For using the Apache Kafka binder, you just need to add it to your Spring Cloud Stream application, using the following Maven coordinates:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-stream-binder-kafka</artifactId> </dependency>
Alternatively, you can also use the Spring Cloud Stream Kafka Starter.
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-stream-kafka</artifactId> </dependency>
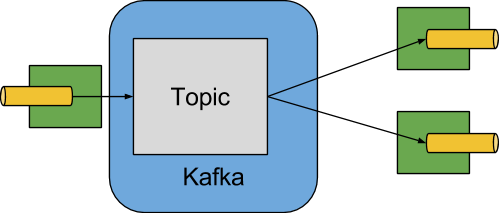
A simplified diagram of how the Apache Kafka binder operates can be seen below.
The Apache Kafka Binder implementation maps each destination to an Apache Kafka topic. The consumer group maps directly to the same Apache Kafka concept. Partitioning also maps directly to Apache Kafka partitions as well.
This section contains the configuration options used by the Apache Kafka binder.
For common configuration options and properties pertaining to binder, refer to the core docs.
- spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.brokers
A list of brokers to which the Kafka binder will connect.
Default:
localhost.- spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.defaultBrokerPort
brokersallows hosts specified with or without port information (e.g.,host1,host2:port2). This sets the default port when no port is configured in the broker list.Default:
9092.- spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.zkNodes
A list of ZooKeeper nodes to which the Kafka binder can connect.
Default:
localhost.- spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.defaultZkPort
zkNodesallows hosts specified with or without port information (e.g.,host1,host2:port2). This sets the default port when no port is configured in the node list.Default:
2181.- spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.configuration
Key/Value map of client properties (both producers and consumer) passed to all clients created by the binder. Due to the fact that these properties will be used by both producers and consumers, usage should be restricted to common properties, especially security settings.
Default: Empty map.
- spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.headers
The list of custom headers that will be transported by the binder.
Default: empty.
- spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.offsetUpdateTimeWindow
The frequency, in milliseconds, with which offsets are saved. Ignored if
0.Default:
10000.- spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.offsetUpdateCount
The frequency, in number of updates, which which consumed offsets are persisted. Ignored if
0. Mutually exclusive withoffsetUpdateTimeWindow.Default:
0.- spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.requiredAcks
The number of required acks on the broker.
Default:
1.- spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.minPartitionCount
Effective only if
autoCreateTopicsorautoAddPartitionsis set. The global minimum number of partitions that the binder will configure on topics on which it produces/consumes data. It can be superseded by thepartitionCountsetting of the producer or by the value ofinstanceCount*concurrencysettings of the producer (if either is larger).Default:
1.- spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.replicationFactor
The replication factor of auto-created topics if
autoCreateTopicsis active.Default:
1.- spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.autoCreateTopics
If set to
true, the binder will create new topics automatically. If set tofalse, the binder will rely on the topics being already configured. In the latter case, if the topics do not exist, the binder will fail to start. Of note, this setting is independent of theauto.topic.create.enablesetting of the broker and it does not influence it: if the server is set to auto-create topics, they may be created as part of the metadata retrieval request, with default broker settings.Default:
true.- spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.autoAddPartitions
If set to
true, the binder will create add new partitions if required. If set tofalse, the binder will rely on the partition size of the topic being already configured. If the partition count of the target topic is smaller than the expected value, the binder will fail to start.Default:
false.- spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.socketBufferSize
Size (in bytes) of the socket buffer to be used by the Kafka consumers.
Default:
2097152.
The following properties are available for Kafka consumers only and
must be prefixed with spring.cloud.stream.kafka.bindings.<channelName>.consumer..
- autoRebalanceEnabled
When
true, topic partitions will be automatically rebalanced between the members of a consumer group. Whenfalse, each consumer will be assigned a fixed set of partitions based onspring.cloud.stream.instanceCountandspring.cloud.stream.instanceIndex. This requires bothspring.cloud.stream.instanceCountandspring.cloud.stream.instanceIndexproperties to be set appropriately on each launched instance. The propertyspring.cloud.stream.instanceCountmust typically be greater than 1 in this case.Default:
true.- autoCommitOffset
Whether to autocommit offsets when a message has been processed. If set to
false, a header with the keykafka_acknowledgmentof the typeorg.springframework.kafka.support.Acknowledgmentheader will be present in the inbound message. Applications may use this header for acknowledging messages. See the examples section for details. When this property is set tofalse, Kafka binder will set the ack mode toorg.springframework.kafka.listener.AbstractMessageListenerContainer.AckMode.MANUAL.Default:
true.- autoCommitOnError
Effective only if
autoCommitOffsetis set totrue. If set tofalseit suppresses auto-commits for messages that result in errors, and will commit only for successful messages, allows a stream to automatically replay from the last successfully processed message, in case of persistent failures. If set totrue, it will always auto-commit (if auto-commit is enabled). If not set (default), it effectively has the same value asenableDlq, auto-committing erroneous messages if they are sent to a DLQ, and not committing them otherwise.Default: not set.
- recoveryInterval
The interval between connection recovery attempts, in milliseconds.
Default:
5000.- resetOffsets
Whether to reset offsets on the consumer to the value provided by
startOffset.Default:
false.- startOffset
The starting offset for new groups, or when
resetOffsetsistrue. Allowed values:earliest,latest.Default: null (equivalent to
earliest).- enableDlq
When set to true, it will send enable DLQ behavior for the consumer. Messages that result in errors will be forwarded to a topic named
error.<destination>.<group>. This provides an alternative option to the more common Kafka replay scenario for the case when the number of errors is relatively small and replaying the entire original topic may be too cumbersome.Default:
false.- configuration
Map with a key/value pair containing generic Kafka consumer properties.
Default: Empty map.
The following properties are available for Kafka producers only and
must be prefixed with spring.cloud.stream.kafka.bindings.<channelName>.producer..
- bufferSize
Upper limit, in bytes, of how much data the Kafka producer will attempt to batch before sending.
Default:
16384.- sync
Whether the producer is synchronous.
Default:
false.- batchTimeout
How long the producer will wait before sending in order to allow more messages to accumulate in the same batch. (Normally the producer does not wait at all, and simply sends all the messages that accumulated while the previous send was in progress.) A non-zero value may increase throughput at the expense of latency.
Default:
0.- configuration
Map with a key/value pair containing generic Kafka producer properties.
Default: Empty map.
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The Kafka binder will use the |
In this section, we illustrate the use of the above properties for specific scenarios.
This example illustrates how one may manually acknowledge offsets in a consumer application.
This example requires that spring.cloud.stream.kafka.bindings.input.consumer.autoCommitOffset is set to false.
Use the corresponding input channel name for your example.
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableBinding(Sink.class)
public class ManuallyAcknowdledgingConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ManuallyAcknowdledgingConsumer.class, args);
}
@StreamListener(Sink.INPUT)
public void process(Message<?> message) {
Acknowledgment acknowledgment = message.getHeaders().get(KafkaHeaders.ACKNOWLEDGMENT, Acknowledgment.class);
if (acknowledgment != null) {
System.out.println("Acknowledgment provided");
acknowledgment.acknowledge();
}
}
}Apache Kafka 0.9 supports secure connections between client and brokers.
To take advantage of this feature, follow the guidelines in the Apache Kafka Documentation as well as the Kafka 0.9 security guidelines from the Confluent documentation.
Use the spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.configuration option to set security properties for all clients created by the binder.
For example, for setting security.protocol to SASL_SSL, set:
spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.configuration.security.protocol=SASL_SSL
All the other security properties can be set in a similar manner.
When using Kerberos, follow the instructions in the reference documentation for creating and referencing the JAAS configuration.
Spring Cloud Stream supports passing JAAS configuration information to the application using a JAAS configuration file and using Spring Boot properties.
The JAAS, and (optionally) krb5 file locations can be set for Spring Cloud Stream applications by using system properties. Here is an example of launching a Spring Cloud Stream application with SASL and Kerberos using a JAAS configuration file:
java -Djava.security.auth.login.config=/path.to/kafka_client_jaas.conf -jar log.jar \ --spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.brokers=secure.server:9092 \ --spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.zkNodes=secure.zookeeper:2181 \ --spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input.destination=stream.ticktock \ --spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.configuration.security.protocol=SASL_PLAINTEXT
As an alternative to having a JAAS configuration file, Spring Cloud Stream provides a mechanism for setting up the JAAS configuration for Spring Cloud Stream applications using Spring Boot properties.
The following properties can be used for configuring the login context of the Kafka client.
- spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.jaas.loginModule
The login module name. Not necessary to be set in normal cases.
Default:
com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule.- spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.jaas.controlFlag
The control flag of the login module.
Default:
required.- spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.jaas.options
Map with a key/value pair containing the login module options.
Default: Empty map.
Here is an example of launching a Spring Cloud Stream application with SASL and Kerberos using Spring Boot configuration properties:
java --spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.brokers=secure.server:9092 \ --spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.zkNodes=secure.zookeeper:2181 \ --spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input.destination=stream.ticktock \ --spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.autoCreateTopics=false \ --spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.configuration.security.protocol=SASL_PLAINTEXT \ --spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.jaas.options.useKeyTab=true \ --spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.jaas.options.storeKey=true \ --spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.jaas.options.keyTab=/etc/security/keytabs/kafka_client.keytab \ --spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.jaas.options.principal=kafka-client-1@EXAMPLE.COM
This represents the equivalent of the following JAAS file:
KafkaClient {
com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required
useKeyTab=true
storeKey=true
keyTab="/etc/security/keytabs/kafka_client.keytab"
principal="[email protected]";
};If the topics required already exist on the broker, or will be created by an administrator, autocreation can be turned off and only client JAAS properties need to be sent. As an alternative to setting spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.autoCreateTopics you can simply remove the broker dependency from the application. See the section called “Excluding Kafka broker jar from the classpath of the binder based application” for details.
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
Do not mix JAAS configuration files and Spring Boot properties in the same application.
If the |
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
Exercise caution when using the |
The binder also supports connecting to Kafka 0.10 brokers.
In order to support this, when you create the project that contains your application, include spring-cloud-starter-stream-kafka as you normally would do for 0.9 based applications.
Then add these dependencies at the top of the <dependencies> section in the pom.xml file to override the Apache Kafka, Spring Kafka, and Spring Integration Kafka with 0.10-compatible versions as in the following example:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId> <artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId> <version>1.1.1.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.integration</groupId> <artifactId>spring-integration-kafka</artifactId> <version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId> <artifactId>kafka_2.11</artifactId> <version>0.10.0.0</version> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency>
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The versions above are provided only for the sake of the example. For best results, we recommend using the most recent 0.10-compatible versions of the projects. |
The Apache Kafka Binder uses the administrative utilities which are part of the Apache Kafka server library to create and reconfigure topics. If the inclusion of the Apache Kafka server library and its dependencies is not necessary at runtime because the application will rely on the topics being configured administratively, the Kafka binder allows for Apache Kafka server dependency to be excluded from the application.
If you use Kafka 10 dependencies as advised above, all you have to do is not to include the kafka broker dependency.
If you use Kafka 0.9, then ensure that you exclude the kafka broker jar from the spring-cloud-starter-stream-kafka dependency as following.
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-stream-kafka</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId> <artifactId>kafka_2.11</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency>
If you exclude the Apache Kafka server dependency and the topic is not present on the server, then the Apache Kafka broker will create the topic if auto topic creation is enabled on the server. Please keep in mind that if you are relying on this, then the Kafka server will use the default number of partitions and replication factors. On the other hand, if auto topic creation is disabled on the server, then care must be taken before running the application to create the topic with the desired number of partitions.
If you want to have full control over how partitions are allocated, then leave the default settings as they are, i.e. do not exclude the kafka broker jar and ensure that spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.autoCreateTopics is set to true, which is the default.