|
This version is still in development and is not considered stable yet. For the latest stable version, please use spring-cloud-contract 5.0.2! |
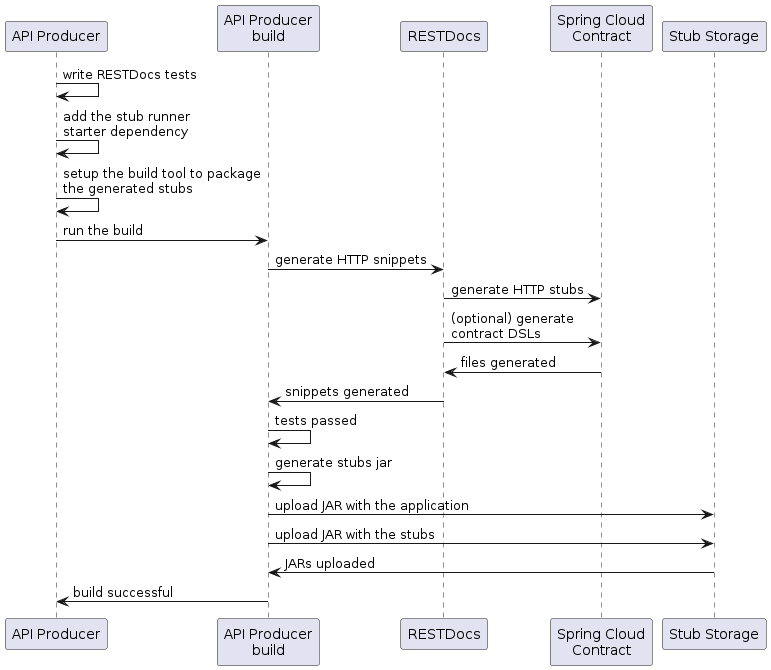
Provider Contract Testing with REST Docs and Stubs in Nexus or Artifactory
In this flow, we do not use a Spring Cloud Contract plugin to generate tests and stubs. We write Spring RESTDocs, and, from them, we automatically generate stubs. Finally, we set up our builds to package the stubs and upload them to the stub storage site — in our case, Nexus or Artifactory.
Producer Flow
As a producer, we:
-
Write RESTDocs tests of our API.
-
Add Spring Cloud Contract Stub Runner starter to our build (
spring-cloud-starter-contract-stub-runner), as follows:- Maven
-
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-contract-stub-runner</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> <version>${spring-cloud.version}</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> - Gradle
-
dependencies { testImplementation 'org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-contract-stub-runner' } dependencyManagement { imports { mavenBom "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-dependencies:${springCloudVersion}" } }
-
We set up the build tool to package our stubs, as follows:
- Maven
-
<!-- pom.xml --> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</artifactId> <executions> <execution> <id>stub</id> <phase>prepare-package</phase> <goals> <goal>single</goal> </goals> <inherited>false</inherited> <configuration> <attach>true</attach> <descriptors> ${basedir}/src/assembly/stub.xml </descriptors> </configuration> </execution> </executions> </plugin> </plugins> <!-- src/assembly/stub.xml --> <assembly xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-assembly-plugin/assembly/1.1.3" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-assembly-plugin/assembly/1.1.3 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/assembly-1.1.3.xsd"> <id>stubs</id> <formats> <format>jar</format> </formats> <includeBaseDirectory>false</includeBaseDirectory> <fileSets> <fileSet> <directory>${project.build.directory}/generated-snippets/stubs</directory> <outputDirectory>META-INF/${project.groupId}/${project.artifactId}/${project.version}/mappings</outputDirectory> <includes> <include>**/*</include> </includes> </fileSet> </fileSets> </assembly> - Gradle
-
task stubsJar(type: Jar) { classifier = "stubs" into("META-INF/${project.group}/${project.name}/${project.version}/mappings") { include('**/*.*') from("${project.buildDir}/generated-snippets/stubs") } } // we need the tests to pass to build the stub jar stubsJar.dependsOn(test) bootJar.dependsOn(stubsJar)
Now, when we run the tests, stubs are automatically published and packaged.
The following UML diagram shows the producer flow:
Consumer Flow
Since the consumer flow is not affected by the tool used to generate the stubs, you can read Developing Your First Spring Cloud Contract-based Application to see the flow for consumer side of the provider contract testing with stubs in Nexus or Artifactory.

