|
For the latest snapshot version, please use Spring AI 1.1.2! |
Upgrade Notes
Upgrading to 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT
Overview
The 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT version includes significant changes to artifact IDs, package names, and module structure. This section provides guidance specific to using the SNAPSHOT version.
Add Snapshot Repositories
To use the 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT version, you need to add the snapshot repositories to your build file. For detailed instructions, refer to the Snapshots - Add Snapshot Repositories section in the Getting Started guide.
Update Dependency Management
Update your Spring AI BOM version to 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT in your build configuration.
For detailed instructions on configuring dependency management, refer to the Dependency Management section in the Getting Started guide.
Artifact ID, Package, and Module Changes
The 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT includes changes to artifact IDs, package names, and module structure.
For details, refer to: - Common Artifact ID Changes - Common Package Changes - Common Module Structure
Upgrading to 1.0.0-RC1
You can automate the upgrade process to 1.0.0-RC1 using an OpenRewrite recipe. This recipe helps apply many of the necessary code changes for this version. Find the recipe and usage instructions at Arconia Spring AI Migrations.
Breaking Changes
Chat Client and Advisors
The main changes that impact end user code are:
-
In
VectorStoreChatMemoryAdvisor:-
The constant
CHAT_MEMORY_RETRIEVE_SIZE_KEYhas been renamed toTOP_K. -
The constant
DEFAULT_CHAT_MEMORY_RESPONSE_SIZE(value: 100) has been renamed toDEFAULT_TOP_Kwith a new default value of 20.
-
-
The constant
CHAT_MEMORY_CONVERSATION_ID_KEYhas been renamed toCONVERSATION_IDand moved fromAbstractChatMemoryAdvisorto theChatMemoryinterface. Update your imports to useorg.springframework.ai.chat.memory.ChatMemory.CONVERSATION_ID.
Self-contained Templates in Advisors
The built-in advisors that perform prompt augmentation have been updated to use self-contained templates. The goal is for each advisor to be able to perform templating operations without affecting nor being affected by templating and prompt decisions in other advisors.
If you were providing custom templates for the following advisors, you’ll need to update them to ensure all expected placeholders are included.
-
The
QuestionAnswerAdvisorexpects a template with the following placeholders (see more details):-
a
queryplaceholder to receive the user question. -
a
question_answer_contextplaceholder to receive the retrieved context.
-
-
The
PromptChatMemoryAdvisorexpects a template with the following placeholders (see more details):-
an
instructionsplaceholder to receive the original system message. -
a
memoryplaceholder to receive the retrieved conversation memory.
-
-
The
VectorStoreChatMemoryAdvisorexpects a template with the following placeholders (see more details):-
an
instructionsplaceholder to receive the original system message. -
a
long_term_memoryplaceholder to receive the retrieved conversation memory.
-
Observability
-
Refactored content observation to use logging instead of tracing (ca843e8)
-
Replaced content observation filters with logging handlers
-
Renamed configuration properties to better reflect their purpose:
-
include-prompt→log-prompt -
include-completion→log-completion -
include-query-response→log-query-response
-
-
Added
TracingAwareLoggingObservationHandlerfor trace-aware logging -
Replaced
micrometer-tracing-bridge-otelwithmicrometer-tracing -
Removed event-based tracing in favor of direct logging
-
Removed direct dependency on the OTel SDK
-
Renamed
includePrompttologPromptin observation properties (inChatClientBuilderProperties,ChatObservationProperties, andImageObservationProperties)
-
Chat Memory Repository Module and Autoconfiguration Renaming
We’ve standardized the naming pattern for chat memory components by adding the repository suffix throughout the codebase. This change affects Cassandra, JDBC, and Neo4j implementations, impacting artifact IDs, Java package names, and class names for clarity.
Artifact IDs
All memory-related artifacts now follow a consistent pattern:
-
spring-ai-model-chat-memory-→spring-ai-model-chat-memory-repository- -
spring-ai-autoconfigure-model-chat-memory-→spring-ai-autoconfigure-model-chat-memory-repository- -
spring-ai-starter-model-chat-memory-→spring-ai-starter-model-chat-memory-repository-
Java Packages
-
Package paths now include
.repository.segment -
Example:
org.springframework.ai.chat.memory.jdbc→org.springframework.ai.chat.memory.repository.jdbc
Configuration Classes
-
Main autoconfiguration classes now use the
Repositorysuffix -
Example:
JdbcChatMemoryAutoConfiguration→JdbcChatMemoryRepositoryAutoConfiguration
Properties
-
Configuration properties renamed from
spring.ai.chat.memory.<storage>…tospring.ai.chat.memory.repository.<storage>…
Migration Required: - Update your Maven/Gradle dependencies to use the new artifact IDs. - Update any imports, class references, or configuration that used the old package or class names.
Message Aggregator Refactoring
Changes
-
MessageAggregatorclass has been moved fromorg.springframework.ai.chat.modelpackage in thespring-ai-client-chatmodule to thespring-ai-modelmodule (same package name) -
The
aggregateChatClientResponsemethod has been removed fromMessageAggregatorand moved to a new classChatClientMessageAggregatorin theorg.springframework.ai.chat.clientpackage
Migration Guide
If you were directly using the aggregateChatClientResponse method from MessageAggregator, you need to use the new ChatClientMessageAggregator class instead:
// Before
new MessageAggregator().aggregateChatClientResponse(chatClientResponses, aggregationHandler);
// After
new ChatClientMessageAggregator().aggregateChatClientResponse(chatClientResponses, aggregationHandler);Don’t forget to add the appropriate import:
import org.springframework.ai.chat.client.ChatClientMessageAggregator;Watson
The Watson AI model was removed as it was based on the older text generation that is considered outdated as there is a new chat generation model available. Hopefully Watson will reappear in a future version of Spring AI
MoonShot and QianFan
Moonshot and Qianfan have been removed since they are not accessible from outside China. These have been moved to the Spring AI Community repository.
Removed Vector Store
-
Removed HanaDB vector store autoconfiguration (f3b4624)
Memory Management
-
Removed CassandraChatMemory implementation (11e3c8f)
-
Simplified chat memory advisor hierarchy and removed deprecated API (848a3fd)
-
Removed deprecations in JdbcChatMemory (356a68f)
-
Refactored chat memory repository artifacts for clarity (2d517ee)
-
Refactored chat memory repository autoconfigurations and Spring Boot starters for clarity (f6dba1b)
Message and Template APIs
-
Removed deprecated UserMessage constructors (06edee4)
-
Removed deprecated PromptTemplate constructors (722c77e)
-
Removed deprecated methods from Media (228ef10)
-
Refactored StTemplateRenderer: renamed supportStFunctions to validateStFunctions (0e15197)
-
Removed left over TemplateRender interface after moving it (52675d8)
Dependencies
-
Removed unused json-path dependency in spring-ai-openai (9de13d1)
Behavior Changes
Azure OpenAI
-
Added Entra ID identity management for Azure OpenAI with clean autoconfiguration (3dc86d3)
Upgrading to 1.0.0-M8
You can automate the upgrade process to 1.0.0-M8 using an OpenRewrite recipe. This recipe helps apply many of the necessary code changes for this version. Find the recipe and usage instructions at Arconia Spring AI Migrations.
Breaking Changes
When upgrading from Spring AI 1.0 M7 to 1.0 M8, users who previously registered tool callbacks are encountering breaking changes that cause tool calling functionality to silently fail. This is specifically impacting code that used the deprecated tools() method.
Example
Here’s an example of code that worked in M7 but no longer functions as expected in M8:
// This worked in M7 but silently fails in M8
ChatClient chatClient = new OpenAiChatClient(api)
.tools(List.of(
new Tool("get_current_weather", "Get the current weather in a given location",
new ToolSpecification.ToolParameter("location", "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA", true))
))
.toolCallbacks(List.of(
new ToolCallback("get_current_weather", (toolName, params) -> {
// Weather retrieval logic
return Map.of("temperature", 72, "unit", "fahrenheit", "description", "Sunny");
})
));Solution
The solution is to use the toolSpecifications() method instead of the deprecated tools() method:
// This works in M8
ChatClient chatClient = new OpenAiChatClient(api)
.toolSpecifications(List.of(
new Tool("get_current_weather", "Get the current weather in a given location",
new ToolSpecification.ToolParameter("location", "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA", true))
))
.toolCallbacks(List.of(
new ToolCallback("get_current_weather", (toolName, params) -> {
// Weather retrieval logic
return Map.of("temperature", 72, "unit", "fahrenheit", "description", "Sunny");
})
));Removed Implementations and APIs
Memory Management
-
Removed CassandraChatMemory implementation (11e3c8f)
-
Simplified chat memory advisor hierarchy and removed deprecated API (848a3fd)
-
Removed deprecations in JdbcChatMemory (356a68f)
-
Refactored chat memory repository artifacts for clarity (2d517ee)
-
Refactored chat memory repository autoconfigurations and Spring Boot starters for clarity (f6dba1b)
Message and Template APIs
-
Removed deprecated UserMessage constructors (06edee4)
-
Removed deprecated PromptTemplate constructors (722c77e)
-
Removed deprecated methods from Media (228ef10)
-
Refactored StTemplateRenderer: renamed supportStFunctions to validateStFunctions (0e15197)
-
Removed left over TemplateRender interface after moving it (52675d8)
Dependencies
-
Removed unused json-path dependency in spring-ai-openai (9de13d1)
Behavior Changes
Observability
-
Refactored content observation to use logging instead of tracing (ca843e8)
-
Replaced content observation filters with logging handlers
-
Renamed configuration properties to better reflect their purpose:
-
include-prompt→log-prompt -
include-completion→log-completion -
include-query-response→log-query-response
-
-
Added
TracingAwareLoggingObservationHandlerfor trace-aware logging -
Replaced
micrometer-tracing-bridge-otelwithmicrometer-tracing -
Removed event-based tracing in favor of direct logging
-
Removed direct dependency on the OTel SDK
-
Renamed
includePrompttologPromptin observation properties (inChatClientBuilderProperties,ChatObservationProperties, andImageObservationProperties)
-
Azure OpenAI
-
Added Entra ID identity management for Azure OpenAI with clean autoconfiguration (3dc86d3)
Upgrading to 1.0.0-M7
Overview of Changes
Spring AI 1.0.0-M7 is the last milestone release before the RC1 and GA releases. It introduces several important changes to artifact IDs, package names, and module structure that will be maintained in the final release.
Artifact ID, Package, and Module Changes
The 1.0.0-M7 includes the same structural changes as 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.
For details, refer to: - Common Artifact ID Changes - Common Package Changes - Common Module Structure
MCP Java SDK Upgrade to 0.9.0
Spring AI 1.0.0-M7 now uses MCP Java SDK version 0.9.0, which includes significant changes from previous versions. If you’re using MCP in your applications, you’ll need to update your code to accommodate these changes.
Key changes include:
Interface Renaming
-
ClientMcpTransport→McpClientTransport -
ServerMcpTransport→McpServerTransport -
DefaultMcpSession→McpClientSessionorMcpServerSession -
All
*Registrationclasses →*Specificationclasses
Server Creation Changes
-
Use
McpServerTransportProviderinstead ofServerMcpTransport
// Before
ServerMcpTransport transport = new WebFluxSseServerTransport(objectMapper, "/mcp/message");
var server = McpServer.sync(transport)
.serverInfo("my-server", "1.0.0")
.build();
// After
McpServerTransportProvider transportProvider = new WebFluxSseServerTransportProvider(objectMapper, "/mcp/message");
var server = McpServer.sync(transportProvider)
.serverInfo("my-server", "1.0.0")
.build();Handler Signature Changes
All handlers now receive an exchange parameter as their first argument:
// Before
.tool(calculatorTool, args -> new CallToolResult("Result: " + calculate(args)))
// After
.tool(calculatorTool, (exchange, args) -> new CallToolResult("Result: " + calculate(args)))Client Interaction via Exchange
Methods previously available on the server are now accessed through the exchange object:
// Before
ClientCapabilities capabilities = server.getClientCapabilities();
CreateMessageResult result = server.createMessage(new CreateMessageRequest(...));
// After
ClientCapabilities capabilities = exchange.getClientCapabilities();
CreateMessageResult result = exchange.createMessage(new CreateMessageRequest(...));Roots Change Handlers
// Before
.rootsChangeConsumers(List.of(
roots -> System.out.println("Roots changed: " + roots)
))
// After
.rootsChangeHandlers(List.of(
(exchange, roots) -> System.out.println("Roots changed: " + roots)
))For a complete guide to migrating MCP code, refer to the MCP Migration Guide.
Enabling/Disabling Model Auto-Configuration
The previous configuration properties for enabling/disabling model auto-configuration have been removed:
-
spring.ai.<provider>.chat.enabled -
spring.ai.<provider>.embedding.enabled -
spring.ai.<provider>.image.enabled -
spring.ai.<provider>.moderation.enabled
By default, if a model provider (e.g., OpenAI, Ollama) is found on the classpath, its corresponding auto-configuration for relevant model types (chat, embedding, etc.) is enabled. If multiple providers for the same model type are present (e.g., both spring-ai-openai-spring-boot-starter and spring-ai-ollama-spring-boot-starter), you can use the following properties to select which provider’s auto-configuration should be active, effectively disabling the others for that specific model type.
To disable auto-configuration for a specific model type entirely, even if only one provider is present, set the corresponding property to a value that does not match any provider on the classpath (e.g., none or disabled).
You can refer to the SpringAIModels enumeration for a list of well-known provider values.
-
spring.ai.model.audio.speech=<model-provider|none> -
spring.ai.model.audio.transcription=<model-provider|none> -
spring.ai.model.chat=<model-provider|none> -
spring.ai.model.embedding=<model-provider|none> -
spring.ai.model.embedding.multimodal=<model-provider|none> -
spring.ai.model.embedding.text=<model-provider|none> -
spring.ai.model.image=<model-provider|none> -
spring.ai.model.moderation=<model-provider|none>
Automating upgrading using AI
You can automate the upgrade process to 1.0.0-M7 using the Claude Code CLI tool with a provided prompt:
-
Download the Claude Code CLI tool
-
Copy the prompt from the update-to-m7.txt file
-
Paste the prompt into the Claude Code CLI
-
The AI will analyze your project and make the necessary changes
| The automated upgrade prompt currently handles artifact ID changes, package relocations, and module structure changes, but does not yet include automatic changes for upgrading to MCP 0.9.0. If you’re using MCP, you’ll need to manually update your code following the guidance in the MCP Java SDK Upgrade section. |
Common Changes Across Versions
Artifact ID Changes
The naming pattern for Spring AI starter artifacts has changed. You’ll need to update your dependencies according to the following patterns:
-
Model starters:
spring-ai-{model}-spring-boot-starter→spring-ai-starter-model-{model} -
Vector Store starters:
spring-ai-{store}-store-spring-boot-starter→spring-ai-starter-vector-store-{store} -
MCP starters:
spring-ai-mcp-{type}-spring-boot-starter→spring-ai-starter-mcp-{type}
Examples
-
Maven
-
Gradle
<!-- BEFORE -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-openai-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- AFTER -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-starter-model-openai</artifactId>
</dependency>// BEFORE
implementation 'org.springframework.ai:spring-ai-openai-spring-boot-starter'
implementation 'org.springframework.ai:spring-ai-redis-store-spring-boot-starter'
// AFTER
implementation 'org.springframework.ai:spring-ai-starter-model-openai'
implementation 'org.springframework.ai:spring-ai-starter-vector-store-redis'Changes to Spring AI Autoconfiguration Artifacts
The Spring AI autoconfiguration has changed from a single monolithic artifact to individual autoconfiguration artifacts per model, vector store, and other components. This change was made to minimize the impact of different versions of dependent libraries conflicting, such as Google Protocol Buffers, Google RPC, and others. By separating autoconfiguration into component-specific artifacts, you can avoid pulling in unnecessary dependencies and reduce the risk of version conflicts in your application.
The original monolithic artifact is no longer available:
<!-- NO LONGER AVAILABLE -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</dependency>Instead, each component now has its own autoconfiguration artifact following these patterns:
-
Model autoconfiguration:
spring-ai-autoconfigure-model-{model} -
Vector Store autoconfiguration:
spring-ai-autoconfigure-vector-store-{store} -
MCP autoconfiguration:
spring-ai-autoconfigure-mcp-{type}
Examples of New Autoconfiguration Artifacts
-
Models
-
Vector Stores
-
MCP
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-autoconfigure-model-openai</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-autoconfigure-model-anthropic</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-autoconfigure-model-vertex-ai</artifactId>
</dependency><dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-autoconfigure-vector-store-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-autoconfigure-vector-store-pgvector</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-autoconfigure-vector-store-chroma</artifactId>
</dependency><dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-autoconfigure-mcp-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-autoconfigure-mcp-server</artifactId>
</dependency>| In most cases, you won’t need to explicitly add these autoconfiguration dependencies. They are included transitively when using the corresponding starter dependencies. |
Package Name Changes
Your IDE should assist with refactoring to the new package locations.
-
KeywordMetadataEnricherandSummaryMetadataEnricherhave moved fromorg.springframework.ai.transformertoorg.springframework.ai.chat.transformer. -
Content,MediaContent, andMediahave moved fromorg.springframework.ai.modeltoorg.springframework.ai.content.
Module Structure
The project has undergone significant changes to its module and artifact structure. Previously, spring-ai-core contained all central interfaces, but this has now been split into specialized domain modules to reduce unnecessary dependencies in your applications.
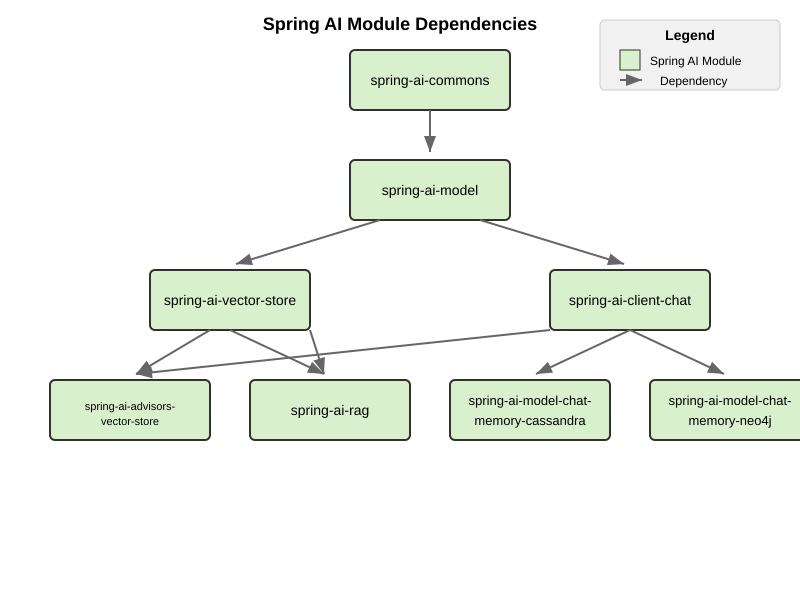
spring-ai-commons
Base module with no dependencies on other Spring AI modules. Contains:
- Core domain models (Document, TextSplitter)
- JSON utilities and resource handling
- Structured logging and observability support
spring-ai-model
Provides AI capability abstractions:
- Interfaces like ChatModel, EmbeddingModel, and ImageModel
- Message types and prompt templates
- Function-calling framework (ToolDefinition, ToolCallback)
- Content filtering and observation support
spring-ai-vector-store
Unified vector database abstraction:
- VectorStore interface for similarity search
- Advanced filtering with SQL-like expressions
- SimpleVectorStore for in-memory usage
- Batching support for embeddings
spring-ai-client-chat
High-level conversational AI APIs:
- ChatClient interface
- Conversation persistence via ChatMemory
- Response conversion with OutputConverter
- Advisor-based interception
- Synchronous and reactive streaming support
spring-ai-advisors-vector-store
Bridges chat with vector stores for RAG:
- QuestionAnswerAdvisor: injects context into prompts
- VectorStoreChatMemoryAdvisor: stores/retrieves conversation history
Dependency Structure
The dependency hierarchy can be summarized as:
-
spring-ai-commons(foundation) -
spring-ai-model(depends on commons) -
spring-ai-vector-storeandspring-ai-client-chat(both depend on model) -
spring-ai-advisors-vector-storeandspring-ai-rag(depend on both client-chat and vector-store) -
spring-ai-model-chat-memory-*modules (depend on client-chat)
ToolContext Changes
The ToolContext class has been enhanced to support both explicit and implicit tool resolution. Tools can now be:
-
Explicitly Included: Tools that are explicitly requested in the prompt and included in the call to the model.
-
Implicitly Available: Tools that are made available for runtime dynamic resolution, but never included in any call to the model unless explicitly requested.
Starting with 1.0.0-M7, tools are only included in the call to the model if they are explicitly requested in the prompt or explicitly included in the call.
Additionally, the ToolContext class has now been marked as final and cannot be extended anymore. It was never supposed to be subclassed. You can add all the contextual data you need when instantiating a ToolContext, in the form of a Map<String, Object>. For more information, check the [documentation](docs.spring.io/spring-ai/reference/api/tools.html#_tool_context).
Upgrading to 1.0.0-M6
Changes to Usage Interface and DefaultUsage Implementation
The Usage interface and its default implementation DefaultUsage have undergone the following changes:
-
Method Rename:
-
getGenerationTokens()is nowgetCompletionTokens()
-
-
Type Changes:
-
All token count fields in
DefaultUsagechanged fromLongtoInteger:-
promptTokens -
completionTokens(formerlygenerationTokens) -
totalTokens
-
-
Required Actions
-
Replace all calls to
getGenerationTokens()withgetCompletionTokens() -
Update
DefaultUsageconstructor calls:
// Old (M5) new DefaultUsage(Long promptTokens, Long generationTokens, Long totalTokens) // New (M6) new DefaultUsage(Integer promptTokens, Integer completionTokens, Integer totalTokens)
| For more information on handling Usage, refer here |
JSON Ser/Deser changes
While M6 maintains backward compatibility for JSON deserialization of the generationTokens field, this field will be removed in M7. Any persisted JSON documents using the old field name should be updated to use completionTokens.
Example of the new JSON format:
{
"promptTokens": 100,
"completionTokens": 50,
"totalTokens": 150
}Changes to usage of FunctionCallingOptions for tool calling
Each ChatModel instance, at construction time, accepts an optional ChatOptions or FunctionCallingOptions instance
that can be used to configure default tools used for calling the model.
Before 1.0.0-M6:
-
any tool passed via the
functions()method of the defaultFunctionCallingOptionsinstance was included in each call to the model from thatChatModelinstance, possibly overwritten by runtime options. -
any tool passed via the
functionCallbacks()method of the defaultFunctionCallingOptionsinstance was only made available for runtime dynamic resolution (see Tool Resolution), but never included in any call to the model unless explicitly requested.
Starting 1.0.0-M6:
-
any tool passed via the
functions()method or thefunctionCallbacks()of the defaultFunctionCallingOptionsinstance is now handled in the same way: it is included in each call to the model from thatChatModelinstance, possibly overwritten by runtime options. With that, there is consistency in the way tools are included in calls to the model and prevents any confusion due to a difference in behavior betweenfunctionCallbacks()and all the other options.
If you want to make a tool available for runtime dynamic resolution and include it in a chat request to the model only when explicitly requested, you can use one of the strategies described in Tool Resolution.
| 1.0.0-M6 introduced new APIs for handling tool calling. Backward compatibility is maintained for the old APIs across all scenarios, except the one described above. The old APIs are still available, but they are deprecated and will be removed in 1.0.0-M7. |
Removal of deprecated Amazon Bedrock chat models
Starting 1.0.0-M6, Spring AI transitioned to using Amazon Bedrock’s Converse API for all Chat conversation implementations in Spring AI. All the Amazon Bedrock Chat models are removed except the Embedding models for Cohere and Titan.
| Refer to Bedrock Converse documentation for using the chat models. |
Changes to use Spring Boot 3.4.2 for dependency management
Spring AI updates to use Spring Boot 3.4.2 for the dependency management. You can refer here for the dependencies managed by Spring Boot 3.4.2
Required Actions
-
If you are upgrading to Spring Boot 3.4.2, please make sure to refer to this documentation for the changes required to configure the REST Client. Notably, if you don’t have an HTTP client library on the classpath, this will likely result in the use of
JdkClientHttpRequestFactorywhereSimpleClientHttpRequestFactorywould have been used previously. To switch to useSimpleClientHttpRequestFactory, you need to setspring.http.client.factory=simple. -
If you are using a different version of Spring Boot (say Spring Boot 3.3.x) and need a specific version of a dependency, you can override it in your build configuration.
Vector Store API changes
In version 1.0.0-M6, the delete method in the VectorStore interface has been modified to be a void operation instead of returning an Optional<Boolean>.
If your code previously checked the return value of the delete operation, you’ll need to remove this check.
The operation now throws an exception if the deletion fails, providing more direct error handling.
Upgrading to 1.0.0.M5
-
Vector Builders have been refactored for consistency.
-
Current VectorStore implementation constructors have been deprecated, use the builder pattern.
-
VectorStore implementation packages have been moved into unique package names, avoiding conflicts across artifact. For example
org.springframework.ai.vectorstoretoorg.springframework.ai.pgvector.vectorstore.
Upgrading to 1.0.0.RC3
-
The type of the portable chat options (
frequencyPenalty,presencePenalty,temperature,topP) has been changed fromFloattoDouble.
Upgrading to 1.0.0.M2
-
The configuration prefix for the Chroma Vector Store has been changes from
spring.ai.vectorstore.chroma.storetospring.ai.vectorstore.chromain order to align with the naming conventions of other vector stores. -
The default value of the
initialize-schemaproperty on vector stores capable of initializing a schema is now set tofalse. This implies that the applications now need to explicitly opt-in for schema initialization on supported vector stores, if the schema is expected to be created at application startup. Not all vector stores support this property. See the corresponding vector store documentation for more details. The following are the vector stores that currently don’t support theinitialize-schemaproperty.-
Hana
-
Pinecone
-
Weaviate
-
-
In Bedrock Jurassic 2, the chat options
countPenalty,frequencyPenalty, andpresencePenaltyhave been renamed tocountPenaltyOptions,frequencyPenaltyOptions, andpresencePenaltyOptions. Furthermore, the type of the chat optionstopSequenceshave been changed fromString[]toList<String>. -
In Azure OpenAI, the type of the chat options
frequencyPenaltyandpresencePenaltyhas been changed fromDoubletoFloat, consistently with all the other implementations.
Upgrading to 1.0.0.M1
On our march to release 1.0.0 M1 we have made several breaking changes. Apologies, it is for the best!
ChatClient changes
A major change was made that took the 'old' ChatClient and moved the functionality into ChatModel. The 'new' ChatClient now takes an instance of ChatModel. This was done to support a fluent API for creating and executing prompts in a style similar to other client classes in the Spring ecosystem, such as RestClient, WebClient, and JdbcClient. Refer to the [JavaDoc](docs.spring.io/spring-ai/docs/api) for more information on the Fluent API, proper reference documentation is coming shortly.
We renamed the 'old' ModelClient to Model and renamed implementing classes, for example ImageClient was renamed to ImageModel. The Model implementation represents the portability layer that converts between the Spring AI API and the underlying AI Model API.
A new package model that contains interfaces and base classes to support creating AI Model Clients for any input/output data type combination. At the moment, the chat and image model packages implement this. We will be updating the embedding package to this new model soon.
A new "portable options" design pattern. We wanted to provide as much portability in the ModelCall as possible across different chat based AI Models. There is a common set of generation options and then those that are specific to a model provider. A sort of "duck typing" approach is used. ModelOptions in the model package is a marker interface indicating implementations of this class will provide the options for a model. See ImageOptions, a subinterface that defines portable options across all text→image ImageModel implementations. Then StabilityAiImageOptions and OpenAiImageOptions provide the options specific to each model provider. All options classes are created via a fluent API builder, all can be passed into the portable ImageModel API. These option data types are used in autoconfiguration/configuration properties for the ImageModel implementations.
Artifact name changes
Renamed POM artifact names: - spring-ai-qdrant → spring-ai-qdrant-store - spring-ai-cassandra → spring-ai-cassandra-store - spring-ai-pinecone → spring-ai-pinecone-store - spring-ai-redis → spring-ai-redis-store - spring-ai-qdrant → spring-ai-qdrant-store - spring-ai-gemfire → spring-ai-gemfire-store - spring-ai-azure-vector-store-spring-boot-starter → spring-ai-azure-store-spring-boot-starter - spring-ai-redis-spring-boot-starter → spring-ai-starter-vector-store-redis
Upgrading to 0.8.1
Former spring-ai-vertex-ai has been renamed to spring-ai-vertex-ai-palm2 and spring-ai-vertex-ai-spring-boot-starter has been renamed to spring-ai-vertex-ai-palm2-spring-boot-starter.
So, you need to change the dependency from
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-vertex-ai</artifactId>
</dependency>To
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-vertex-ai-palm2</artifactId>
</dependency>and the related Boot starter for the Palm2 model has changed from
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-vertex-ai-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>to
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-vertex-ai-palm2-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>-
Renamed Classes (01.03.2024)
-
VertexAiApi → VertexAiPalm2Api
-
VertexAiClientChat → VertexAiPalm2ChatClient
-
VertexAiEmbeddingClient → VertexAiPalm2EmbeddingClient
-
VertexAiChatOptions → VertexAiPalm2ChatOptions
-
Upgrading to 0.8.0
January 24, 2024 Update
-
Moving the
promptandmessagesandmetadatapackages to subpackages oforg.springframework.ai.chat -
New functionality is text to image clients. Classes are
OpenAiImageModelandStabilityAiImageModel. See the integration tests for usage, docs are coming soon. -
A new package
modelthat contains interfaces and base classes to support creating AI Model Clients for any input/output data type combination. At the moment, the chat and image model packages implement this. We will be updating the embedding package to this new model soon. -
A new "portable options" design pattern. We wanted to provide as much portability in the
ModelCallas possible across different chat based AI Models. There is a common set of generation options and then those that are specific to a model provider. A sort of "duck typing" approach is used.ModelOptionsin the model package is a marker interface indicating implementations of this class will provide the options for a model. SeeImageOptions, a subinterface that defines portable options across all text→imageImageModelimplementations. ThenStabilityAiImageOptionsandOpenAiImageOptionsprovide the options specific to each model provider. All options classes are created via a fluent API builder, all can be passed into the portableImageModelAPI. These option data types are used in autoconfiguration/configuration properties for theImageModelimplementations.
January 13, 2024 Update
The following OpenAi Autoconfiguration chat properties have changed
-
from
spring.ai.openai.modeltospring.ai.openai.chat.options.model. -
from
spring.ai.openai.temperaturetospring.ai.openai.chat.options.temperature.
Find updated documentation about the OpenAi properties: docs.spring.io/spring-ai/reference/api/chat/openai-chat.html
December 27, 2023 Update
Merge SimplePersistentVectorStore and InMemoryVectorStore into SimpleVectorStore * Replace InMemoryVectorStore with SimpleVectorStore
December 20, 2023 Update
Refactor the Ollama client and related classes and package names
-
Replace the org.springframework.ai.ollama.client.OllamaClient by org.springframework.ai.ollama.OllamaModelCall.
-
The OllamaChatClient method signatures have changed.
-
Rename the org.springframework.ai.autoconfigure.ollama.OllamaProperties into org.springframework.ai.model.ollama.autoconfigure.OllamaChatProperties and change the suffix to:
spring.ai.ollama.chat. Some of the properties have changed as well.
December 19, 2023 Update
Renaming of AiClient and related classes and package names
-
Rename AiClient to ChatClient
-
Rename AiResponse to ChatResponse
-
Rename AiStreamClient to StreamingChatClient
-
Rename package org.sf.ai.client to org.sf.ai.chat
Rename artifact ID of
-
transformers-embeddingtospring-ai-transformers
Moved Maven modules from top-level directory and embedding-clients subdirectory to all be under a single models directory.
December 1, 2023
We are transitioning the project’s Group ID:
-
FROM:
org.springframework.experimental.ai -
TO:
org.springframework.ai
Artifacts will still be hosted in the snapshot repository as shown below.
The main branch will move to the version 0.8.0-SNAPSHOT.
It will be unstable for a week or two.
Please use the 0.7.1-SNAPSHOT if you don’t want to be on the bleeding edge.
You can access 0.7.1-SNAPSHOT artifacts as before and still access 0.7.1-SNAPSHOT Documentation.
0.7.1-SNAPSHOT Dependencies
-
Azure OpenAI
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.experimental.ai</groupId> <artifactId>spring-ai-azure-openai-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>0.7.1-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency> -
OpenAI
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.experimental.ai</groupId> <artifactId>spring-ai-openai-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>0.7.1-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency>

