Embeddings Model API
Embeddings are numerical representations of text, images, or videos that capture relationships between inputs.
Embeddings work by converting text, image, and video into arrays of floating point numbers, called vectors. These vectors are designed to capture the meaning of the text, images, and videos. The length of the embedding array is called the vector’s dimensionality.
By calculating the numerical distance between the vector representations of two pieces of text, an application can determine the similarity between the objects used to generate the embedding vectors.
The EmbeddingModel interface is designed for straightforward integration with embedding models in AI and machine learning.
Its primary function is to convert text into numerical vectors, commonly referred to as embeddings.
These embeddings are crucial for various tasks such as semantic analysis and text classification.
The design of the EmbeddingModel interface centers around two primary goals:
-
Portability: This interface ensures easy adaptability across various embedding models. It allows developers to switch between different embedding techniques or models with minimal code changes. This design aligns with Spring’s philosophy of modularity and interchangeability.
-
Simplicity: EmbeddingModel simplifies the process of converting text to embeddings. By providing straightforward methods like
embed(String text)andembed(Document document), it takes the complexity out of dealing with raw text data and embedding algorithms. This design choice makes it easier for developers, especially those new to AI, to utilize embeddings in their applications without delving deep into the underlying mechanics.
API Overview
The Embedding Model API is built on top of the generic Spring AI Model API, which is a part of the Spring AI library.
As such, the EmbeddingModel interface extends the Model interface, which provides a standard set of methods for interacting with AI models. The EmbeddingRequest and EmbeddingResponse classes extend from the ModelRequest and ModelResponse are used to encapsulate the input and output of the embedding models, respectively.
The Embedding API in turn is used by higher-level components to implement Embedding Models for specific embedding models, such as OpenAI, Titan, Azure OpenAI, Ollie, and others.
Following diagram illustrates the Embedding API and its relationship with the Spring AI Model API and the Embedding Models:
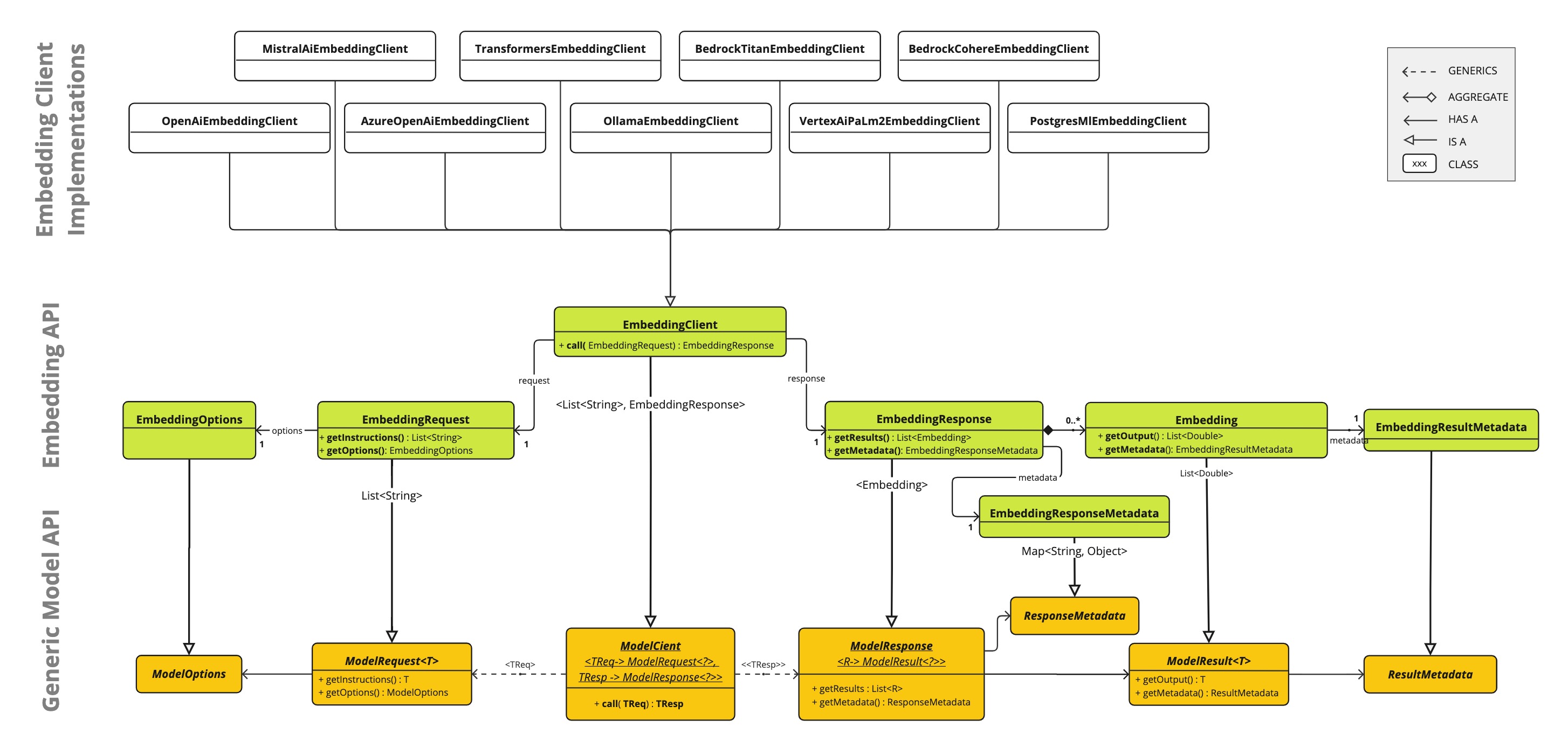
EmbeddingModel
This section provides a guide to the EmbeddingModel interface and associated classes.
public interface EmbeddingModel extends Model<EmbeddingRequest, EmbeddingResponse> {
@Override
EmbeddingResponse call(EmbeddingRequest request);
/**
* Embeds the given document's content into a vector.
* @param document the document to embed.
* @return the embedded vector.
*/
float[] embed(Document document);
/**
* Embeds the given text into a vector.
* @param text the text to embed.
* @return the embedded vector.
*/
default float[] embed(String text) {
Assert.notNull(text, "Text must not be null");
return this.embed(List.of(text)).iterator().next();
}
/**
* Embeds a batch of texts into vectors.
* @param texts list of texts to embed.
* @return list of list of embedded vectors.
*/
default List<float[]> embed(List<String> texts) {
Assert.notNull(texts, "Texts must not be null");
return this.call(new EmbeddingRequest(texts, EmbeddingOptions.EMPTY))
.getResults()
.stream()
.map(Embedding::getOutput)
.toList();
}
/**
* Embeds a batch of texts into vectors and returns the {@link EmbeddingResponse}.
* @param texts list of texts to embed.
* @return the embedding response.
*/
default EmbeddingResponse embedForResponse(List<String> texts) {
Assert.notNull(texts, "Texts must not be null");
return this.call(new EmbeddingRequest(texts, EmbeddingOptions.EMPTY));
}
/**
* @return the number of dimensions of the embedded vectors. It is generative
* specific.
*/
default int dimensions() {
return embed("Test String").size();
}
}The embed methods offer various options for converting text into embeddings, accommodating single strings, structured Document objects, or batches of text.
Multiple shortcut methods are provided for embedding text, including the embed(String text) method, which takes a single string and returns the corresponding embedding vector.
All shortcuts are implemented around the call method, which is the primary method for invoking the embedding model.
Typically the embedding returns a lists of floats, representing the embeddings in a numerical vector format.
The embedForResponse method provides a more comprehensive output, potentially including additional information about the embeddings.
The dimensions method is a handy tool for developers to quickly ascertain the size of the embedding vectors, which is important for understanding the embedding space and for subsequent processing steps.
EmbeddingRequest
The EmbeddingRequest is a ModelRequest that takes a list of text objects and optional embedding request options.
The following listing shows a truncated version of the EmbeddingRequest class, excluding constructors and other utility methods:
public class EmbeddingRequest implements ModelRequest<List<String>> {
private final List<String> inputs;
private final EmbeddingOptions options;
// other methods omitted
}EmbeddingResponse
The structure of the EmbeddingResponse class is as follows:
public class EmbeddingResponse implements ModelResponse<Embedding> {
private List<Embedding> embeddings;
private EmbeddingResponseMetadata metadata = new EmbeddingResponseMetadata();
// other methods omitted
}The EmbeddingResponse class holds the AI Model’s output, with each Embedding instance containing the result vector data from a single text input.
The EmbeddingResponse class also carries a EmbeddingResponseMetadata metadata about the AI Model’s response.

