For this reason, by default, in the Spring Cloud Contract plugin, we set the value of failOnInProgress to true. If you want to allow such contracts when tests are to be generated, set the flag to false.