1.0.0.M1
Copyright © 2012 VMware, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Spring Migration Analyzer is a command-line tool that can be used to analyze Java EE applications and produce a report that describes the application and how it can be migrated to Spring.
Before installaing Spring Migration Analyzer, please ensure your system meets the following requirements:
- A Windows, OS X or Linux operating system
-
A Java 5 or later installation, with the
JAVA_HOMEenvironment variable configured to point to it
The Spring Migration Analyzer installation is available as a zip file from the
download site. Once you have downloaded
the zip, Spring Migration Analyzer can be installed by unzipping it into a
directory of your choice. Once unzipped, you may wish to add Spring Migration
Analyzer's bin directory to your PATH.
Next, verify that Spring Migration Analyzer has been installed correctly. To do so on Windows, run the following command:
>migration-analysis.bat
To do so on OS X and Linux, run the following command:
>migration-analysis.sh
In both cases, you should be presented with a description of Spring Migration Analyzer and its usage information:
Usage: migration-analysis.sh <inputPath> [OPTION]...
Description:
Produces a migration analysis report for each archive found at the specified
input path. The input path may be either a single archive or a directory. In
the case of a directory, the entire directory structure is examined and all
archives that are found are analyzed. The reports are written to the output
path with each report being written into a sub-directory with the same name as
its input archive. For example, if my-app.ear is analyzed its report will be
written to <outputPath>/my-app.ear.
Options:
-e,--exclude <excludedPaths> Paths within the input to be excluded from the
analysis. Supports Ant-style patterns and can be
specified multiple times.
-o <outputPath> The path of the output directory. Defaults to
the current working directory
-t <outputType> The type of the output to be created. Defaults
to html.
To analyze an application you run the migration-analysis
script, passing it the path of the application archive that you want to
be analyzed. For example:
>migration-analysis.sh /path/to/my-app.ear
This will perform an analysis of my-app.ear, producing
a migration report in the current working directory. The report will be
in HTML. The report is written into a directory with the same name as the
archive that we analyzed. For example if you analyzed
my-app.ear, the report will be written into a directory
named my-app.ear.
A number of different options may be passed to
migration-analysis, allowing you to customize its
behaviour:
Table 2.1. Command line options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -e, --exclude | A path within the input that should be excluded from the analysis. Supports Ant-style path patterns. This option can be specified mutiple times. |
| -o | The path of the output directory to which the analysis reports will be written. If not specified, the reports are written to the current working directory. |
| -t | Allows you to specify the the type of report to create. Defaults to html which is currently the only supported report type. |
Spring Migration Analyzer can analyze multiple archives at the same time. To analyze multiple archives you provide an input path that points to a directory containing all of the archives that you want to be analyzed.
When Spring Migration Analyzer analyzes multiple archives it produces a
separate report for each archive that it analyzes. Each report is written into
a directory with the same name as its corresponding archive. For example, with
three applications in a directory named apps:
apps/
one.ear
two.ear
three.ear
Running Spring Migration Analyzer with the following options:
>migration-analysis apps -o reports
Will produce the following set of reports, each in its own directory:
reports/
one.ear/
index.html
...
two.ear/
index.html
...
three.ear/
index.html
...
An HTML migration analysis report can be viewed by opening its
index.html file in any modern web browser.
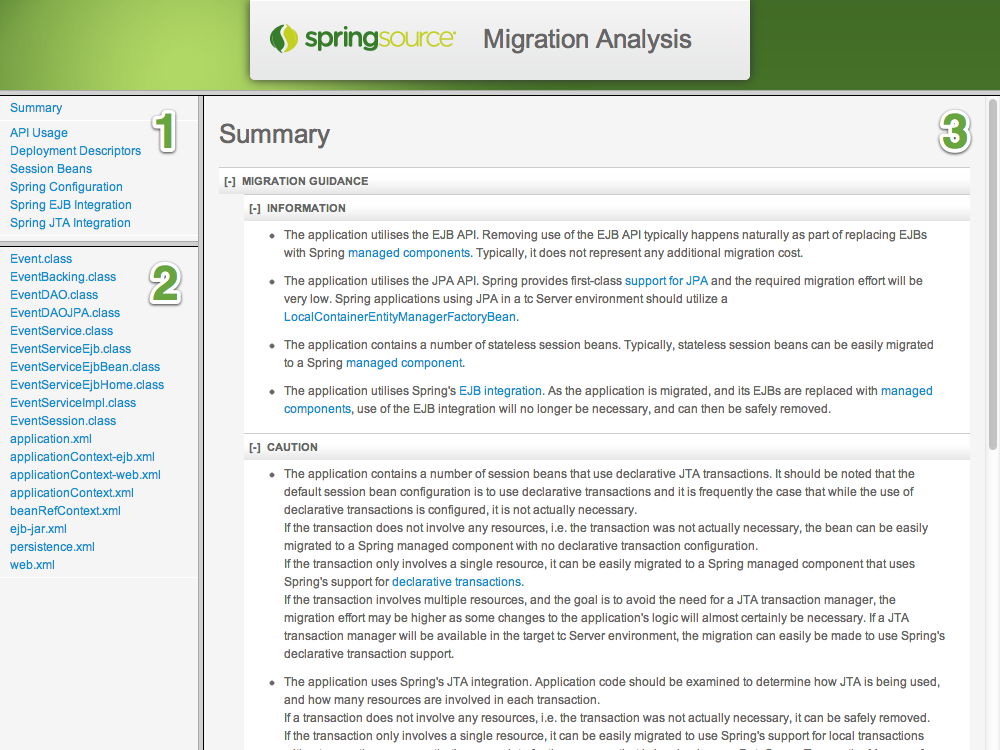
As shown in the image above, the report is divided into three main sections. Sections one and two are used for navigation and the third section is used to show the report's content. Section one lists the different categories that the report's information falls into. Clicking on a category will show details of that category's analysis. Section two lists all of the files in the application that the report contains information for. Clicking on a file will show all of the analysis for that file.
When the report is first viewed, or by clicking on
Summary in the top-left navigation section, a summary
of the report is shown. Reading the summary should help you to get a feel
for the effort involved in migrating the application. It provides a
high-level description of the application and provides some guidance on how
it can be migrated to Spring. Where applicable, the guidance provides links
to the relevant sections of the Spring reference documentation to help you get
started.
If you're interested in more details about the information in the report, you can use the links in the summary text or on the left-hand side. For example, you may want to look at a particular class to see how extensive its use of a Java EE API is, or you may want to find out more about the application's use of programmatic transaction management.
For detailed information about everything that Spring Migration Analyzer can detect, please refer to the chapter entitled "What is detected".
The analysis performed by Spring Migration Analyzer can detect many different things about an application. Depending on the nature and complexity of an application, some or even all of the following may appear in a migration report.
Detects the usage of a variety of different APIs within the application's code.
The following APIs are detected:
- EJB
javax.ejb.*
- JBoss
org.jboss.*
- JCA
javax.resource.*
- JMS
javax.jms.*
- JNDI
javax.naming.*
- JPA
javax.persistence.*
- JTA
javax.transaction.*
- Spring's EJB integration
org.springframework.ejb.*
- Spring's JNDI integration
org.springframework.jndi.*
- WebLogic
weblogic.*
- WebSphere
com.ibm.websphere.*com.ibm.wsspi.*
Detects the presence of deployment descriptors within the application.
The following Java EE and vendor-specific deployment descriptors are detected:
- Java EE:
application.xmlapplication-client.xmlejb-jar.xmlpersistence.xmlra.xmlweb.xmlwebservices.xml
- JBoss:
jaws.xmljboss.xmljbosscmp-jdbc.xmljboss-service.xmljboss-web.xml
- WebLogic:
weblogic.xmlweblogic-cmp-rdbms-jar.xmlweblogic-ejb-jar.xmlweblogic-ra.xmlpersistence-configuration.xmlweblogic-webservices.xmlweblogic-wsee-clientHandlerChain.xmlwebservice-policy-ref.xmlweblogic-wsee-standaloneclient.xmlweblogic-application.xml
- WebSphere:
client-resource.xmiibm-application-bnd.xmiibm-application-bnd.xmlibm-application-client-bnd.xmiibm-application-client-bnd.xmlibm-application-client-ext.xmiibm-application-client-ext.xmlibm-application-ext.xmiibm-application-ext.xmlibm-ejb-access-bean.xmlibm-ejb-jar-bnd.xmiibm-ejb-jar-bnd.xmlibm-ejb-jar-ext.xmiibm-ejb-jar-ext.xmlibm-ejb-jar-ext-pme.xmiibm-ejb-jar-ext-pme.xmlibm-webservices-bnd.xmiibm-webservices-ext.xmiibm-web-bnd.xmiibm-web-bnd.xmlibm-web-ext.xmiibm-web-ext.xmlibm-web-ext-pme.xmiibm-web-ext-pme.xmlj2c_plugin.xml
Detects the presence of EJBs in an application. Both EJBs declared in deployment descriptors and EJBs identified by Java annotations are detected.
The following EJB-related information is detected:
- Entity beans
- Persistence type: container-managed persistence (CMP) or bean-managed persistence (BMP)
- Primary key class
- CMP version
- Reentrancy
- CMP fields
- Session beans
- Session type: stateful or stateless
- Transaction type: container-managed transactions (CMT) or bean-managed transactions (BMT)
- Transaction propagation configuration (required, requires new, not supported, supports, never, or mandatory)
- Message-driven beans (MDBs)
- Transaction type: container-managed transactions (CMT) or bean-managed transactions (BMT)
- Transaction propagation configuration (required or not supported)
Detects any existing usage of Spring in an application, focusing on usage that relates to Java EE.
The following usage of Spring is detected:
- Spring configuration files
- Use of Spring's EJB integration namespace
- Use of Spring's JNDI namespace
- Use of Spring's JTA integration
http://www.springsource.org/download/community?project=Spring%20Migration%20Analyzer
The latest release of Spring Migration Analyzer, and all previous releases, are available for download.
http://github.com/SpringSource/spring-migration-analyzer
Spring Migration Analyzer's source code is available on GitHub
http://jira.springsource.org/browse/SMA
If you've found a bug in Spring Migration Analyzer, or you have a suggestion for a new feature or enhancement, please let us know. If you're reporting a bug, please include detailed steps of how to reproduce the problem. If you're suggesting a new feature or enhancement, please include a detailed description of what you'd like to be added.