The Spring Cloud Data Flow server is a Spring Boot application that includes the Actuator library which adds several production ready features to help you monitor and manage your application.
The Actuator library adds http endpoints under the context path /management that is also
a discovery page for available endpoints. For example, there is a health endpoint
that shows application health information and an env that lists properties from
Spring’s ConfigurableEnvironment. By default only the health and application info
endpoints are accessible. The other endpoints are considered to be sensitive
and need to be enabled explicitly via configuration. If you are enabling
sensitive endpoints then you should also
secure the Data Flow server’s endpoints so that
information is not inadvertantly exposed to unauthenticated users. The local Data Flow server has security disabled by default, so all actuator endpoints are available.
The Data Flow server requires the a relational database and if the feature toggled for
analytics is enabled, a Redis server is also required. The Data Flow server will
autoconfigure the DataSourceHealthIndicator and RedisHealthIndicator if needed. The health of these two services is incorporated to the overall health status of the server through the health endpoint.
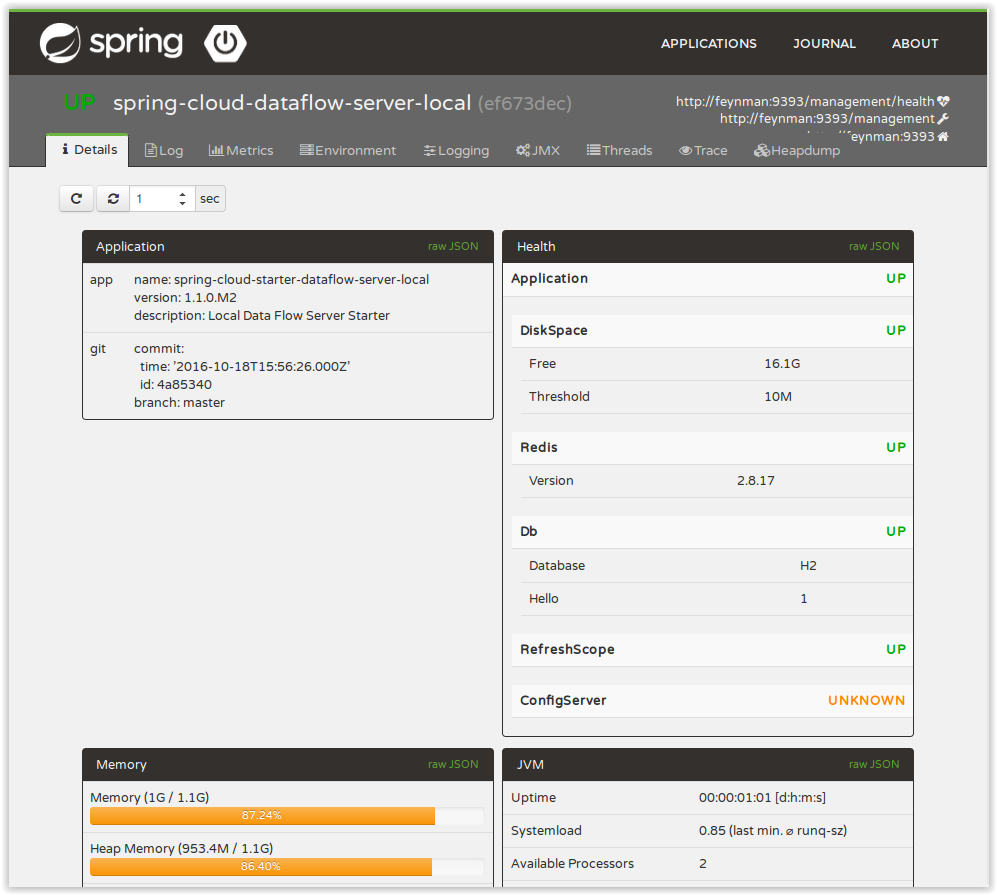
A nice way to visualize and interact with actuator endpoints is to incorporate the Spring Boot Admin client library into the Spring Cloud Data Flow server. You can create the Spring Boot Admin application by following a few simple steps.
An easy way to include the client library into the Data Flow server is to create a new Data Flow Server project from start.spring.io. Type 'flow' in the "Search for dependencies" text box and select the server runtime you want to customize. A simple way to have the Spring Cloud Data Flow server be a client to the Spring Boot Admin Server is by adding a dependency to the Data Flow server’s pom and an additional configuration property as documented in Registering Client Applications.
This will result in a UI with a tabs for each of the actuator endpoints.
Additional configuration is required to interact with JMX beans and logging levels. Refer
to the Spring Boot admin documentation for more information. As only the info
and health endpoints are available to unauthenticated users, you should enable security on
the Data Flow Server and also configure Spring Boot Admin server’s security so that it
can securely access the actuator endpoints.