For using the RabbitMQ binder, you just need to add it to your Spring Cloud Stream application, using the following Maven coordinates:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-stream-binder-rabbit</artifactId> </dependency>
Alternatively, you can also use the Spring Cloud Stream RabbitMQ Starter.
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-stream-rabbit</artifactId> </dependency>
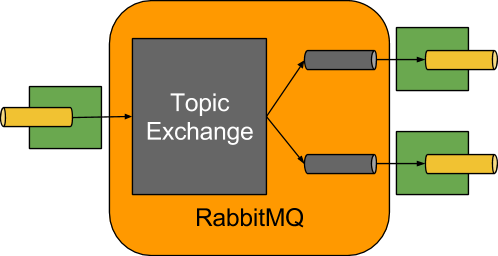
A simplified diagram of how the RabbitMQ binder operates can be seen below.
The RabbitMQ Binder implementation maps each destination to a TopicExchange.
For each consumer group, a Queue will be bound to that TopicExchange.
Each consumer instance have a corresponding RabbitMQ Consumer instance for its group’s Queue.
For partitioned producers/consumers the queues are suffixed with the partition index and use the partition index as routing key.
Using the autoBindDlq option, you can optionally configure the binder to create and configure dead-letter queues (DLQs) (and a dead-letter exchange DLX).
The dead letter queue has the name of the destination, appended with .dlq.
If retry is enabled (maxAttempts > 1) failed messages will be delivered to the DLQ.
If retry is disabled (maxAttempts = 1), you should set requeueRejected to false so the failed message will be routed to the DLQ, instead of being requeued.
In addition, republishToDlq causes the binder to publish a failed message to the DLQ (instead of rejecting it); this enables additional information to be added to the message in headers, such as the stack trace in the x-exception-stacktrace header.
This option does not need retry enabled or the requeueRejected property set to true.
See Section 13.3.1, “RabbitMQ Binder Properties” for more information about these properties.
The framework does not provide any standard mechanism to consume dead-letter messages (or to re-route them back to the primary queue). Some options are described in ???.
This section contains settings specific to the RabbitMQ Binder and bound channels.
For general binding configuration options and properties, please refer to the Spring Cloud Stream core documentation.
By default, the RabbitMQ binder uses Spring Boot’s ConnectionFactory, and it therefore supports all Spring Boot configuration options for RabbitMQ.
(For reference, consult the Spring Boot documentation.)
RabbitMQ configuration options use the spring.rabbitmq prefix.
In addition to Spring Boot options, the RabbitMQ binder supports the following properties:
- spring.cloud.stream.rabbit.binder.adminAddresses
A comma-separated list of RabbitMQ management plugin URLs. Only used when
nodescontains more than one entry. Each entry in this list must have a corresponding entry inspring.rabbitmq.addresses.Default: empty.
- spring.cloud.stream.rabbit.binder.nodes
A comma-separated list of RabbitMQ node names. When more than one entry, used to locate the server address where a queue is located. Each entry in this list must have a corresponding entry in
spring.rabbitmq.addresses.Default: empty.
- spring.cloud.stream.rabbit.binder.compressionLevel
Compression level for compressed bindings. See
java.util.zip.Deflater.Default:
1(BEST_LEVEL).
The following properties are available for Rabbit consumers only and
must be prefixed with spring.cloud.stream.rabbit.bindings.<channelName>.consumer..
- acknowledgeMode
The acknowledge mode.
Default:
AUTO.- autoBindDlq
Whether to automatically declare the DLQ and bind it to the binder DLX.
Default:
false.- durableSubscription
Whether subscription should be durable. Only effective if
groupis also set.Default:
true.- maxConcurrency
- Default:
1. - prefetch
Prefetch count.
Default:
1.- prefix
A prefix to be added to the name of the
destinationand queues.Default: "".
- recoveryInterval
The interval between connection recovery attempts, in milliseconds.
Default:
5000.- requeueRejected
Whether delivery failures should be requeued.
Default:
true.- requestHeaderPatterns
The request headers to be transported.
Default:
[STANDARD_REQUEST_HEADERS,'*'].- replyHeaderPatterns
The reply headers to be transported.
Default:
[STANDARD_REPLY_HEADERS,'*'].- republishToDlq
- By default, messages which fail after retries are exhausted are rejected.
If a dead-letter queue (DLQ) is configured, RabbitMQ will route the failed message (unchanged) to the DLQ.
If set to
true, the bus will republish failed messages to the DLQ with additional headers, including the exception message and stack trace from the cause of the final failure. - transacted
Whether to use transacted channels.
Default:
false.- txSize
The number of deliveries between acks.
Default:
1.
The following properties are available for Rabbit producers only and
must be prefixed with spring.cloud.stream.rabbit.bindings.<channelName>.producer..
- autoBindDlq
Whether to automatically declare the DLQ and bind it to the binder DLX.
Default:
false.- batchingEnabled
Whether to enable message batching by producers.
Default:
false.- batchSize
The number of messages to buffer when batching is enabled.
Default:
100.- batchBufferLimit
- Default:
10000. - batchTimeout
- Default:
5000. - compress
Whether data should be compressed when sent.
Default:
false.- deliveryMode
Delivery mode.
Default:
PERSISTENT.- prefix
A prefix to be added to the name of the
destinationexchange.Default: "".
- requestHeaderPatterns
The request headers to be transported.
Default:
[STANDARD_REQUEST_HEADERS,'*'].- replyHeaderPatterns
The reply headers to be transported.
Default:
[STANDARD_REPLY_HEADERS,'*'].
![[Note]](images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
In the case of RabbitMQ, content type headers can be set by external applications. Spring Cloud Stream supports them as part of an extended internal protocol used for any type of transport (including transports, such as Kafka, that do not normally support headers). |