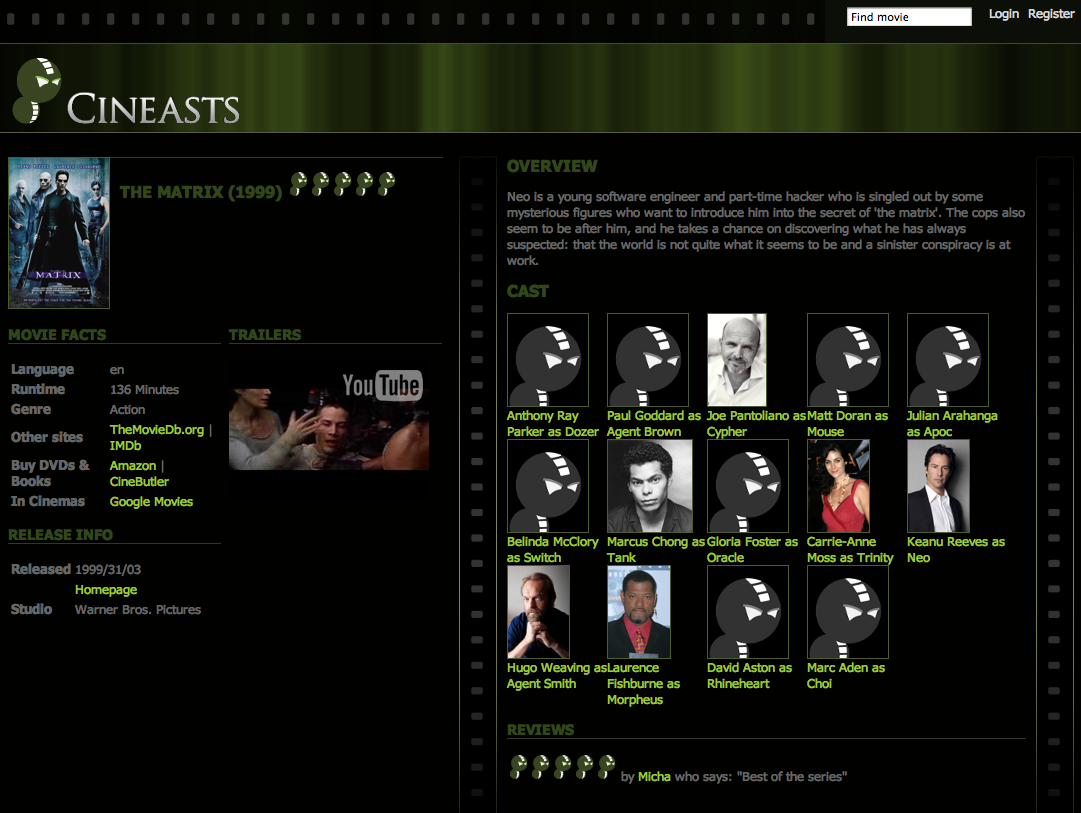
After having put some data in the graph database, we also wanted to show it to the user. Adding the controller method to show a single movie with its attributes and cast in a JSP was straightforward. It basically just involved using the repository to look the movie up and add it to the model, and then forwarding to the /movies/show view and voilá.
Example 11.1. Controller for showing movies
@RequestMapping(value = "/movies/{movieId}", method = RequestMethod.GET, headers = "Accept=text/html") public String singleMovieView(final Model model, @PathVariable String movieId) { Movie movie = repository.getMovie(movieId); model.addAttribute("id", movieId); if (movie != null) { model.addAttribute("movie", movie); model.addAttribute("stars", movie.getStars()); } return "/movies/show"; }
The UI had now evolved to this:
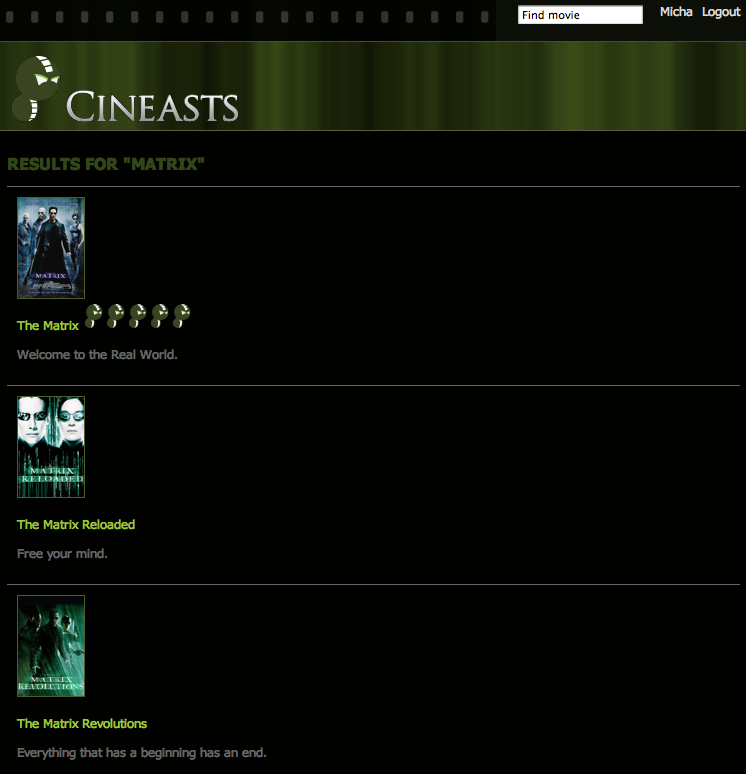
The next thing was to allow users to search for movies, so we needed some fulltext search capabilities. As the index provider implementation of Neo4j is based on Apache Lucene, we were delighted to see that fulltext indexes were supported out of the box.
We happily annotated the title field of the Movie class with @Indexed(fulltext = true). We got an exception back telling us that we have to specify a separate index name. So we simply changed it to @Indexed(fulltext = true, indexName = "search"). The corresponding repository method is called findAllByQuery. To restrict the size of the returned set we simply added a limit that truncates the result.
Example 11.2. Searching for movies
public class CineastRepository { .... public void List<Movie> findMovies(String query, int count) { List<Movie> movies=new ArrayList<Movie>(count); ClosableIterable<Movie> searchResults = movieRepository.findAllByQuery("title", query); for (Movie movie : searchResults) { movies.add(movie); if (count-- == 0) break; } searchResults.close(); return movies; } }
We then used this result in the controller to render a list of movies, driven by a search box. The movie properties and the cast were accessible through the getters in the domain classes.
Example 11.3. Search controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/movies", method = RequestMethod.GET, headers = "Accept=text/html") public String findMovies(Model model, @RequestParam("q") String query) { List<Movie> movies = repository.findMovies(query, 20); model.addAttribute("movies", movies); model.addAttribute("query", query); return "/movies/list"; }
Example 11.4. Search Results JSP
<h2>Movies</h2> <c:choose> <c:when test="${not empty movies}"> <dl class="listings"> <c:forEach items="${movies}" var="movie"> <dt> <a href="/movies/${movie.id}"><c:out value="${movie.title}" /></a><br/> </dt> <dd> <c:out value="${movie.description}" escapeXml="true" /> </dd> </c:forEach> </dl> </c:when> <c:otherwise> No movies found for query "${query}". </c:otherwise> </c:choose>
The UI now looked like this: