|
For the latest snapshot version, please use Spring AI 1.1.2! |
Structured Output Converter
As of 02.05.2024 the old OutputParser, BeanOutputParser, ListOutputParser and MapOutputParser classes are deprecated in favor of the new StructuredOutputConverter, BeanOutputConverter, ListOutputConverter and MapOutputConverter implementations.
the latter are drop-in replacements for the former ones and provide the same functionality. The reason for the change was primarily naming, as there isn’t any parsing being done, but also have aligned with the Spring org.springframework.core.convert.converter package bringing in some improved functionality.
|
The ability of LLMs to produce structured outputs is important for downstream applications that rely on reliably parsing output values. Developers want to quickly turn results from an AI model into data types, such as JSON, XML or Java classes, that can be passed to other application functions and methods.
The Spring AI Structured Output Converters help to convert the LLM output into a structured format.
As shown in the following diagram, this approach operates around the LLM text completion endpoint:
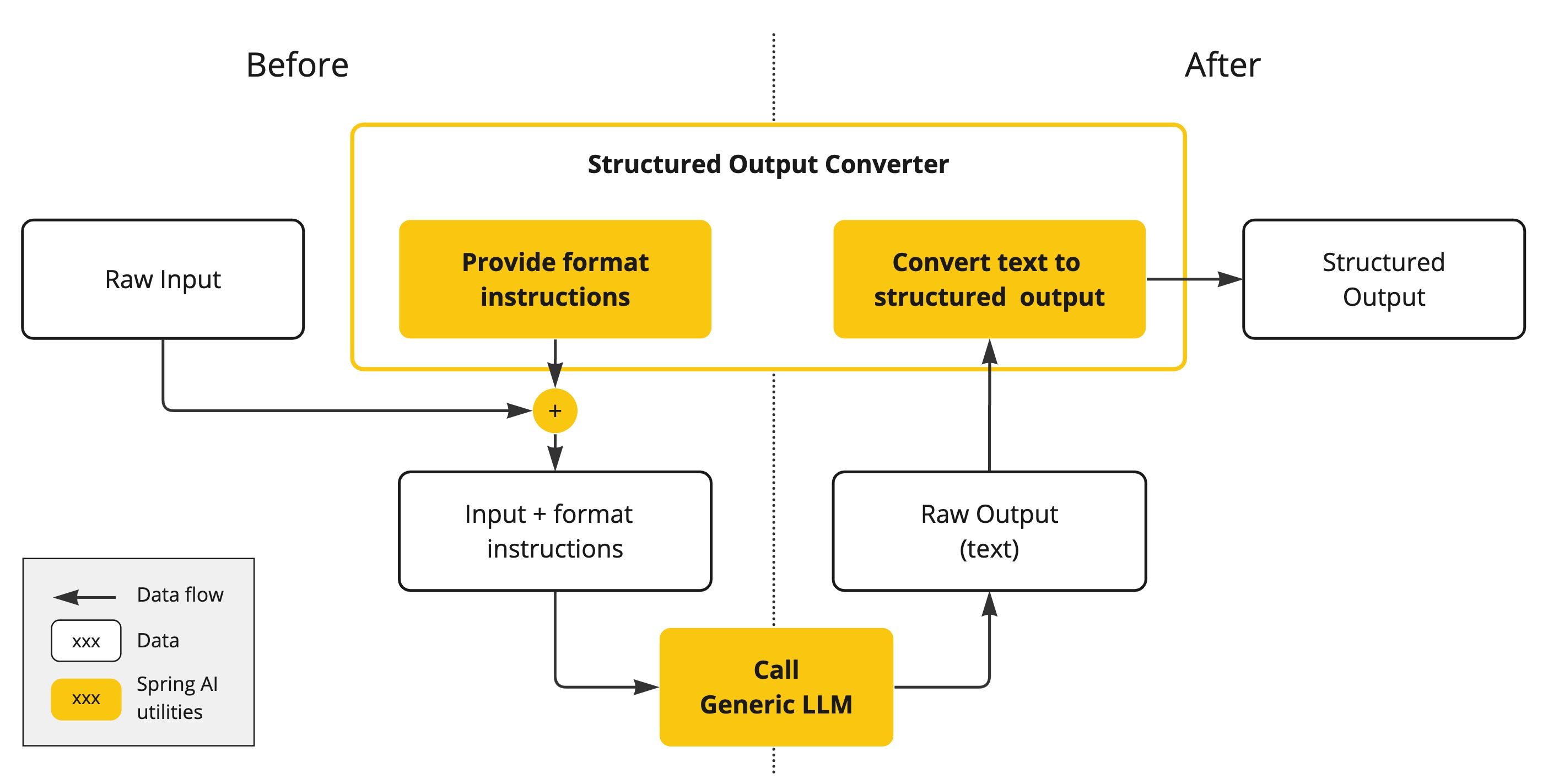
Generating structured outputs from Large Language Models (LLMs) using generic completion APIs requires careful handling of inputs and outputs. The structured output converter plays a crucial role before and after the LLM call, ensuring the desired output structure is achieved.
Before the LLM call, the converter appends format instructions to the prompt, providing explicit guidance to the models on generating the desired output structure. These instructions act as a blueprint, shaping the model’s response to conform to the specified format.
After the LLM call, the converter takes the model’s output text and transforms it into instances of the structured type. This conversion process involves parsing the raw text output and mapping it to the corresponding structured data representation, such as JSON, XML, or domain-specific data structures.
The StructuredOutputConverter is a best effort to convert the model output into a structured output.
The AI Model is not guaranteed to return the structured output as requested.
The model may not understand the prompt or be unable to generate the structured output as requested.
Consider implementing a validation mechanism to ensure the model output is as expected.
|
The StructuredOutputConverter is not used for LLM Tool Calling, as this feature inherently provides structured outputs by default.
|
Structured Output API
The StructuredOutputConverter interface allows you to obtain structured output, such as mapping the output to a Java class or an array of values from the text-based AI Model output.
The interface definition is:
public interface StructuredOutputConverter<T> extends Converter<String, T>, FormatProvider {
}It combines the Spring Converter<String, T> interface and the FormatProvider interface
public interface FormatProvider {
String getFormat();
}The following diagram shows the data flow when using the structured output API.
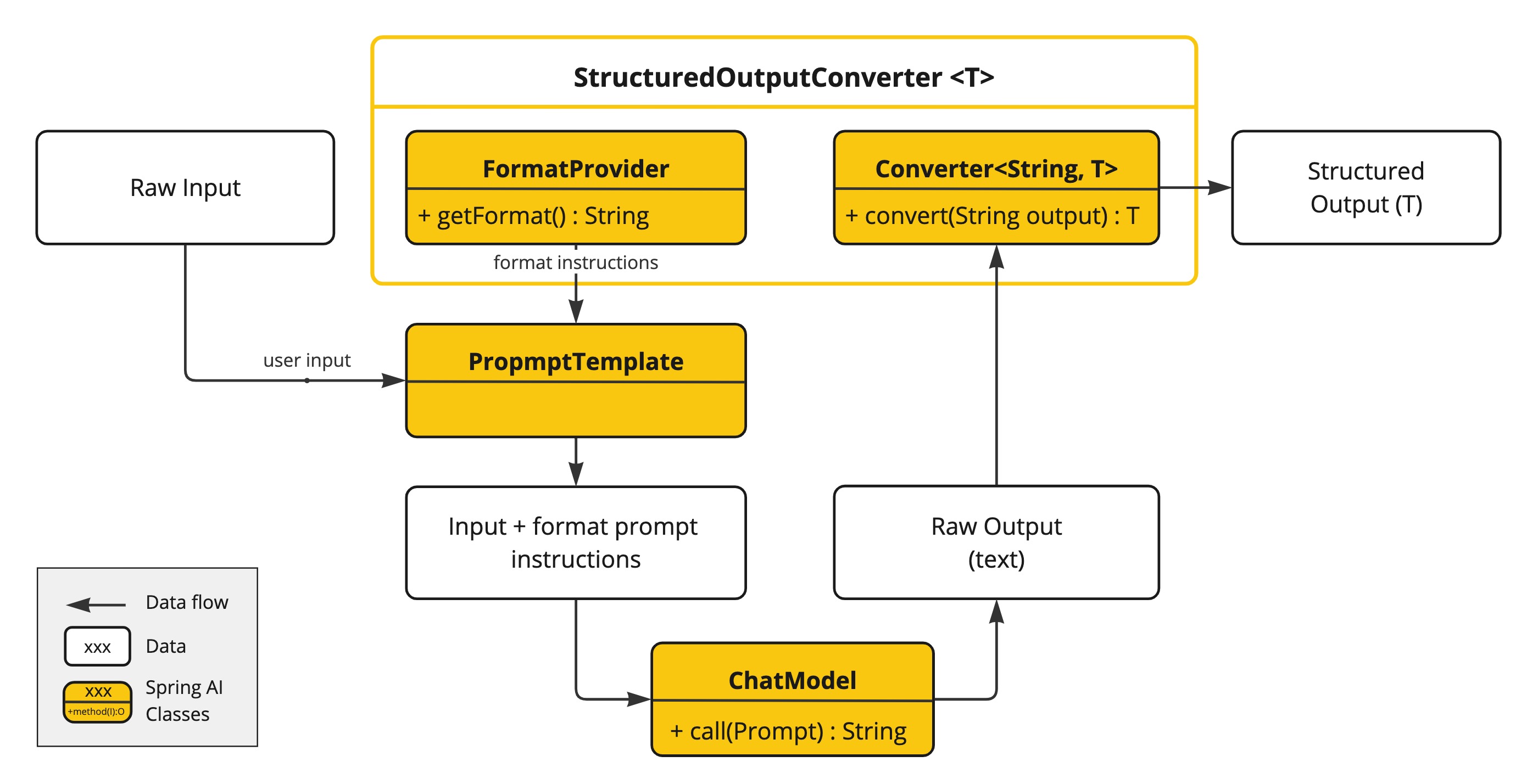
The FormatProvider supplies specific formatting guidelines to the AI Model, enabling it to produce text outputs that can be converted into the designated target type T using the Converter. Here is an example of such formatting instructions:
Your response should be in JSON format. The data structure for the JSON should match this Java class: java.util.HashMap Do not include any explanations, only provide a RFC8259 compliant JSON response following this format without deviation.
The format instructions are most often appended to the end of the user input using the PromptTemplate like this:
StructuredOutputConverter outputConverter = ...
String userInputTemplate = """
... user text input ....
{format}
"""; // user input with a "format" placeholder.
Prompt prompt = new Prompt(
PromptTemplate.builder()
.template(this.userInputTemplate)
.variables(Map.of(..., "format", this.outputConverter.getFormat())) // replace the "format" placeholder with the converter's format.
.build().createMessage()
);The Converter<String, T> is responsible to transform output text from the model into instances of the specified type T.
Available Converters
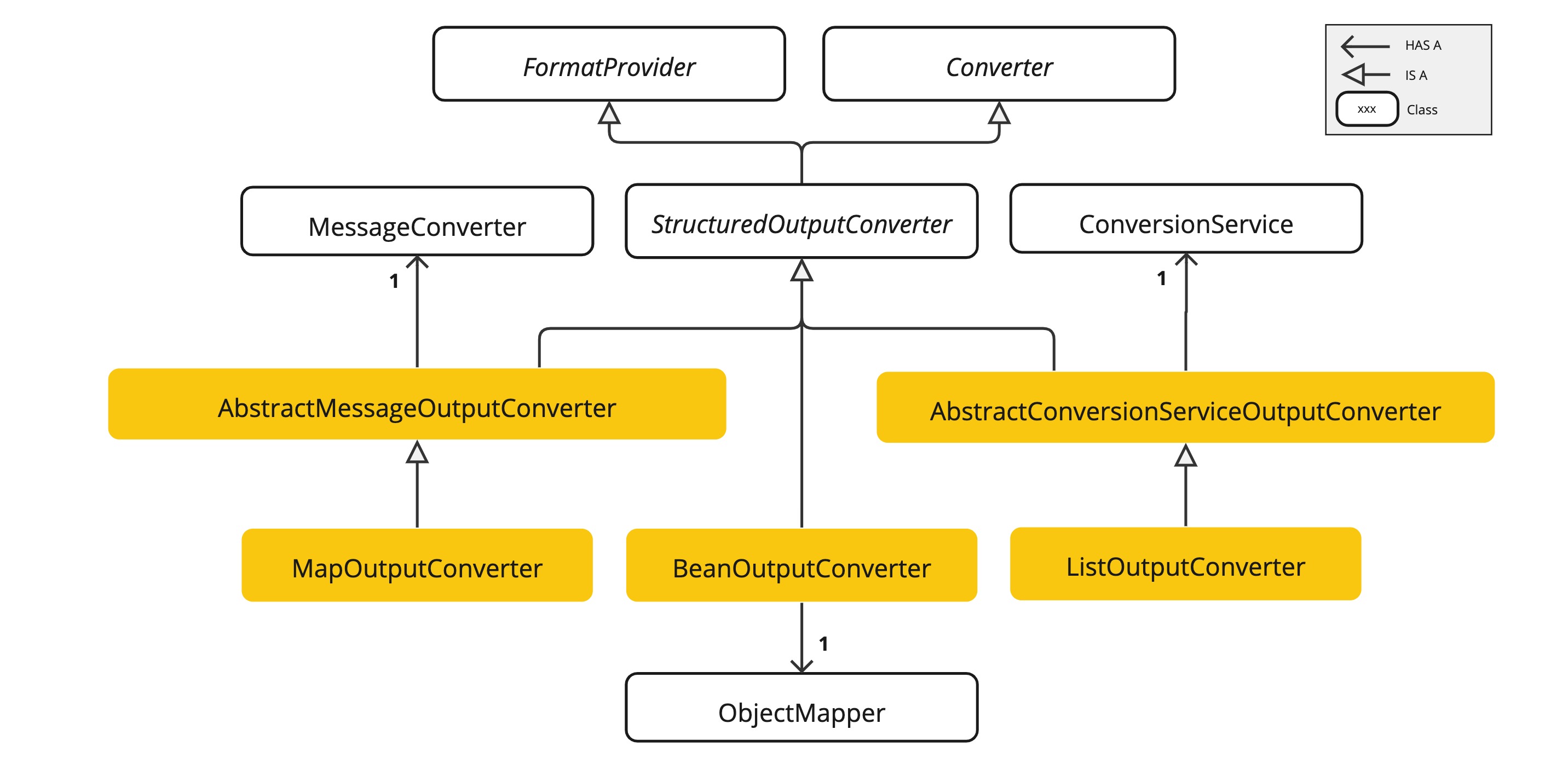
Currently, Spring AI provides AbstractConversionServiceOutputConverter, AbstractMessageOutputConverter, BeanOutputConverter, MapOutputConverter and ListOutputConverter implementations:
-
AbstractConversionServiceOutputConverter<T>- Offers a pre-configured GenericConversionService for transforming LLM output into the desired format. No defaultFormatProviderimplementation is provided. -
AbstractMessageOutputConverter<T>- Supplies a pre-configured MessageConverter for converting LLM output into the desired format. No defaultFormatProviderimplementation is provided. -
BeanOutputConverter<T>- Configured with a designated Java class (e.g., Bean) or a ParameterizedTypeReference, this converter employs aFormatProviderimplementation that directs the AI Model to produce a JSON response compliant with aDRAFT_2020_12,JSON Schemaderived from the specified Java class. Subsequently, it utilizes anObjectMapperto deserialize the JSON output into a Java object instance of the target class. -
MapOutputConverter- Extends the functionality ofAbstractMessageOutputConverterwith aFormatProviderimplementation that guides the AI Model to generate an RFC8259 compliant JSON response. Additionally, it incorporates a converter implementation that utilizes the providedMessageConverterto translate the JSON payload into ajava.util.Map<String, Object>instance. -
ListOutputConverter- Extends theAbstractConversionServiceOutputConverterand includes aFormatProviderimplementation tailored for comma-delimited list output. The converter implementation employs the providedConversionServiceto transform the model text output into ajava.util.List.
Using Converters
The following sections provide guides how to use the available converters to generate structured outputs.
Bean Output Converter
The following example shows how to use BeanOutputConverter to generate the filmography for an actor.
The target record representing actor’s filmography:
record ActorsFilms(String actor, List<String> movies) {
}Here is how to apply the BeanOutputConverter using the high-level, fluent ChatClient API:
ActorsFilms actorsFilms = ChatClient.create(chatModel).prompt()
.user(u -> u.text("Generate the filmography of 5 movies for {actor}.")
.param("actor", "Tom Hanks"))
.call()
.entity(ActorsFilms.class);or using the low-level ChatModel API directly:
BeanOutputConverter<ActorsFilms> beanOutputConverter =
new BeanOutputConverter<>(ActorsFilms.class);
String format = this.beanOutputConverter.getFormat();
String actor = "Tom Hanks";
String template = """
Generate the filmography of 5 movies for {actor}.
{format}
""";
Generation generation = chatModel.call(
PromptTemplate.builder().template(this.template).variables(Map.of("actor", this.actor, "format", this.format)).build().create()).getResult();
ActorsFilms actorsFilms = this.beanOutputConverter.convert(this.generation.getOutput().getText());Property Ordering in Generated Schema
The BeanOutputConverter supports custom property ordering in the generated JSON schema through the @JsonPropertyOrder annotation.
This annotation allows you to specify the exact sequence in which properties should appear in the schema, regardless of their declaration order in the class or record.
For example, to ensure specific ordering of properties in the ActorsFilms record:
@JsonPropertyOrder({"actor", "movies"})
record ActorsFilms(String actor, List<String> movies) {}This annotation works with both records and regular Java classes.
Generic Bean Types
Use the ParameterizedTypeReference constructor to specify a more complex target class structure.
For example, to represent a list of actors and their filmographies:
List<ActorsFilms> actorsFilms = ChatClient.create(chatModel).prompt()
.user("Generate the filmography of 5 movies for Tom Hanks and Bill Murray.")
.call()
.entity(new ParameterizedTypeReference<List<ActorsFilms>>() {});or using the low-level ChatModel API directly:
BeanOutputConverter<List<ActorsFilms>> outputConverter = new BeanOutputConverter<>(
new ParameterizedTypeReference<List<ActorsFilms>>() { });
String format = this.outputConverter.getFormat();
String template = """
Generate the filmography of 5 movies for Tom Hanks and Bill Murray.
{format}
""";
Prompt prompt = PromptTemplate.builder().template(this.template).variables(Map.of("format", this.format)).build().create();
Generation generation = chatModel.call(this.prompt).getResult();
List<ActorsFilms> actorsFilms = this.outputConverter.convert(this.generation.getOutput().getText());Map Output Converter
The following snippet shows how to use MapOutputConverter to convert the model output to a list of numbers in a map.
Map<String, Object> result = ChatClient.create(chatModel).prompt()
.user(u -> u.text("Provide me a List of {subject}")
.param("subject", "an array of numbers from 1 to 9 under they key name 'numbers'"))
.call()
.entity(new ParameterizedTypeReference<Map<String, Object>>() {});or using the low-level ChatModel API directly:
MapOutputConverter mapOutputConverter = new MapOutputConverter();
String format = this.mapOutputConverter.getFormat();
String template = """
Provide me a List of {subject}
{format}
""";
Prompt prompt = PromptTemplate.builder().template(this.template)
.variables(Map.of("subject", "an array of numbers from 1 to 9 under they key name 'numbers'", "format", this.format)).build().create();
Generation generation = chatModel.call(this.prompt).getResult();
Map<String, Object> result = this.mapOutputConverter.convert(this.generation.getOutput().getText());List Output Converter
The following snippet shows how to use ListOutputConverter to convert the model output into a list of ice cream flavors.
List<String> flavors = ChatClient.create(chatModel).prompt()
.user(u -> u.text("List five {subject}")
.param("subject", "ice cream flavors"))
.call()
.entity(new ListOutputConverter(new DefaultConversionService()));or using the low-level ChatModel API directly:
ListOutputConverter listOutputConverter = new ListOutputConverter(new DefaultConversionService());
String format = this.listOutputConverter.getFormat();
String template = """
List five {subject}
{format}
""";
Prompt prompt = PromptTemplate.builder().template(this.template).variables(Map.of("subject", "ice cream flavors", "format", this.format)).build().create();
Generation generation = this.chatModel.call(this.prompt).getResult();
List<String> list = this.listOutputConverter.convert(this.generation.getOutput().getText());Supported AI Models
The following AI Models have been tested to support List, Map and Bean structured outputs.
Model |
Integration Tests / Samples |
Built-in JSON mode
Some AI Models provide dedicated configuration options to generate structured (usually JSON) output.
-
OpenAI Structured Outputs can ensure your model generates responses conforming strictly to your provided JSON Schema. You can choose between the
JSON_OBJECTthat guarantees the message the model generates is valid JSON orJSON_SCHEMAwith a supplied schema that guarantees the model will generate a response that matches your supplied schema (spring.ai.openai.chat.options.responseFormatoption). -
Azure OpenAI - provides a
spring.ai.azure.openai.chat.options.responseFormatoptions specifying the format that the model must output. Setting to{ "type": "json_object" }enables JSON mode, which guarantees the message the model generates is valid JSON. -
Ollama - provides a
spring.ai.ollama.chat.options.formatoption to specify the format to return a response in. Currently, the only accepted value isjson. -
Mistral AI - provides a
spring.ai.mistralai.chat.options.responseFormatoption to specify the format to return a response in. Setting it to{ "type": "json_object" }enables JSON mode, which guarantees the message the model generates is valid JSON.

