Spring Security 3.0 requires a Java 5.0 Runtime Environment or higher. As Spring Security aims to operate in a self-contained manner, there is no need to place any special configuration files into your Java Runtime Environment. In particular, there is no need to configure a special Java Authentication and Authorization Service (JAAS) policy file or place Spring Security into common classpath locations.
Similarly, if you are using an EJB Container or Servlet Container there is no need to put any special configuration files anywhere, nor include Spring Security in a server classloader. All the required files will be contained within your application.
This design offers maximum deployment time flexibility, as you can simply copy your target artifact (be it a JAR, WAR or EAR) from one system to another and it will immediately work.
In Spring Security 3.0, the contents of the spring-security-core jar were stripped down to the bare minimum. It no longer contains any code related to web-application security, LDAP or namespace configuration. We’ll take a look here at some of the Java types that you’ll find in the core module. They represent the building blocks of the the framework, so if you ever need to go beyond a simple namespace configuration then it’s important that you understand what they are, even if you don’t actually need to interact with them directly.
The most fundamental object is SecurityContextHolder. This is where we store details of the present security context of the application, which includes details of the principal currently using the application. By default the SecurityContextHolder uses a ThreadLocal to store these details, which means that the security context is always available to methods in the same thread of execution, even if the security context is not explicitly passed around as an argument to those methods. Using a ThreadLocal in this way is quite safe if care is taken to clear the thread after the present principal’s request is processed. Of course, Spring Security takes care of this for you automatically so there is no need to worry about it.
Some applications aren’t entirely suitable for using a ThreadLocal, because of the specific way they work with threads. For example, a Swing client might want all threads in a Java Virtual Machine to use the same security context. SecurityContextHolder can be configured with a strategy on startup to specify how you would like the context to be stored. For a standalone application you would use the SecurityContextHolder.MODE_GLOBAL strategy. Other applications might want to have threads spawned by the secure thread also assume the same security identity. This is achieved by using SecurityContextHolder.MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL. You can change the mode from the default SecurityContextHolder.MODE_THREADLOCAL in two ways. The first is to set a system property, the second is to call a static method on SecurityContextHolder. Most applications won’t need to change from the default, but if you do, take a look at the JavaDocs for SecurityContextHolder to learn more.
Inside the SecurityContextHolder we store details of the principal currently interacting with the application. Spring Security uses an Authentication object to represent this information. You won’t normally need to create an Authentication object yourself, but it is fairly common for users to query the Authentication object. You can use the following code block - from anywhere in your application - to obtain the name of the currently authenticated user, for example:
Object principal = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal(); if (principal instanceof UserDetails) { String username = ((UserDetails)principal).getUsername(); } else { String username = principal.toString(); }
The object returned by the call to getContext() is an instance of the SecurityContext interface. This is the object that is kept in thread-local storage. As we’ll see below, most authentication mechanisms withing Spring Security return an instance of UserDetails as the principal.
Another item to note from the above code fragment is that you can obtain a principal from the Authentication object. The principal is just an Object. Most of the time this can be cast into a UserDetails object. UserDetails is a core interface in Spring Security. It represents a principal, but in an extensible and application-specific way. Think of UserDetails as the adapter between your own user database and what Spring Security needs inside the SecurityContextHolder. Being a representation of something from your own user database, quite often you will cast the UserDetails to the original object that your application provided, so you can call business-specific methods (like`getEmail(), `getEmployeeNumber() and so on).
By now you’re probably wondering, so when do I provide a UserDetails object? How do I do that? I thought you said this thing was declarative and I didn’t need to write any Java code - what gives? The short answer is that there is a special interface called UserDetailsService. The only method on this interface accepts a String-based username argument and returns a UserDetails:
UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException;
This is the most common approach to loading information for a user within Spring Security and you will see it used throughout the framework whenever information on a user is required.
On successful authentication, UserDetails is used to build the Authentication object that is stored in the SecurityContextHolder (more on this below). The good news is that we provide a number of UserDetailsService implementations, including one that uses an in-memory map (InMemoryDaoImpl) and another that uses JDBC (JdbcDaoImpl). Most users tend to write their own, though, with their implementations often simply sitting on top of an existing Data Access Object (DAO) that represents their employees, customers, or other users of the application. Remember the advantage that whatever your UserDetailsService returns can always be obtained from the SecurityContextHolder using the above code fragment.
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
|
There is often some confusion about |
Besides the principal, another important method provided by Authentication is getAuthorities(). This method provides an array of GrantedAuthority objects. A GrantedAuthority is, not surprisingly, an authority that is granted to the principal. Such authorities are usually "roles", such as ROLE_ADMINISTRATOR or ROLE_HR_SUPERVISOR. These roles are later on configured for web authorization, method authorization and domain object authorization. Other parts of Spring Security are capable of interpreting these authorities, and expect them to be present. GrantedAuthority objects are usually loaded by the UserDetailsService.
Usually the GrantedAuthority objects are application-wide permissions. They are not specific to a given domain object. Thus, you wouldn’t likely have a GrantedAuthority to represent a permission to Employee object number 54, because if there are thousands of such authorities you would quickly run out of memory (or, at the very least, cause the application to take a long time to authenticate a user). Of course, Spring Security is expressly designed to handle this common requirement, but you’d instead use the project’s domain object security capabilities for this purpose.
Just to recap, the major building blocks of Spring Security that we’ve seen so far are:
-
SecurityContextHolder, to provide access to theSecurityContext. -
SecurityContext, to hold theAuthenticationand possibly request-specific security information. -
Authentication, to represent the principal in a Spring Security-specific manner. -
GrantedAuthority, to reflect the application-wide permissions granted to a principal. -
UserDetails, to provide the necessary information to build an Authentication object from your application’s DAOs or other source of security data. -
UserDetailsService, to create aUserDetailswhen passed in aString-based username (or certificate ID or the like).
Now that you’ve gained an understanding of these repeatedly-used components, let’s take a closer look at the process of authentication.
Spring Security can participate in many different authentication environments. While we recommend people use Spring Security for authentication and not integrate with existing Container Managed Authentication, it is nevertheless supported - as is integrating with your own proprietary authentication system.
Let’s consider a standard authentication scenario that everyone is familiar with.
- A user is prompted to log in with a username and password.
- The system (successfully) verifies that the password is correct for the username.
- The context information for that user is obtained (their list of roles and so on).
- A security context is established for the user
- The user proceeds, potentially to perform some operation which is potentially protected by an access control mechanism which checks the required permissions for the operation against the current security context information.
The first three items constitute the authentication process so we’ll take a look at how these take place within Spring Security.
-
The username and password are obtained and combined into an instance of
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(an instance of theAuthenticationinterface, which we saw earlier). -
The token is passed to an instance of
AuthenticationManagerfor validation. -
The
AuthenticationManagerreturns a fully populatedAuthenticationinstance on successful authentication. -
The security context is established by calling
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(…), passing in the returned authentication object.
From that point on, the user is considered to be authenticated. Let’s look at some code as an example.
import org.springframework.security.authentication.*; import org.springframework.security.core.*; import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority; import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder; public class AuthenticationExample { private static AuthenticationManager am = new SampleAuthenticationManager(); public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); while(true) { System.out.println("Please enter your username:"); String name = in.readLine(); System.out.println("Please enter your password:"); String password = in.readLine(); try { Authentication request = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(name, password); Authentication result = am.authenticate(request); SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(result); break; } catch(AuthenticationException e) { System.out.println("Authentication failed: " + e.getMessage()); } } System.out.println("Successfully authenticated. Security context contains: " + SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication()); } } class SampleAuthenticationManager implements AuthenticationManager { static final List<GrantedAuthority> AUTHORITIES = new ArrayList<GrantedAuthority>(); static { AUTHORITIES.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_USER")); } public Authentication authenticate(Authentication auth) throws AuthenticationException { if (auth.getName().equals(auth.getCredentials())) { return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(auth.getName(), auth.getCredentials(), AUTHORITIES); } throw new BadCredentialsException("Bad Credentials"); } }
Here
we have written a little program that asks the user to enter a username and password
and performs the above sequence. The
AuthenticationManager which we’ve implemented here will authenticate any user whose username and password are the same. It assigns a single role to every user. The output from the above will be something like:
Please enter your username: bob Please enter your password: password Authentication failed: Bad Credentials Please enter your username: bob Please enter your password: bob Successfully authenticated. Security context contains: \ org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken@441d0230: \ Principal: bob; Password: [PROTECTED]; \ Authenticated: true; Details: null; \ Granted Authorities: ROLE_USER
Note that you don’t normally need to write any code like this. The process will normally occur internally, in a web authentication filter for example. We’ve just included the code here to show that the question of what actually constitutes authentication in Spring Security has quite a simple answer. A user is authenticated when the SecurityContextHolder contains a fully populated Authentication object.
In fact, Spring Security doesn’t mind how you put the Authentication object inside the SecurityContextHolder. The only critical requirement is that the SecurityContextHolder contains an Authentication which represents a principal before the AbstractSecurityInterceptor (which we’ll see more about later) needs to authorize a user operation.
You can (and many users do) write their own filters or MVC controllers to provide interoperability with authentication systems that are not based on Spring Security. For example, you might be using Container-Managed Authentication which makes the current user available from a ThreadLocal or JNDI location. Or you might work for a company that has a legacy proprietary authentication system, which is a corporate "standard" over which you have little control. In situations like this it’s quite easy to get Spring Security to work, and still provide authorization capabilities. All you need to do is write a filter (or equivalent) that reads the third-party user information from a location, build a Spring Security-specific Authentication object, and put it into the SecurityContextHolder. In this case you also need to think about things which are normally taken care of automatically by the built-in authentication infrastructure. For example, you might need to pre-emptively create an HTTP session to cache the context between requests, before you write the response to the client footnote:[It isn’t possible to create a session once the response has been committed.
If you’re wondering how the AuthenticationManager is implemented in a real world example, we’ll look at that in the core services chapter.
Now let’s explore the situation where you are using Spring Security in a web application (without web.xml security enabled). How is a user authenticated and the security context established?
Consider a typical web application’s authentication process:
- You visit the home page, and click on a link.
- A request goes to the server, and the server decides that you’ve asked for a protected resource.
- As you’re not presently authenticated, the server sends back a response indicating that you must authenticate. The response will either be an HTTP response code, or a redirect to a particular web page.
- Depending on the authentication mechanism, your browser will either redirect to the specific web page so that you can fill out the form, or the browser will somehow retrieve your identity (via a BASIC authentication dialogue box, a cookie, a X.509 certificate etc.).
- The browser will send back a response to the server. This will either be an HTTP POST containing the contents of the form that you filled out, or an HTTP header containing your authentication details.
- Next the server will decide whether or not the presented credentials are valid. If they’re valid, the next step will happen. If they’re invalid, usually your browser will be asked to try again (so you return to step two above).
- The original request that you made to cause the authentication process will be retried. Hopefully you’ve authenticated with sufficient granted authorities to access the protected resource. If you have sufficient access, the request will be successful. Otherwise, you’ll receive back an HTTP error code 403, which means "forbidden".
Spring Security has distinct classes responsible for most of the steps described above. The main participants (in the order that they are used) are the ExceptionTranslationFilter, an AuthenticationEntryPoint and an "authentication mechanism", which is responsible for calling the AuthenticationManager which we saw in the previous section.
ExceptionTranslationFilter is a Spring Security filter that has responsibility for detecting any Spring Security exceptions that are thrown. Such exceptions will generally be thrown by an AbstractSecurityInterceptor, which is the main provider of authorization services. We will discuss AbstractSecurityInterceptor in the next section, but for now we just need to know that it produces Java exceptions and knows nothing about HTTP or how to go about authenticating a principal. Instead the ExceptionTranslationFilter offers this service, with specific responsibility for either returning error code 403 (if the principal has been authenticated and therefore simply lacks sufficient access - as per step seven above), or launching an AuthenticationEntryPoint (if the principal has not been authenticated and therefore we need to go commence step three).
The AuthenticationEntryPoint is responsible for step three in the above list. As you can imagine, each web application will have a default authentication strategy (well, this can be configured like nearly everything else in Spring Security, but let’s keep it simple for now). Each major authentication system will have its own AuthenticationEntryPoint implementation, which typically performs one of the actions described in step 3.
Once your browser submits your authentication credentials (either as an HTTP form post or HTTP header) there needs to be something on the server that"collects" these authentication details. By now we’re at step six in the above list. In Spring Security we have a special name for the function of collecting authentication details from a user agent (usually a web browser), referring to it as the "authentication mechanism". Examples are form-base login and Basic authentication. Once the authentication details have been collected from the user agent, an Authentication`"request" object is built and then presented to the `AuthenticationManager.
After the authentication mechanism receives back the fully-populated Authentication object, it will deem the request valid, put the Authentication into the SecurityContextHolder, and cause the original request to be retried (step seven above). If, on the other hand, the AuthenticationManager rejected the request, the authentication mechanism will ask the user agent to retry (step two above).
Depending on the type of application, there may need to be a strategy in place to store the security context between user operations. In a typical web application, a user logs in once and is subsequently identified by their session Id. The server caches the principal information for the duration session. In Spring Security, the responsibility for storing the SecurityContext between requests falls to the SecurityContextPersistenceFilter, which by default stores the context as an HttpSession attribute between HTTP requests. It restores the context to the SecurityContextHolder for each request and, crucially, clears the SecurityContextHolder when the request completes. You shouldn’t interact directly with the HttpSession for security purposes. There is simply no justification for doing so - always use the SecurityContextHolder instead.
Many other types of application (for example, a stateless RESTful web service) do not use HTTP sessions and will re-authenticate on every request. However, it is still important that the SecurityContextPersistenceFilter is included in the chain to make sure that the SecurityContextHolder is cleared after each request.
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
|
In an application which receives concurrent requests in a single session, the same |
The main interface responsible for making access-control decisions in Spring Security is the AccessDecisionManager. It has a decide method which takes an Authentication object representing the principal requesting access, a "secure object" (see below) and a list of security metadata attributes which apply for the object (such as a list of roles which are required for access to be granted).
If you’re familiar with AOP, you’d be aware there are different types of advice available: before, after, throws and around. An around advice is very useful, because an advisor can elect whether or not to proceed with a method invocation, whether or not to modify the response, and whether or not to throw an exception. Spring Security provides an around advice for method invocations as well as web requests. We achieve an around advice for method invocations using Spring’s standard AOP support and we achieve an around advice for web requests using a standard Filter.
For those not familiar with AOP, the key point to understand is that Spring Security can help you protect method invocations as well as web requests. Most people are interested in securing method invocations on their services layer. This is because the services layer is where most business logic resides in current-generation Java EE applications. If you just need to secure method invocations in the services layer, Spring’s standard AOP will be adequate. If you need to secure domain objects directly, you will likely find that AspectJ is worth considering.
You can elect to perform method authorization using AspectJ or Spring AOP, or you can elect to perform web request authorization using filters. You can use zero, one, two or three of these approaches together. The mainstream usage pattern is to perform some web request authorization, coupled with some Spring AOP method invocation authorization on the services layer.
So what is a "secure object" anyway? Spring Security uses the term to refer to any object that can have security (such as an authorization decision) applied to it. The most common examples are method invocations and web requests.
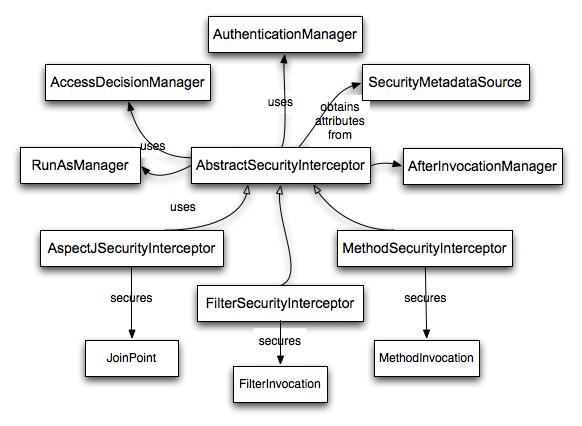
Each supported secure object type has its own interceptor class, which is a subclass of AbstractSecurityInterceptor. Importantly, by the time the AbstractSecurityInterceptor is called, the SecurityContextHolder will contain a valid Authentication if the principal has been authenticated.
AbstractSecurityInterceptor provides a consistent workflow for handling secure object requests, typically:
- Look up the "configuration attributes" associated with the present request
-
Submitting the secure object, current
Authenticationand configuration attributes to theAccessDecisionManagerfor an authorization decision -
Optionally change the
Authenticationunder which the invocation takes place - Allow the secure object invocation to proceed (assuming access was granted)
-
Call the
AfterInvocationManagerif configured, once the invocation has returned. If the invocation raised an exception, theAfterInvocationManagerwill not be invoked.
A "configuration attribute" can be thought of as a String that has special meaning to the classes used by AbstractSecurityInterceptor. They are represented by the interface ConfigAttribute within the framework. They may be simple role names or have more complex meaning, depending on the how sophisticated the AccessDecisionManager implementation is. The AbstractSecurityInterceptor is configured with a SecurityMetadataSource which it uses to look up the attributes for a secure object. Usually this configuration will be hidden from the user. Configuration attributes will be entered as annotations on secured methods or as access attributes on secured URLs. For example, when we saw something like <intercept-url pattern='/secure/**' access='ROLE_A,ROLE_B'/> in the namespace introduction, this is saying that the configuration attributes ROLE_A and ROLE_B apply to web requests matching the given pattern. In practice, with the default AccessDecisionManager configuration, this means that anyone who has a GrantedAuthority matching either of these two attributes will be allowed access. Strictly speaking though, they are just attributes and the interpretation is dependent on the AccessDecisionManager implementation. The use of the prefix ROLE_ is a marker to indicate that these attributes are roles and should be consumed by Spring Security’s`RoleVoter`. This is only relevant when a voter-based AccessDecisionManager is in use. We’ll see how the AccessDecisionManager is implemented in the authorization chapter.
Assuming AccessDecisionManager decides to allow the request, the AbstractSecurityInterceptor will normally just proceed with the request. Having said that, on rare occasions users may want to replace the Authentication inside the SecurityContext with a different Authentication, which is handled by the AccessDecisionManager calling a RunAsManager. This might be useful in reasonably unusual situations, such as if a services layer method needs to call a remote system and present a different identity. Because Spring Security automatically propagates security identity from one server to another (assuming you’re using a properly-configured RMI or HttpInvoker remoting protocol client), this may be useful.
Following the secure object invocation proceeding and then returning - which may mean a method invocation completing or a filter chain proceeding - the AbstractSecurityInterceptor gets one final chance to handle the invocation. At this stage the AbstractSecurityInterceptor is interested in possibly modifying the return object. We might want this to happen because an authorization decision couldn’t be made "on the way in" to a secure object invocation. Being highly pluggable, AbstractSecurityInterceptor will pass control to an AfterInvocationManager to actually modify the object if needed. This class can even entirely replace the object, or throw an exception, or not change it in any way as it chooses. The after-invocation checks will only be executed if the invocation is successful. If an exception occurs, the additional checks will be skipped.
AbstractSecurityInterceptor and its related objects are shown in Figure 7.1, “Security interceptors and the "secure object" model”
Only developers contemplating an entirely new way of intercepting and authorizing requests would need to use secure objects directly. For example, it would be possible to build a new secure object to secure calls to a messaging system. Anything that requires security and also provides a way of intercepting a call (like the AOP around advice semantics) is capable of being made into a secure object. Having said that, most Spring applications will simply use the three currently supported secure object types (AOP Alliance MethodInvocation, AspectJ JoinPoint and web request FilterInvocation) with complete transparency.
Spring Security supports localization of exception messages that end users are likely to see. If your application is designed for English-speaking users, you don’t need to do anything as by default all Security Security messages are in English. If you need to support other locales, everything you need to know is contained in this section.
All exception messages can be localized, including messages related to authentication failures and access being denied (authorization failures). Exceptions and logging messages that are focused on developers or system deployers (including incorrect attributes, interface contract violations, using incorrect constructors, startup time validation, debug-level logging) are not localized and instead are hard-coded in English within Spring Security’s code.
Shipping in the spring-security-core-xx.jar you will find an org.springframework.security package that in turn contains a messages.properties file, as well as localized versions for some common languages. This should be referred to by your`ApplicationContext`, as Spring Security classes implement Spring’s MessageSourceAware interface and expect the message resolver to be dependency injected at application context startup time. Usually all you need to do is register a bean inside your application context to refer to the messages. An example is shown below:
<bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource"> <property name="basename" value="classpath:org/springframework/security/messages"/> </bean>
The messages.properties is named in accordance with standard resource bundles and represents the default language supported by Spring Security messages. This default file is in English.
If you wish to customize the messages.properties file, or support other languages, you should copy the file, rename it accordingly, and register it inside the above bean definition. There are not a large number of message keys inside this file, so localization should not be considered a major initiative. If you do perform localization of this file, please consider sharing your work with the community by logging a JIRA task and attaching your appropriately-named localized version of messages.properties.
Spring Security relies on Spring’s localization support in order to actually lookup the appropriate message. In order for this to work, you have to make sure that the locale from the incoming request is stored in Spring’s org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder. Spring MVC’s DispatcherServlet does this for your application automatically, but since Spring Security’s filters are invoked before this, the LocaleContextHolder needs to be set up to contain the correct Locale before the filters are called. You can either do this in a filter yourself (which must come before the Spring Security filters in`web.xml`) or you can use Spring’s RequestContextFilter. Please refer to the Spring Framework documentation for further details on using localization with Spring.
The "contacts" sample application is set up to use localized messages.