Security is a state machine example using most of a combinations of securing a state machine. It is securing sending events, transitions and actions.
@n1:~# java -jar spring-statemachine-samples-secure-2.1.1.RELEASE.jar
We secure event sending with a users having a role USER. None of
a other users imposed by a Spring Security can’t send events into a
state machine.
@Override public void configure(StateMachineConfigurationConfigurer<States, Events> config) throws Exception { config .withConfiguration() .autoStartup(true) .and() .withSecurity() .enabled(true) .event("hasRole('USER')"); }
In this sample we define two users, user having a role USER and
admin having both roles USER and ADMIN. Authentication for both
user for password is password.
@EnableWebSecurity @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true) static class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Autowired public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth .inMemoryAuthentication() .withUser("user") .password("password") .roles("USER") .and() .withUser("admin") .password("password") .roles("USER", "ADMIN"); } }
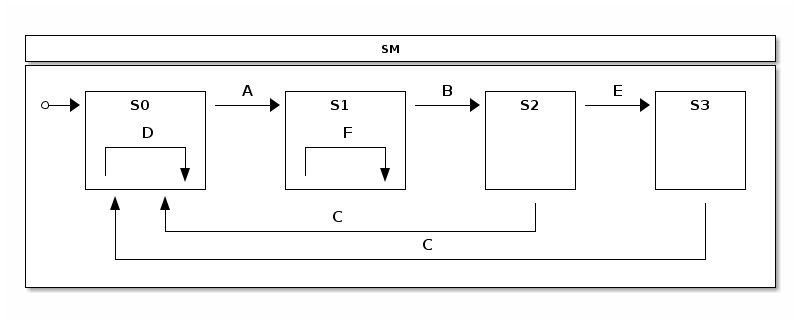
We define various transitions between states according to a statechart
seen above. Only a user with active ADMIN role can execute
external transitions between S2 and S3. Similarly ADMIN can only
execute internal transition in a state S1.
@Override public void configure(StateMachineTransitionConfigurer<States, Events> transitions) throws Exception { transitions .withExternal() .source(States.S0).target(States.S1).event(Events.A) .and() .withExternal() .source(States.S1).target(States.S2).event(Events.B) .and() .withExternal() .source(States.S2).target(States.S0).event(Events.C) .and() .withExternal() .source(States.S2).target(States.S3).event(Events.E) .secured("ROLE_ADMIN", ComparisonType.ANY) .and() .withExternal() .source(States.S3).target(States.S0).event(Events.C) .and() .withInternal() .source(States.S0).event(Events.D) .action(adminAction()) .and() .withInternal() .source(States.S1).event(Events.F) .action(transitionAction()) .secured("ROLE_ADMIN", ComparisonType.ANY); }
Action adminAction is secured with a role ADMIN.
@Scope(proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS) @Bean public Action<States, Events> adminAction() { return new Action<States, Events>() { @Secured("ROLE_ADMIN") @Override public void execute(StateContext<States, Events> context) { log.info("Executed only for admin role"); } }; }
Below Action would only be executed with internal transition in a
state S1 when event F is send. Transition itself is secured with a
role ADMIN so this transition will not be executed if current user
does not hate that role.
@Bean public Action<States, Events> transitionAction() { return new Action<States, Events>() { @Override public void execute(StateContext<States, Events> context) { log.info("Executed only for admin role"); } }; }