

A traditional Spring application uses either a single application context, or a parent context containing service layer, data layer, and domain objects with a child context containing web layer components. The application context may well be formed by aggregating the contents of multiple configuration files.
When deploying an application to OSGi the more natural structure is to package the application as a set of peer bundles (application contexts) interacting via the OSGi service registry. Independent subsystems should be packaged as independent bundles or sets of bundles (vertical partitioning). A subsystem may be package in a single bundle, or divided into several bundles partitioned by layer (horizontal partitioning). A straightforward web application may for example be divided into four modules (bundles): a web bundle, service layer bundle, data layer bundle, and domain model bundle. Such an application would look like this:
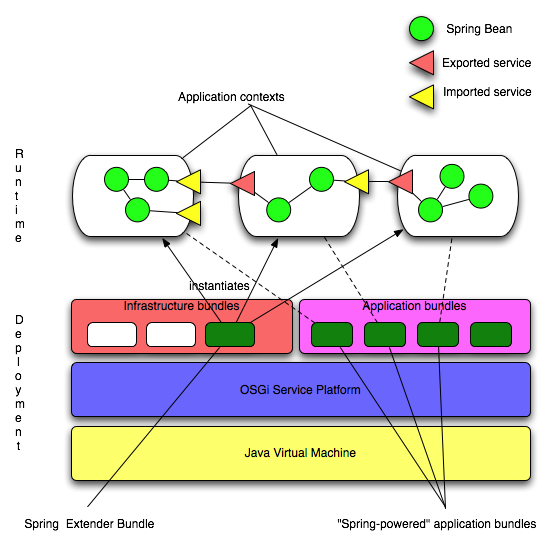
In this example the data layer bundle yields a data layer application context that contains a number of internal components (beans). Two of those beans are made publicly available outside of the application context by publishing them as services in the OSGi service registry.
The service layer bundle yields a service layer application context that contains a number of internal components (beans). Some of those components depend on data layer services, and import those services from the OSGi service registry. Two of the service layer components are made externally available as services in the OSGi service registry.
The web component bundle yields a web application context that contains a number of internal components (beans). Some of those components depend on application services, and import those services from the OSGi service registry. Since the domain model bundle contributes only domain model types, but does not need to create any components of its own, it has no associated application context.
Each application module should be packaged as an OSGi bundle. A
bundle is essentially a jar file with a
META-INF/MANIFEST.MF file containing a series of
headers recognized by the OSGi Service Platform. See the OSGi Service
Platform Core Specification section 3.2 for details. Some OSGi
implementations may support exploded jar files, but the format remains
the same.
The Spring extender recognizes a bundle as "Spring-powered" and will create an associated application context when the bundle is started and one or both of the following conditions is true:
The bundle path contains a folder
META-INF/spring with one or more files in that
folder with a '.xml' extension.
META-INF/MANIFEST.MF contains a manifest
header Spring-Context.
In addition, if the optional
SpringExtender-Version header is declared in the
bundle manifest, then the extender will only recognize bundles where the
specified version constraints are satisfied by the version of the
extender bundle (Bundle-Version). The value of the
SpringExtender-Version header must follow the syntax
for a version range as specified in section 3.2.5 of the OSGi Service
Platform Core Specification.
In the absence of the Spring-Context header the
extender expects every ".xml" file in the
META-INF/spring folder to be a valid Spring
configuration file, and all directives (see below) take on their default
values.
The Spring-Context manifest header may be used
to specify an alternate set of configuration files. The resource paths
are treated as relative resource paths and resolve to entries defined in
the bundle and the set of attached fragments.
When the
Spring-Context header defines at least one
configuration file location, any files in
META-INF/spring are ignored unless directly
referenced from the Spring-Context header.
The syntax for the Spring-Context header value
is:
Spring-Context-Value ::= context ( ',' context ) *
context ::= path ( ';' path ) * (';' directive) *
This syntax is consistent with the OSGi Service Platform common header syntax defined in section 3.2.3 of the OSGi Service Platform Core Specification.
For example, the manifest entry:
Spring-Context: config/account-data-context.xml, config/account-security-context.xml
will cause an application context to be instantiated using the
configuration found in the files
account-data-context.xml and
account-security-context.xml in the bundle jar
file.
A number of directives are available for use with the
Spring-Context header. These directives are:
create-asynchronously (false|true): controls whether the application context is created asynchronously (the default), or synchronously.
For example:
Spring-Context: *;create-asynchronously:=false
Creates an application context synchronously, using all of the
"*.xml" files contained in the META-INF/spring
folder.
Spring-Context: config/account-data-context.xml;create-asynchrously:=false
Creates an application context synchronously using the
config/account-data-context.xml configuration file.
Care must be taken when specifying synchronous context creation as the
application context will be created on the OSGi event thread, blocking
further event delivery until the context is fully initialized. If an
error occurs during the synchronous creation of the application context
then a FrameworkEvent.ERROR event is raised. The bundle will still
proceed to the ACTIVE state.
wait-for-dependencies (true|false): controls whether or not application context creation should wait for any mandatory service dependencies to be satisfied before proceeding (the default), or proceed immediately without waiting if dependencies are not satisfied upon startup.
For example:
Spring-Context: config/osgi-*.xml;wait-for-dependencies:=false
Creates an application context using all the files matching
"osgi-*.xml" in the config directory. Context creation will begin
immediately even if dependencies are not satisfied. This essentially
means that mandatory service references are treated as though they were
optional - clients will be injected with a service object that may not
be backed by an actual service in the registry initially. See
Section 8.2.2.9, “reference And OSGi Service Dynamics” for more details.
timeout (300): the time to wait (in
seconds) for mandatory dependencies to be satisfied before giving up
and failing application context creation. This setting is ignored if
wait-for-dependencies:=false is specified. The
default is 5 minutes (300 seconds).
For example:
Spring-Context: *;timeout:=60
Creates an application context that waits up to 1 minute (60 seconds) for its mandatory dependencies to appear.
publish-context (true|false): controls whether or not the application context object itself should be published in the OSGi service registry. The default is to publish the context.
For example:
Spring-Context: *;publish-context:=false
If there is no Spring-Context manifest entry, or no value is
specified for a given directive in that entry, then the directive takes
on its default value.
The table below summarizes the differences between the manifest configuration options in Spring DM and Blueprint Container:
Table 7.1. Configuration Setting Differences
| Option | Spring DM | Blueprint |
|---|---|---|
| Default Configuration Location | META-INF/spring | OSGI-INF/blueprint |
| Custom Locations Header | Spring-Context | Bundle-Blueprint |
| Attribute Header | Spring-Context | Bundle-SymbolicName |
| Asynchronous Creation Attribute | create-asynchronously | - |
| Startup Mandatory Dependencies Attribute | wait-for-dependencies | blueprint.graceperiod |
| Startup Mandatory Timeout Attribute | timeout (in s) | blueprint.timeout (in ms) |
| Container API Service Publication Attribute | publish-context | - |
The manifests below are equivalent in terms of settings:
Bundle-SymbolicName: org.example.account.bundle Spring-Context: config/account-data-context.xml, config/osgi-*.xml;wait-for-dependencies:=true; timeout:=10
 | All Spring DM specific attributes are grouped under |
 | Timeout specified in seconds. |
Bundle-SymbolicName: org.example.account.bundle;blueprint.graceperiod:=true; blueprint.timeout:=10000
Blueprint-Bundle: config/account-data-context.xml, config/osgi-*.xml
 | Blueprint settings are spread between |
 | Timeout specified in milliseconds. |
Aside from bundle-specific configurations, Spring DM allows the core extender generic behaviour be configured. This is useful when
embedding Spring DM inside a managed environment or when a bundles-wide functionality is desired. To allow for extensible configuration,
the extender relies on OSGi fragments to override its defaults. The extender looks for all XML files
under META-INF/spring/extender folder in its bundle space and assembled them into an application context
(of type OsgiBundleXmlApplicationContext)
that is used internally as its configuration. To override a default setting of the extender, look up the appropriate bean
name from the table below, define it in a suitable manner and then attach it as a fragment to the
spring-osgi-extender.jar, using:
Fragment-Host: org.springframework.osgi.extender
The following beans are currently recognized by the extender:
Table 7.2. Extender Configuration Options
| Bean Name | Type | Role | Default Behaviour/Value |
|---|---|---|---|
taskExecutor | TaskExecutor
[a] | Creates and runs the Spring application contexts associated with each bundle. The task executor is responsible for managing its own pool of threads used by the application contexts | SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor is used by default which means a new thread will be created for each application contexts. While this
is suitable for testing and development, we strongly recommend to use a thread pool
in a production environment |
shutdownTaskExecutor | TaskExecutor
[b] | Destroys managed Spring application contexts associated with each bundle. The task executor is responsible for managing its own pool of threads used by the application contexts | TimerTaskExecutor is used by default which means all application context will be destroyed in a serialized manner (which is
desired). Since the shutdown order normally matters, it is recommended to keep the default implementation or, for managed environments, to use a thread-pool
that executes only one task at a time (so that contexts are stopped in the given order). |
extenderProperties | java.util.Properties | Defines simple properties such as the maximum time for contexts to gracefully close | See the defaults below |
osgiApplicationEventMulticaster | ApplicationEventMulticaster
[c]
|
ApplicationEventMultiCaster used for propagating Spring DM events
to third parties.
| An instance of
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster is used.
See AbstractApplicationContext
javadoc
for more information regarding available beans in an application context. |
applicationContextCreator | OsgiApplicationContextCreator
[d]
| Allows customization of the application context created by the extender. This includes changing the application context class type or additional processing (see below). | The Extender default behaviour applies. |
| (irrelevant) | OsgiBeanFactoryPostProcessor
[d]
| Similar to Spring's BeanFactoryPostProcessor interface, beans of type
OsgiBeanFactoryPostProcessor are automatically detected and applied to all contexts created by the
extender (whether user-defined or not). This type of post processor
is useful as it allows customization of the bean factory such as adding/removing/changing existing bean definitions or adding new bean
instances. | The Extender default behaviour applies. |
osgiApplicationContextListener | OsgiBundleApplicationContextListener
[e]
| Application context event listener registered automatically by the extender. | Default implementation provides logging of the managed application contexts lifecycle. |
[a] org.springframework.core.task[b] org.springframework.core.task[c] org.springframework.context.event[d] org.springframework.osgi.extender package[e] org.springframework.osgi.context.event package | |||
From the extenderProperties bean, the following properties are recognized:
Table 7.3. Available extenderProperties
| Name | Type | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
shutdown.wait.time | java.lang.Long | The amount of time the extender will wait for each application context to shutdown gracefully. Expressed in milliseconds. | 10000 ms (10 s) |
process.annotations | java.lang.Boolean | Flag indicating whether or not, the extender will process Spring DM annotations. Note that this can be enabled in each process bundle by adding the appropriate bean post processor. See Section A.1, “Annotation-Based Injection” for more information. | false |
dependencies.wait.time | java.lang.Long | The amount of time the newly created application contexts will wait for their mandatory service dependencies during startup. Expressed in milliseconds. This settings is used only if the context owning bundle manifest does not define a value. | 300000 ms (300 s or 5 min) |
![[Note]](images/admons/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
| Since an application context is used, the full power of the Spring IoC container can be used for creating the extender configuration beans |
There are cases when the failure or succesful startup of an application context needs to be acknowledged for logging purposes (for example).
For these cases, Spring DM offers a dedicated package org.springframework.osgi.context.event which defines the events that
OSGi application contexts can send during their lifecycle. At the moment, the following events are available:
Table 7.4. Spring DM build-in events
| Event | Explanation |
|---|---|
OsgiBundleContextRefreshedEvent | Published when an OSGi application context has been succesfully initialized or refreshed (e.g. using the
refresh() method on the ConfigurableApplicationContext interface).
There are no guarantees on how many times this event might be received during the lifecycle of an application context - this is
left up to the used implementation. |
OsgiBundleContextFailedEvent | Published when an OSGi application context is closed due to a failure. This event can appear any time during the lifecycle of an application context - before, during or after refresh. Usually the cause indicates an error in the configuration - syntax typo, incorrect wiring, missing bean and so forth. |
OsgiBundleContextClosedEvent | Published when an OSGi application context is closed after a successful refresh (normally issued a Spring bundle is being stopped). |
Parties interested in receiving these events should implement OsgiBundleApplicationContextListener and
then publish it as an OSGi service. The Spring DM extender will automatically detect the listener and will send the events to it. By taking advantage
of the OSGi service registry, the extender decouples the received from the event publisher and moreover, makes the registration/unregistration process
easier. For example, there is nothing special a client should do to unregister the listener - simply stopping the bundle will automatically
unregister all its published services (including the listener), an event which will detected by the extender which will remove the listener.
Of course, it is also possible for the client to unregister the listener manually during a bundle lifecycle.
![[Note]](images/admons/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
| The Spring DM events semantics are slightly different then Spring's. The OSGi events are not sent to beans inside the causing application context but to other parties (possible beans in other application contexts) interested in monitoring its behaviour. |
The Spring Dynamic Modules project provides a number of bundle artifacts that must be installed in your OSGi platform in order for the Spring extender to function correctly:
The extender bundle itself,
org.springframework.osgi.extender
The core implementation bundle for the Spring Dynamic Modules
support, org.springframework.osgi.core
The Spring Dynamic Modules I/O support library bundle,
org.springframework.osgi.io
In addition, the Spring Framework provides a number of bundles that are required to be installed as dependencies. As of release 2.5 of the Spring Framework, the Spring jars included in the Spring distribution are valid OSGi bundles and can be installed directly into an OSGi platform. The minimum required set of bundles is:
org.springframework.aop.jar (bundle symbolic name
org.springframework.aop)
org.springframework.asm.jar (bundle symbolic name
org.springframework.asm)
org.springframework.beans.jar (bundle symbolic name
org.springframework.beans)
org.springframework.core.jar (bundle symbolic name
org.springframework.core)
org.springframework.context.jar (bundle symbolic name
org.springframework.context)
org.springframework.expression.jar (bundle symbolic name
org.springframework.expression)
In additional the following supporting library bundles are required. OSGi-ready versions of these libraries are shipped with the Spring Dynamic Modules distribution.
aopalliance
cglib-nodep (when proxying classes rather then interfaces, needed in most cases)
commons-logging API (SLF4J version highly recommended:
SLF4J API (com.springsource.sfl4j.api.jar)
SLF4J Implementation Bridge (such as Log4j - com.springsource.sfl4j.log4j.jar)
SLF4J commons logging adapter (com.springsource.sfl4j.org.apache.commons.logging.jar)
logging implementation suitable for commons-logging (such as log4j)
Spring 2.0 introduced (among other things) easier XML configuration and extensible XML authoring. The latter gives the ability of creating custom schemas that are discovered automatically (in non-OSGi environment) by the Spring XML infrastructure by including them in the classpath. Spring DM is aware of this process and supports it in OSGi environments so that custom schemas are available to bundles that use them without any extra code or manifest declaration.
All bundles deployed in the OSGi space (whether they are Spring-powered or not) are scanned by Spring DM for
custom Spring namespace declaration (by checking the bundle space forMETA-INF/spring.handlers and
META-INF/spring.schemas). If these are found, Spring DM will make the schemas and the namespaces available through an OSGi
service that will be automatically used by Spring-powered bundles. This mean that if you deploy a bundle that uses a custom schema, all you have to do
is deploy the library that provides the namespace parser and the schema.
Bundles that embedded inside their classpath libraries that provide custom schemas will use these over those available in the OSGi space. However,
the namespaces of the embedded libraries will not shared with other bundles, that is, they will not be seen by any other bundle.
In short, when using Spring DM, custom Spring namespaces are supported transparently without any additional work. Embedded namespace providers will have priority but will not be shared, as opposed to providers deployed as bundles which will be seen (and used) by others.
Refer to the OSGi Service Platform for details of the
Import-Package and Export-Package
manifest headers. Your bundle will need an
Import-Package entry for every external package that
the bundle depends on. If your bundle provides types that other bundles
need access to, you will need Export-Package entries
for every package that should be available from outside of the
bundle.
![[Important]](images/admons/important.png) | Important |
|---|---|
Both Export and Import-Package have a crucial role in defining a bundle class space. If used incorrectly,
the bundle might not be able to load certain classes or resources, load incorrect versions or even load multiple versions at the same time which usually
result in ClassCastException, NoClassDefFoundError or LinkageError. We strongly
recommend that you get familiar with the basics and, at least for starters, use tools
(such as Bundlor or BND) for creating proper
OSGi manifests. |
Many enterprise application libraries assume that all of the types and resources that comprise the application are accessible through the context class loader. While most developers do not use the context class loader, the loader is used heavily by application servers, containers or applications that are multi-threaded.
In OSGi R4, the set of types and resources available through the context class loader is undefined. This means that the OSGi platform does not make a guarantee of the thread context class loader value or in other words, it does not manage it.
Thus code (for example libraries) that performs manual class loading or that generates new classes dynamically can cause problems when executed inside an OSGi environment.
Spring Dynamic Modules guarantees that during the creation of an application context on behalf of a given bundle, all of the types and resources on the bundle's classpath are accessible via the context class loader. Spring Dynamic Modules also allows you to control what is accessible through the context class loader when invoking external services and when servicing requests on exported services. See Chapter 8, The Service Registry for details on this.
Work is underway in the OSGi R5 timeframe to provide standardized
support for dealing with generated classes and implicit class path
dependencies introduced by third-party libraries. In the interim you may
need to rely on workarounds such as the
DynamicImport-Package manifest header, or the
facilities provided by specific OSGi implementations such as Equinox's
buddy mechanism. The Spring Dynamic Modules documentation contains more
details on known issues with common enterprise libraries and the
workarounds.
Your chosen OSGi platform implementation should be able to provide
you with a good deal of information about the current status of the OSGi
environment. For example, starting Equinox with the
-console argument provides a command-line console
through which you can determine which bundles are installed and their
states, the packages and services exported by bundles, find out why a
bundle has failed to resolve, and drive bundles through the
lifecycle. All the OSGi platform tested, provide their own logging, which
can be enabled and customized through dedicated settings. For more information,
please refer to OSGi platforms documentation.
In addition, Spring itself and the Spring Dynamic Modules bundles
contain extensive logging instrumentation that can help you diagnose
problems. The recommended approach is to deploy the Simple Logging
Facade for Java (slf4j)
slf4j-api.jar and slf4j-log4j13.jar bundles (the jar files distributed
by the project are valid OSGi bundles). Then you simply need to create a
log4j.properties file in the root of your bundle
classpath.
Managed, OSGi-aware runtime environments such as dmServer provide additional logging and insight not just for the bundle at hand, but also regarding the application context and the VM among other things.
Note that Spring Dynamic Modules uses commons-logging API internally which means that its logging implementation is fully pluggable. Please see the FAQ and Resources pages for more information on other logging libraries besides log4j.