|
For the latest snapshot version, please use Spring AI 1.1.2! |
Chat Model API
The Chat Model API offers developers the ability to integrate AI-powered chat completion capabilities into their applications. It leverages pre-trained language models, such as GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer), to generate human-like responses to user inputs in natural language.
The API typically works by sending a prompt or partial conversation to the AI model, which then generates a completion or continuation of the conversation based on its training data and understanding of natural language patterns. The completed response is then returned to the application, which can present it to the user or use it for further processing.
The Spring AI Chat Model API is designed to be a simple and portable interface for interacting with various AI Models, allowing developers to switch between different models with minimal code changes.
This design aligns with Spring’s philosophy of modularity and interchangeability.
Also with the help of companion classes like Prompt for input encapsulation and ChatResponse for output handling, the Chat Model API unifies the communication with AI Models.
It manages the complexity of request preparation and response parsing, offering a direct and simplified API interaction.
You can find more about available implementations in the Available Implementations section as well as detailed comparison in the Chat Models Comparison section.
API Overview
This section provides a guide to the Spring AI Chat Model API interface and associated classes.
ChatModel
Here is the ChatModel interface definition:
public interface ChatModel extends Model<Prompt, ChatResponse>, StreamingChatModel {
default String call(String message) {...}
@Override
ChatResponse call(Prompt prompt);
}The call() method with a String parameter simplifies initial use, avoiding the complexities of the more sophisticated Prompt and ChatResponse classes.
In real-world applications, it is more common to use the call() method that takes a Prompt instance and returns a ChatResponse.
StreamingChatModel
Here is the StreamingChatModel interface definition:
public interface StreamingChatModel extends StreamingModel<Prompt, ChatResponse> {
default Flux<String> stream(String message) {...}
@Override
Flux<ChatResponse> stream(Prompt prompt);
}The stream() method takes a String or Prompt parameter similar to ChatModel but it streams the responses using the reactive Flux API.
Prompt
The Prompt is a ModelRequest that encapsulates a list of Message objects and optional model request options.
The following listing shows a truncated version of the Prompt class, excluding constructors and other utility methods:
public class Prompt implements ModelRequest<List<Message>> {
private final List<Message> messages;
private ChatOptions modelOptions;
@Override
public ChatOptions getOptions() {...}
@Override
public List<Message> getInstructions() {...}
// constructors and utility methods omitted
}Message
The Message interface encapsulates a Prompt textual content, a collection of metadata attributes, and a categorization known as MessageType.
The interface is defined as follows:
public interface Content {
String getText();
Map<String, Object> getMetadata();
}
public interface Message extends Content {
MessageType getMessageType();
}The multimodal message types implement also the MediaContent interface providing a list of Media content objects.
public interface MediaContent extends Content {
Collection<Media> getMedia();
}The Message interface has various implementations that correspond to the categories of messages that an AI model can process:
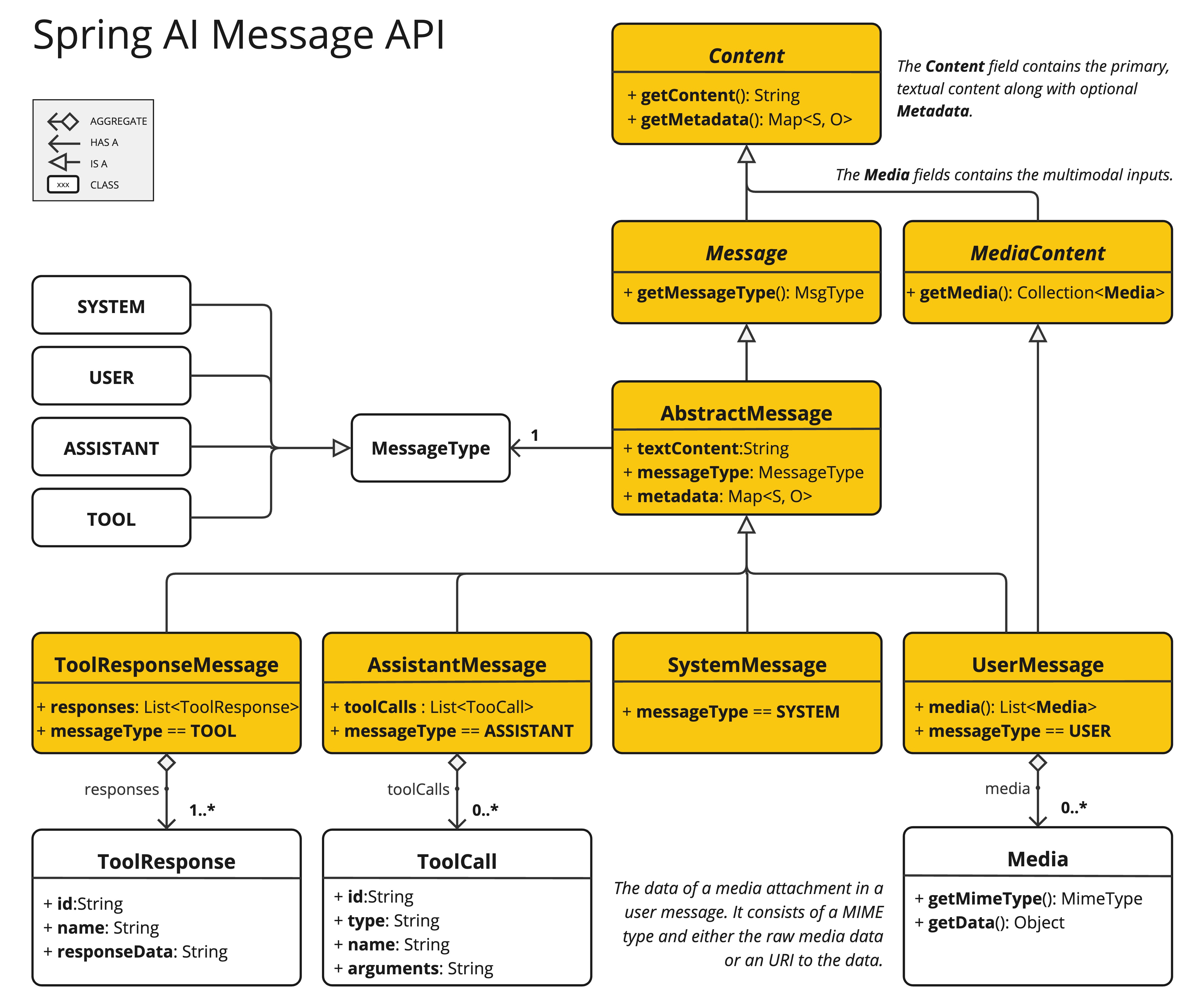
The chat completion endpoint, distinguish between message categories based on conversational roles, effectively mapped by the MessageType.
For instance, OpenAI recognizes message categories for distinct conversational roles such as system, user, function, or assistant.
While the term MessageType might imply a specific message format, in this context it effectively designates the role a message plays in the dialogue.
For AI models that do not use specific roles, the UserMessage implementation acts as a standard category, typically representing user-generated inquiries or instructions.
To understand the practical application and the relationship between Prompt and Message, especially in the context of these roles or message categories, see the detailed explanations in the Prompts section.
Chat Options
Represents the options that can be passed to the AI model. The ChatOptions class is a subclass of ModelOptions and is used to define few portable options that can be passed to the AI model.
The ChatOptions class is defined as follows:
public interface ChatOptions extends ModelOptions {
String getModel();
Float getFrequencyPenalty();
Integer getMaxTokens();
Float getPresencePenalty();
List<String> getStopSequences();
Float getTemperature();
Integer getTopK();
Float getTopP();
ChatOptions copy();
}Additionally, every model specific ChatModel/StreamingChatModel implementation can have its own options that can be passed to the AI model. For example, the OpenAI Chat Completion model has its own options like logitBias, seed, and user.
This is a powerful feature that allows developers to use model-specific options when starting the application and then override them at runtime using the Prompt request.
Spring AI provides a sophisticated system for configuring and using Chat Models. It allows for default configurations to be set at start-up, while also providing the flexibility to override these settings on a per-request basis. This approach enables developers to easily work with different AI models and adjust parameters as needed, all within a consistent interface provided by the Spring AI framework.
Following flow diagram illustrates how Spring AI handles the configuration and execution of Chat Models, combining start-up and runtime options:
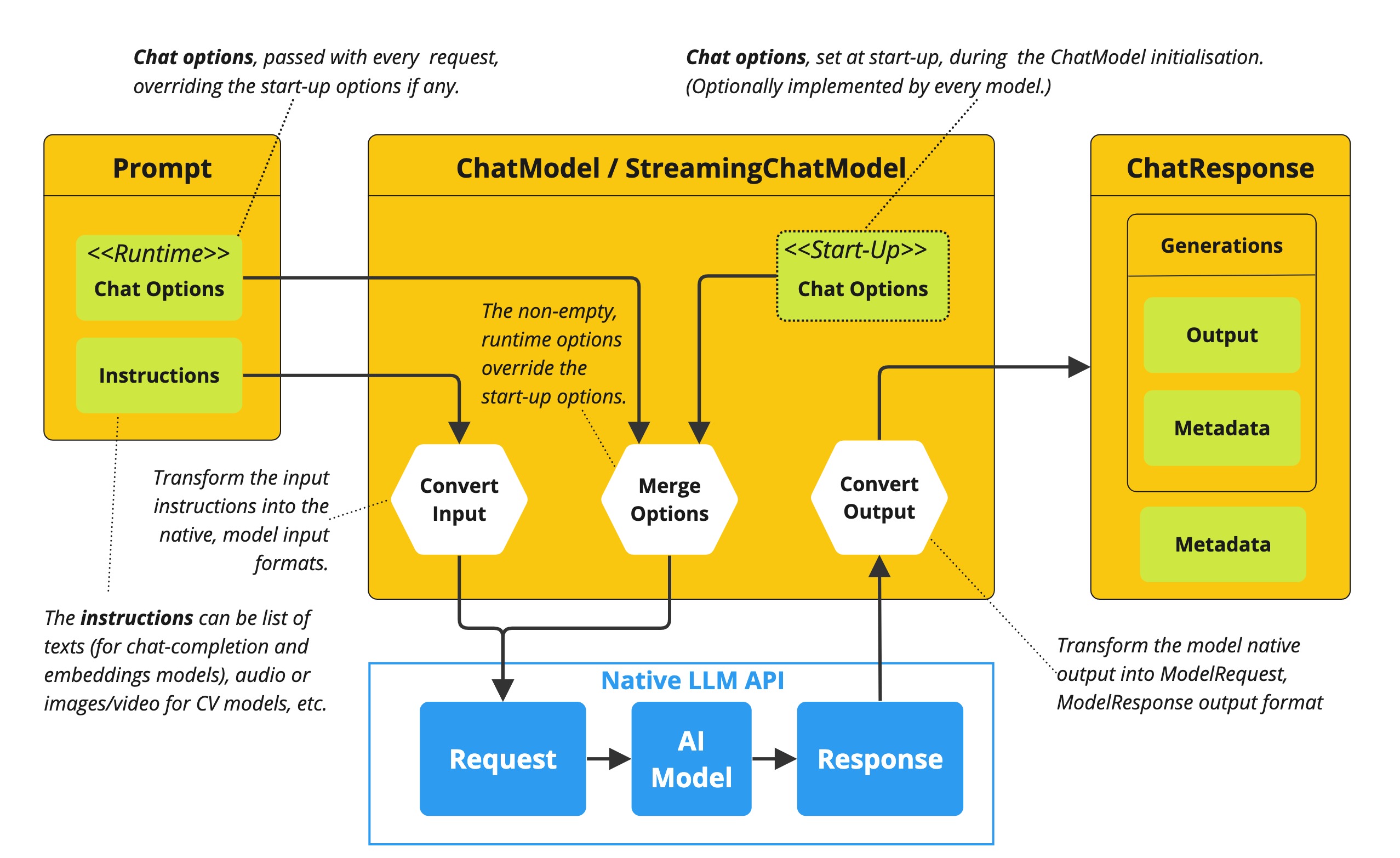
-
Start-up Configuration - The ChatModel/StreamingChatModel is initialized with "Start-Up" Chat Options. These options are set during the ChatModel initialization and are meant to provide default configurations.
-
Runtime Configuration - For each request, the Prompt can contain a Runtime Chat Options: These can override the start-up options.
-
Option Merging Process - The "Merge Options" step combines the start-up and runtime options. If runtime options are provided, they take precedence over the start-up options.
-
Input Processing - The "Convert Input" step transforms the input instructions into native, model-specific formats.
-
Output Processing - The "Convert Output" step transforms the model’s response into a standardized
ChatResponseformat.
The separation of start-up and runtime options allows for both global configurations and request-specific adjustments.
ChatResponse
The structure of the ChatResponse class is as follows:
public class ChatResponse implements ModelResponse<Generation> {
private final ChatResponseMetadata chatResponseMetadata;
private final List<Generation> generations;
@Override
public ChatResponseMetadata getMetadata() {...}
@Override
public List<Generation> getResults() {...}
// other methods omitted
}The ChatResponse class holds the AI Model’s output, with each Generation instance containing one of potentially multiple outputs resulting from a single prompt.
The ChatResponse class also carries a ChatResponseMetadata metadata about the AI Model’s response.
Generation
Finally, the Generation class extends from the ModelResult to represent the model output (assistant message) and related metadata:
public class Generation implements ModelResult<AssistantMessage> {
private final AssistantMessage assistantMessage;
private ChatGenerationMetadata chatGenerationMetadata;
@Override
public AssistantMessage getOutput() {...}
@Override
public ChatGenerationMetadata getMetadata() {...}
// other methods omitted
}Available Implementations
This diagram illustrates the unified interfaces, ChatModel and StreamingChatModel, are used for interacting with various AI chat models from different providers, allowing easy integration and switching between different AI services while maintaining a consistent API for the client application.
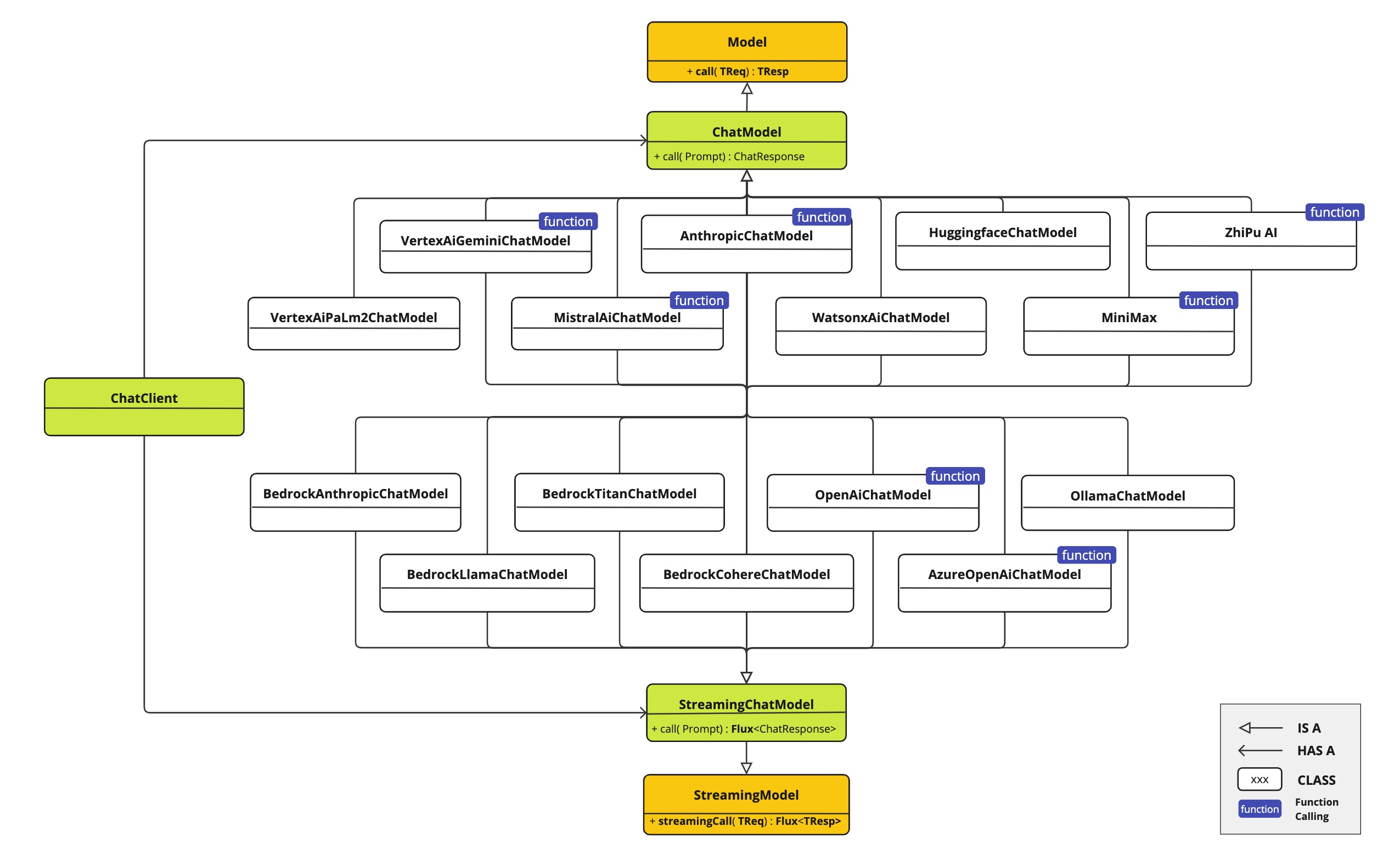
-
OpenAI Chat Completion (streaming, multi-modality & function-calling support)
-
Microsoft Azure Open AI Chat Completion (streaming & function-calling support)
-
Ollama Chat Completion (streaming, multi-modality & function-calling support)
-
Hugging Face Chat Completion (no streaming support)
-
Google Vertex AI Gemini Chat Completion (streaming, multi-modality & function-calling support)
-
Mistral AI Chat Completion (streaming & function-calling support)
-
Anthropic Chat Completion (streaming & function-calling support)
| Find a detailed comparison of the available Chat Models in the Chat Models Comparison section. |
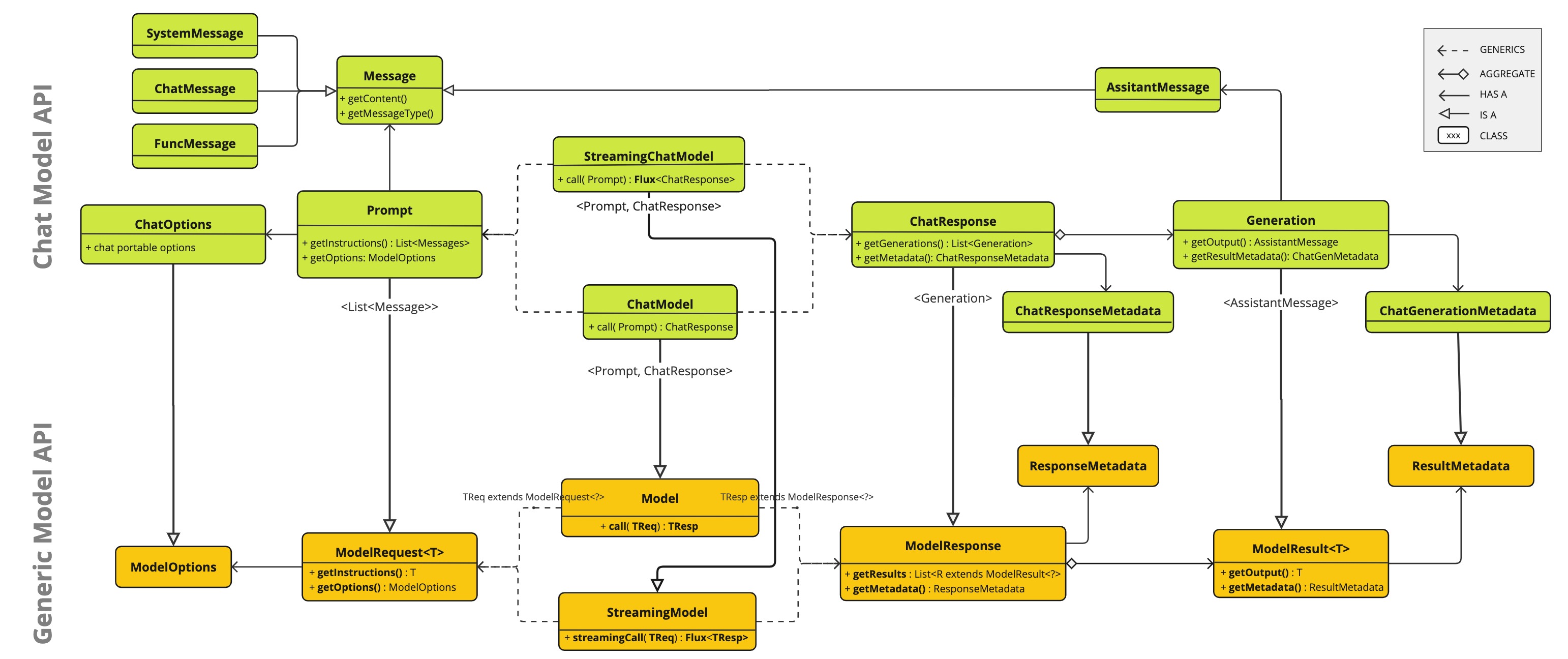
Chat Model API
The Spring AI Chat Model API is built on top of the Spring AI Generic Model API providing Chat specific abstractions and implementations.
This allows an easy integration and switching between different AI services while maintaining a consistent API for the client application.
The following class diagram illustrates the main classes and interfaces of the Spring AI Chat Model API.