|
This version is still in development and is not considered stable yet. For the latest snapshot version, please use Spring AI 1.0.3! |
Model Context Protocol (MCP)
| New to MCP? Start with our Getting Started with MCP guide for a quick introduction and hands-on examples. |
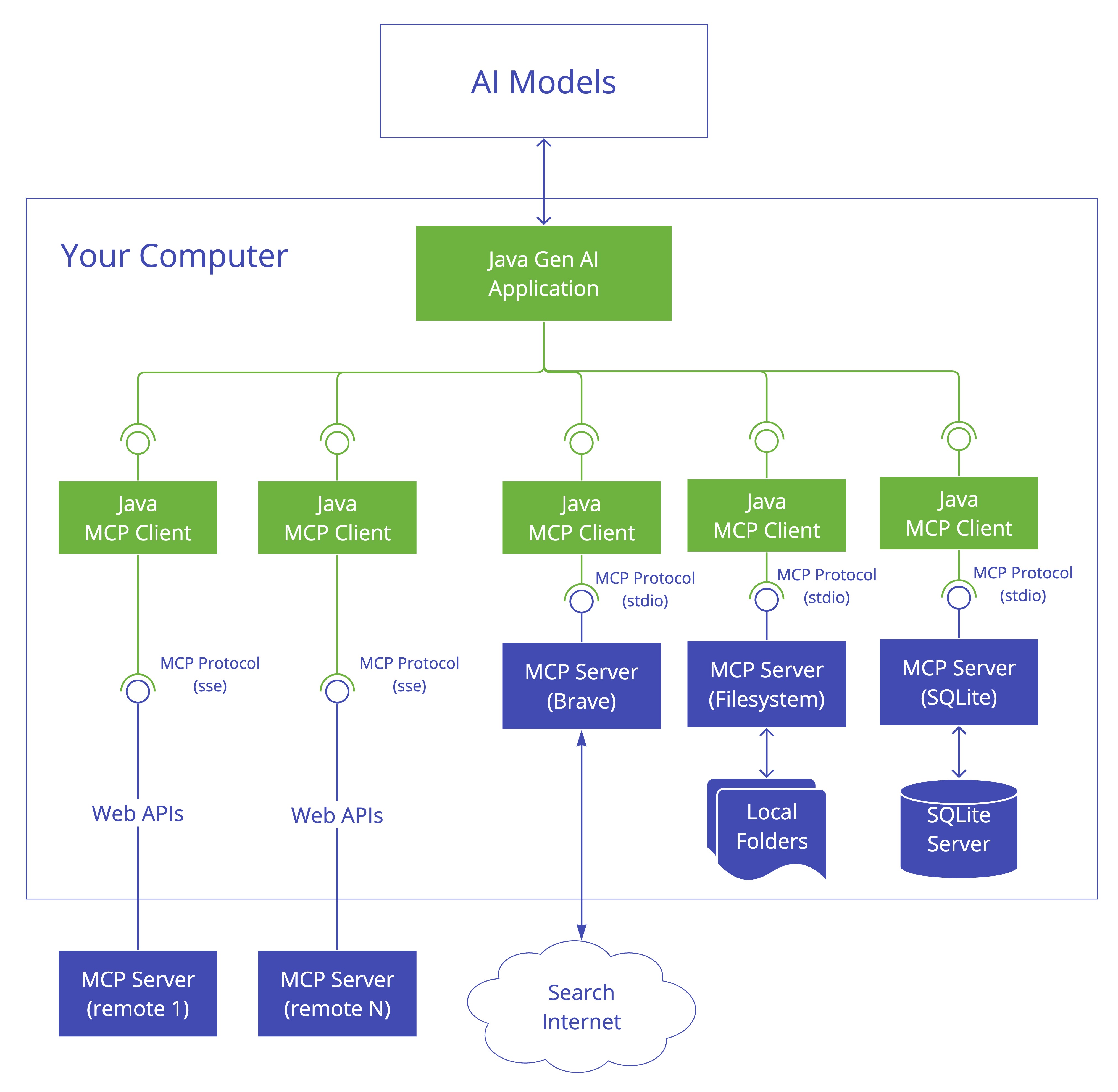
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is a standardized protocol that enables AI models to interact with external tools and resources in a structured way. Think of it as a bridge between your AI models and the real world - allowing them to access databases, APIs, file systems, and other external services through a consistent interface. It supports multiple transport mechanisms to provide flexibility across different environments.
The MCP Java SDK provides a Java implementation of the Model Context Protocol, enabling standardized interaction with AI models and tools through both synchronous and asynchronous communication patterns.
Spring AI embraces MCP with comprehensive support through dedicated Boot Starters and MCP Java Annotations, making it easier than ever to build sophisticated AI-powered applications that can seamlessly connect to external systems. This means Spring developers can participate in both sides of the MCP ecosystem - building AI applications that consume MCP servers and creating MCP servers that expose Spring-based services to the wider AI community. Bootstrap your AI applications with MCP support using Spring Initializer.
MCP Java SDK Architecture
| This section provides an overview for the MCP Java SDK architecture. For the Spring AI MCP integration, refer to the Spring AI MCP Boot Starters documentation. |
The Java MCP implementation follows a three-layer architecture that separates concerns for maintainability and flexibility:
Client/Server Layer (Top)
The top layer handles the main application logic and protocol operations:
-
McpClient - Manages client-side operations and server connections
-
McpServer - Handles server-side protocol operations and client requests
-
Both components utilize the session layer below for communication management
Session Layer (Middle)
The middle layer manages communication patterns and maintains connection state:
-
McpSession - Core session management interface
-
McpClientSession - Client-specific session implementation
-
McpServerSession - Server-specific session implementation
Transport Layer (Bottom)
The bottom layer handles the actual message transport and serialization:
-
McpTransport - Manages JSON-RPC message serialization and deserialization
-
Supports multiple transport implementations (STDIO, HTTP/SSE, Streamable-HTTP, etc.)
-
Provides the foundation for all higher-level communication
| MCP Client | |
|---|---|
The MCP Client is a key component in the Model Context Protocol (MCP) architecture, responsible for establishing and managing connections with MCP servers. It implements the client-side of the protocol, handling:
|
|
| MCP Server | |
|---|---|
The MCP Server is a foundational component in the Model Context Protocol (MCP) architecture that provides tools, resources, and capabilities to clients. It implements the server-side of the protocol, responsible for:
|

|
For detailed implementation guidance, using the low-level MCP Client/Server APIs, refer to the MCP Java SDK documentation. For simplified setup using Spring Boot, use the MCP Boot Starters described below.
Spring AI MCP Integration
Spring AI provides MCP integration through the following Spring Boot starters:
Client Starters
-
spring-ai-starter-mcp-client- Core starter providingSTDIO, Servlet-basedStreamable-HTTP,Stateless Streamable-HTTPandSSEsupport -
spring-ai-starter-mcp-client-webflux- WebFlux-basedStreamable-HTTP,Stateless Streamable-HTTPandSSEtransport implementation
Server Starters
WebMVC
Server Type |
Dependency |
Property |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Spring AI MCP Annotations
In addition to the programmatic MCP client & server configuration, Spring AI provides annotation-based method handling for MCP servers and clients through the MCP Annotations module. This approach simplifies the creation and registration of MCP operations using a clean, declarative programming model with Java annotations.
The MCP Annotations module enables developers to:
-
Create MCP tools, resources, and prompts using simple annotations
-
Handle client-side notifications and requests declaratively
-
Reduce boilerplate code and improve maintainability
-
Automatically generate JSON schemas for tool parameters
-
Access special parameters and context information
Key features include:
-
Server Annotations:
@McpTool,@McpResource,@McpPrompt,@McpComplete -
Client Annotations:
@McpLogging,@McpSampling,@McpElicitation,@McpProgress -
Special Parameters:
McpSyncServerExchange,McpAsyncServerExchange,McpTransportContext,McpMeta -
Automatic Discovery: Annotation scanning with configurable package inclusion/exclusion
-
Spring Boot Integration: Seamless integration with MCP Boot Starters

