|
For the latest snapshot version, please use Spring AI 1.1.2! |
Multimodality API
"All things that are naturally connected ought to be taught in combination" - John Amos Comenius, "Orbis Sensualium Pictus", 1658
Humans process knowledge, simultaneously across multiple modes of data inputs. The way we learn, our experiences are all multimodal. We don’t have just vision, just audio and just text.
Contrary to those principles, the Machine Learning was often focused on specialized models tailored to process a single modality. For instance, we developed audio models for tasks like text-to-speech or speech-to-text, and computer vision models for tasks such as object detection and classification.
However, a new wave of multimodal large language models starts to emerge. Examples include OpenAI’s GPT-4o , Google’s Vertex AI Gemini 1.5, Anthropic’s Claude3, and open source offerings Llama3.2, LLaVA and BakLLaVA are able to accept multiple inputs, including text images, audio and video and generate text responses by integrating these inputs.
| The multimodal large language model (LLM) features enable the models to process and generate text in conjunction with other modalities such as images, audio, or video. |
Spring AI Multimodality
Multimodality refers to a model’s ability to simultaneously understand and process information from various sources, including text, images, audio, and other data formats.
The Spring AI Message API provides all necessary abstractions to support multimodal LLMs.
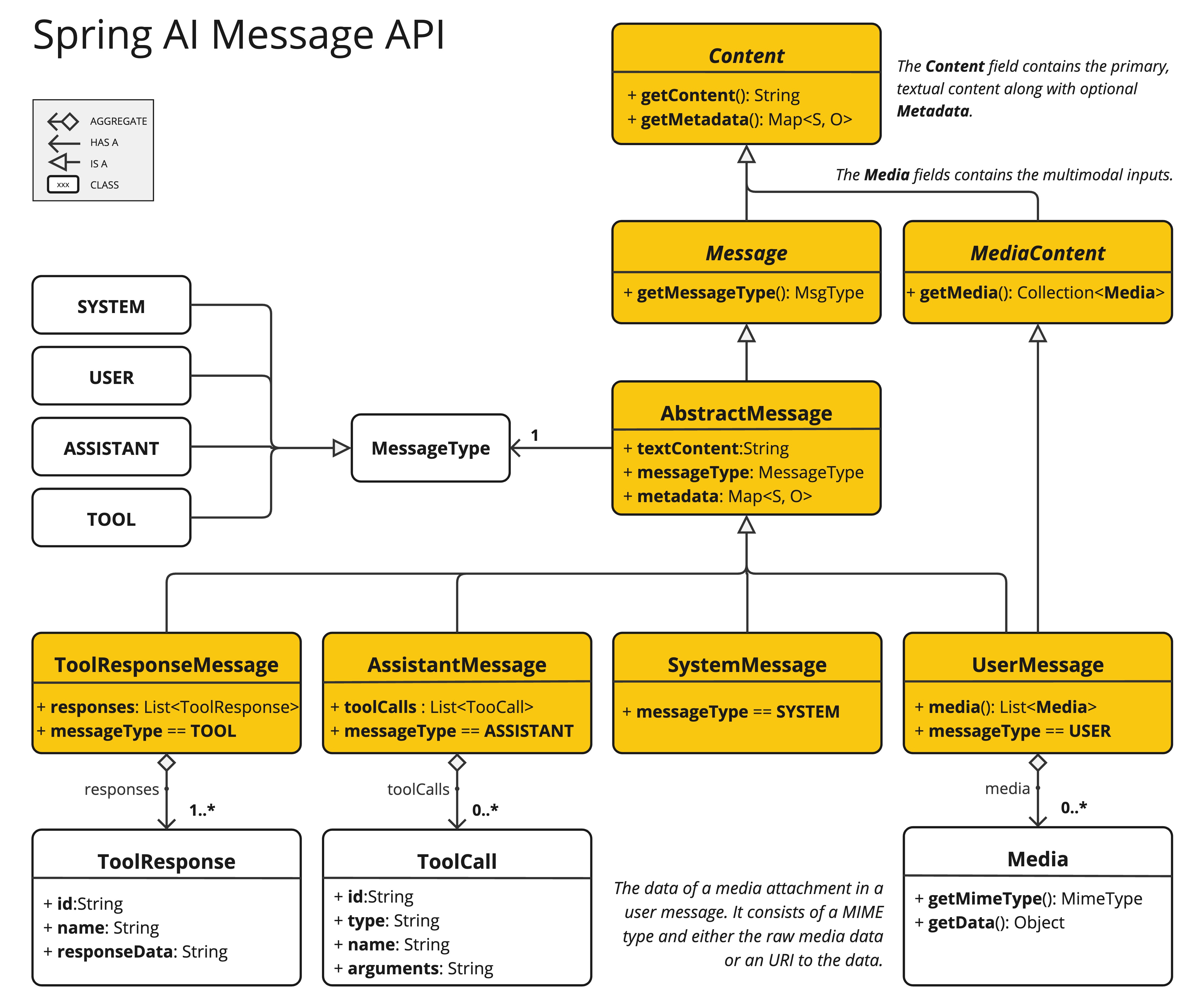
The UserMessage’s content field is used primarily for text inputs, while the optional media field allows adding one or more additional content of different modalities such as images, audio and video.
The MimeType specifies the modality type.
Depending on the used LLMs, the Media data field can be either the raw media content as a Resource object or a URI to the content.
The media field is currently applicable only for user input messages (e.g., UserMessage). It does not hold significance for system messages. The AssistantMessage, which includes the LLM response, provides text content only. To generate non-text media outputs, you should utilize one of the dedicated, single-modality models.*
|
For example, we can take the following picture (multimodal.test.png) as an input and ask the LLM to explain what it sees.

For most of the multimodal LLMs, the Spring AI code would look something like this:
var imageResource = new ClassPathResource("/multimodal.test.png");
var userMessage = UserMessage.builder()
.text("Explain what do you see in this picture?") // content
.media(new Media(MimeTypeUtils.IMAGE_PNG, this.imageResource)) // media
.build();
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(new Prompt(this.userMessage));or with the fluent ChatClient API:
String response = ChatClient.create(chatModel).prompt()
.user(u -> u.text("Explain what do you see on this picture?")
.media(MimeTypeUtils.IMAGE_PNG, new ClassPathResource("/multimodal.test.png")))
.call()
.content();and produce a response like:
This is an image of a fruit bowl with a simple design. The bowl is made of metal with curved wire edges that create an open structure, allowing the fruit to be visible from all angles. Inside the bowl, there are two yellow bananas resting on top of what appears to be a red apple. The bananas are slightly overripe, as indicated by the brown spots on their peels. The bowl has a metal ring at the top, likely to serve as a handle for carrying. The bowl is placed on a flat surface with a neutral-colored background that provides a clear view of the fruit inside.
Spring AI provides multimodal support for the following chat models:

