Persist is a sample using recipe Chapter 23, Persist to demonstate how a database entry update logic can be controlled by a state machine.
The state machine logic and configuration is shown above:
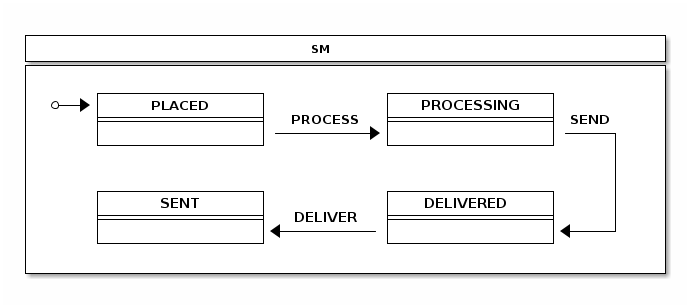
StateMachine Config.
@Configuration @EnableStateMachine static class StateMachineConfig extends StateMachineConfigurerAdapter<String, String> { @Override public void configure(StateMachineStateConfigurer<String, String> states) throws Exception { states .withStates() .initial("PLACED") .state("PROCESSING") .state("SENT") .state("DELIVERED"); } @Override public void configure(StateMachineTransitionConfigurer<String, String> transitions) throws Exception { transitions .withExternal() .source("PLACED").target("PROCESSING") .event("PROCESS") .and() .withExternal() .source("PROCESSING").target("SENT") .event("SEND") .and() .withExternal() .source("SENT").target("DELIVERED") .event("DELIVER"); } }
PersistStateMachineHandler can be created using a below config:
Handler Config.
@Configuration static class PersistHandlerConfig { @Autowired private StateMachine<String, String> stateMachine; @Bean public Persist persist() { return new Persist(persistStateMachineHandler()); } @Bean public PersistStateMachineHandler persistStateMachineHandler() { return new PersistStateMachineHandler(stateMachine); } }
Order class used with this sample is shown below:
Order Class.
public static class Order { int id; String state; public Order(int id, String state) { this.id = id; this.state = state; } @Override public String toString() { return "Order [id=" + id + ", state=" + state + "]"; } }
Now let’s see how this example works.
sm>persist db Order [id=1, state=PLACED] Order [id=2, state=PROCESSING] Order [id=3, state=SENT] Order [id=4, state=DELIVERED] sm>persist process 1 Exit state PLACED Entry state PROCESSING sm>persist db Order [id=2, state=PROCESSING] Order [id=3, state=SENT] Order [id=4, state=DELIVERED] Order [id=1, state=PROCESSING] sm>persist deliver 3 Exit state SENT Entry state DELIVERED sm>persist db Order [id=2, state=PROCESSING] Order [id=4, state=DELIVERED] Order [id=1, state=PROCESSING] Order [id=3, state=DELIVERED]
What happened in above run:
- We listed rows from an existing embedded database which is already populated with sample data.
-
We request to update order
1intoPROCESSINGstate. -
We list db entries again and see that state has been changed from
PLACEDinto aPROCESSING. -
We do update for order
3to update state fromSENTintoDELIVERED.
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
|
If you’re wondering where is the database because there are literally no
signs of it in a sample code. Sample is based on Spring Boot and
because necessary classes are in a classpath, embedded Spring Boot will even create an instance of @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; |
Finally we need to handle state changes:
public void change(int order, String event) { Order o = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select id, state from orders where id = ?", new Object[]{order}, new RowMapper<Order>() { public Order mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException { return new Order(rs.getInt("id"), rs.getString("state")); } }); handler.handleEventWithState(MessageBuilder.withPayload(event).setHeader("order", order).build(), o.state); }
And use a PersistStateChangeListener to update database:
private class LocalPersistStateChangeListener implements PersistStateChangeListener { @Override public void onPersist(State<String, String> state, Message<String> message, Transition<String, String> transition, StateMachine<String, String> stateMachine) { if (message != null && message.getHeaders().containsKey("order")) { Integer order = message.getHeaders().get("order", Integer.class); jdbcTemplate.update("update orders set state = ? where id = ?", state.getId(), order); } } }